Perinatal encephalopathy is a group of diseases associated with damage to the brain, often of hypoxic-ischemic origin. Pathology is detected in newborns, which means that damaging factors affect the nervous tissue during intrauterine development, childbirth, or in the first week of a baby’s life. In 90% of cases, mothers of newborns with diagnosed PEP have a complicated medical history (threat of miscarriage, toxicosis in the first and second trimesters, premature birth).
Characteristic
Encephalopathy is a medical term that means damage to the brain substance of non-infectious origin. Perinatal is a word that means that this period of time includes the period from the 22nd week of gestation to the 7th day of the baby’s life. The perinatal period includes antenatal (from 28 weeks before birth), intranatal (childbirth), neonatal (from birth to 7 days of life) periods. During the neonatal period, the newborn adapts to new external conditions.
Perinatal encephalopathy (PEP) in children is a pathology that reflects damage to the brain matter, which occurs against the background of various pathological processes. PEP in newborns is a group of diseases that imply structural, morphological or functional disorders of the brain.
The disease perinatal encephalopathy is not identified as a separate code in ICD-10. However, a similar diagnosis is found in pediatric practice for children under one year of age who have neurological disorders, including motor and mental disorders. After 1 month of the newborn’s life, a neurologist, based on neurological symptoms and based on the results of an instrumental examination, makes an accurate diagnosis indicating the etiological nature of the pathology.
The prevalence of perinatal encephalopathy reaches about 700 cases per 1 thousand newborns. Infants receiving hospital treatment are given a primary or concomitant diagnosis of PEP in 90% of cases. Clinical studies show that in most cases the diagnosis is not true. The doctor often indicates this pathology if he has not found out the causes of the syndrome of motor and other neurological disorders.
Studies by foreign authors provide other figures that more objectively reflect the prevalence of the disease - about 6 cases per 1 thousand full-term newborns, about 33-70% of cases among premature infants. Diseases combined into the AED group are presented in ICD-10 under the codes “G51.0, 51.8”, “G90.9”, “G91.0-91.2”, “G91.8”, “G93.2”.
Main types of perinatal encephalopathy
To make a more accurate diagnosis and take adequate treatment measures, the disease is further classified into groups.
By etiology
Based on the causes and conditions of origin, encephalopathy is divided into several types.
Bilirubin occurs for several reasons:
- conflict between the Rh factor of mother and child;
- jaundice due to prematurity;
- the presence of diabetes mellitus in the mother;
- birth injuries;
- sepsis in a newborn.

Familiarize yourself with the features of diagnosis, development and nutrition of premature babies.
Hypoxic-ischemic , that is, lack of oxygen and blood circulation in the fetus. Possible reasons:
- entanglement of the fetus with the umbilical cord;
- premature placental abruption;
- premature discharge of amniotic fluid;
- heart disease and iron deficiency in the mother;
- breech presentation during labor;
- multiple pregnancy.
Traumatic develops due to injuries caused by the child during childbirth.
Toxic-metabolic occurs due to the bad habits of the mother and the use of prohibited medications.
Infectious - inflammatory processes of an infectious nature in the maternal body.
By period of illness
According to periods, that is, according to the duration of observation of various symptoms, AEDs are divided into 3 main groups:
- The acute period lasts until the baby is 1 month old.
- Subacute - up to the age of 3-4 months.
- The late recovery period can last from 4 months to 2 years in premature babies and up to a year in those born at full term.

We recommend that you familiarize yourself with the child development calendar at 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11 months and 1 year.
By severity
Based on the severity and severity of symptoms, encephalopathy is divided into 3 degrees:
- Easy.
- Average
- Heavy.
According to the level of damage to the NS
Depending on the severity of the disease, damage to the following elements of the nervous system occurs:
- membranes of the brain (performs a protective function and is responsible for blood flow);
- liquor-conducting pathways (a system of nerve fibers supplying impulses to the brain from the whole body);
- cerebral cortex (responsible for vision, hearing, touch, thinking, speech, smell, taste);
- subcortical structures (regulate the functioning of the cardiovascular, digestive, endocrine systems, are responsible for sleep and wakefulness);
- brain stem (controls basic reflexes and sensory organs, as well as blood circulation and breathing);
- cerebellum (main function is coordination of movements).

Did you know? Unlike adults, babies up to 9 months old can swallow and breathe at the same time. By the way, animals also have this feature.
Classification
Classification of perinatal encephalopathy in newborns is carried out taking into account etiological factors. Depending on the dominant damaging factor, the following forms are distinguished:
- Hypoxic, caused by oxygen deficiency.
- Traumatic, associated with mechanical damage to the fetal brain.
- Toxic-metabolic, correlating with metabolic disorders and toxic effects.
- Infectious, caused by infectious and inflammatory processes.

Hypoxia plays a leading role in the structure of the causes of PEP. Toxic effects and infectious processes, in addition to direct damaging effects on nervous tissue, provoke disruption of the uteroplacental circulation, which leads to the development of intrauterine hypoxia, which occurs in a chronic form. Against the background of oxygen starvation, ischemia of the nervous tissue develops.
Injuries received by the fetus during labor are associated with mechanical damage to brain structures and often lead to impaired blood circulation in the vertebrobasilar system, which affects the aggravation of hypoxic-ischemic processes. In case of unfavorable course of pregnancy and childbirth, hypoxia becomes a universal damaging factor that provokes the development of PEP.
Why is perinatal encephalopathy dangerous?

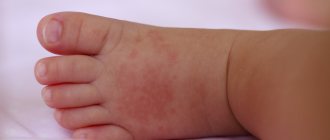
The degree of danger of perinatal encephalopathy in newborns depends on the degree and severity of damage to brain tissue, as well as on the specific type of affected area. First of all, a serious lesion can disrupt the physical-motor and rational functions of the body. Consequences of perinatal encephalopathy: impaired vision, hearing, speech (if the speech center is affected), convulsive activity, disorders of memory and consciousness, paralysis - complete or partial, general weakness, frequent dizziness and loss of consciousness, delayed psychomotor development, and much more, i.e. The concept of encephalopathy is a very generalized term for a huge number of disorders, some of which may not even manifest themselves.
Many modern mothers, having heard such a diagnosis, unfortunately, try to terminate a long-awaited pregnancy or abandon their children in the maternity hospital, fearing that they will end up with a severely disabled or mentally handicapped child. But with such a diagnosis often made, most children are able to lead an active, full-fledged lifestyle, if the diagnosis is made on time and treatment is started.
You shouldn’t write your baby off and take the diagnosis as a death sentence. All human organs have increased regeneration at an early age, which is especially pronounced in infants, and the consequences of perinatal encephalopathy in adulthood may not even appear, only special treatment, care and a correct lifestyle are necessary.
Causes
PEP in newborns is a diagnosis that is characterized by damage to the brain matter, which negatively affects the functions of the central nervous system. The main causes of the disease are associated with the damaging effects of pathological factors and processes:
- Fetal hypoxia (oxygen deficiency) – intrauterine, intrapartum.
- Mechanical injuries to the fetus during childbirth.
- Infectious and viral lesions of the fetus.
- Toxic effects on the fetus.
- Hereditary predisposition.
PEP of mixed origin is more often diagnosed, which suggests the participation of several factors in the pathological process. Perinatal pathology of hypoxic origin is a common form, which is characterized by damage to the tissues of the nervous system due to oxygen starvation.
Hypoxia is accompanied by a complex of disorders that affect the rheological properties of blood, hemodynamics and microcirculation, and affect metabolic processes. As a result, damage to the nervous tissue occurs due to hemorrhagic infarction and ischemia.
Against the background of ischemic processes, leukomalacia subsequently develops - damage to the white brain matter. Perinatal encephalopathy is a pathology that occurs against the background of diseases and adverse effects aimed at pregnant women, which is often associated with the following reasons:
- Somatic diseases accompanied by the effects of intoxication suffered by the mother during gestation.
- Infectious diseases (new forms or exacerbation of chronic infections) suffered by the mother during gestation.
- Immaturity of the body of a woman carrying a fetus.
- Poor nutrition, causing a deficiency of vitamins and other nutrients.
- Hereditary diseases in the mother.
- Metabolic disorders.
- Unfavorable environmental conditions, harmful external influences (air and water pollution with toxic substances, ionizing radiation).

Among the factors that provoke the development of perinatal hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy, it is worth noting the pathological course of pregnancy (threat of miscarriage, toxicosis) and childbirth (injury to the child due to the use of auxiliary instruments, slowdown of labor, rapid labor).
AEDs in newborns
As soon as the baby is born, he is examined by doctors. PEP in newborns is one of the most common diagnoses today. Often this inscription appears on the child’s card, but parents do not receive a proper explanation of what to do.
What is PEP?
The abbreviation PEP stands for perinatal encephalopathy. If we translate the name from scientific into simple language, it turns out that the child has brain disorders acquired during development in the womb or at birth. But such a diagnosis does not provide a specific explanation of how these disorders were obtained and what exactly their nature is. The name PEP can hide either a serious disease of the nervous system or a simple desire of the pediatrician to play it safe.
Most often, damage to the child’s nervous system occurs due to oxygen starvation of the brain or improper blood supply. The disorder is also possible due to trauma during childbirth.
The diagnosis of PEP in newborns is often made by a pediatrician based on clinical symptoms:
- behavioral disorder: excessive lethargy, or, on the contrary, activity;
- frequent, strong, prolonged crying for no apparent reason;
- copious and frequent regurgitation, often in a fountain, sometimes before meals, which cannot be explained by simple overeating;
- weight disorder;
- prematurity;
- complications during pregnancy (anemia, umbilical cord entanglement or knot, intrauterine infection, etc.);
- injuries during childbirth;
- dysfunction of the gastrointestinal tract;
- chin tremor.
Young parents should remember that symptoms matter if they recur. That is, if a child burped once or was a little naughty, this is most likely not a reason for concern. But if the symptoms are systematic, you should definitely tell your doctor about it.
After the pediatrician sees the risk of PEP in the child, he refers the baby for examination to a neurologist. Next, the doctor prescribes procedures and sometimes medications.
Treatment of AEDs in newborns
There are three main stages in perinatal encephalopathy:
- Acute period (from birth to 1 month).
- Recovery period (from 1 month to 2 years in premature babies and up to 1 year in full-term babies).
- Outcome of the disease.
Treatment depends on the stage of PEP. In the first month, drug treatment is effective; in the second stage, physiotherapy is most often used. Massage during PEP in newborns is one of the most effective means of restoring the nervous system. But it must be done by a professional, using special techniques.
Also, the use of medications and procedures depends on the specific disease of the child. PEP is a collective concept that unites many different disorders, not all of them are truly dangerous.
There is a risk group for PEP in newborns; it includes babies who had complications during birth. There are no specific time criteria for oxygen starvation of the brain, as a result of which complications arise. It happens that doctors enter a diagnosis of PEP into the baby’s record precisely because the baby is at risk, even if the child has no obvious symptoms.
Consequences of AEDs in newborns
If perinatal encephalopathy is detected in time and appropriate treatment is started, there may be no consequences at all in the future. With unqualified treatment, delays in the development of speech and the motor system, hyperactivity, absent-mindedness, neurotic reactions may occur, and in the case of severe illnesses, epilepsy may develop.
PEP is a very vague diagnosis; various diseases can be hidden behind it, so treatment should be prescribed by a qualified doctor. Often doctors are in no hurry to explain to parents what it is: PEP in newborns, which is why young mothers and fathers panic. Do not rush to get upset; perhaps your baby needs additional consultation with a qualified neurologist. The main thing is that the parents are next to the baby and are ready to help him, which means that together they can cope with the disease.
Clinical manifestations
Perinatal encephalopathy is a pathology that manifests itself in characteristic syndromes, which suggests a similar clinical picture regardless of the leading etiological factors. Clinical syndromes:
- Increased neuro-reflex excitability.
- SDN is a complex of motor disorders (paresis - weakness of central and peripheral muscles, extrapyramidal disorders, cerebellar disorders).
- Convulsive (sudden attacks of uncontrolled muscle contractions).
- Hydrocephalic (impaired cerebrospinal fluid dynamics against the background of increased production and deterioration of absorption of cerebrospinal fluid with a subsequent increase in intracranial pressure values).
The diagnosis of PEP (stands for perinatal encephalopathy) in a child is a pathology that leads to a slowdown in mental and physical development, which is manifested by slow growth and weight gain, impaired formation of pre-speech and speech skills, and deterioration in the development of cortical functions.
Symptoms of PEP in newborns appear depending on the nosological form of the pathology. For example, with a mild form of cerebral ischemia, excitation or depression of the central nervous system is observed, which lasts no more than 7 days.
With moderate cerebral ischemia, the clinical picture is supplemented by signs: convulsions, increased intracranial pressure, disturbances in the functioning of the autonomic part of the central nervous system (impaired respiratory and cardiac activity). If cerebral ischemia is severe, the depression of central nervous system activity is progressive and lasts longer than 10 days. Severe ischemia variably leads to the following consequences:
- Going into a comatose state.
- Transformation into an excited state, accompanied by a stable convulsive status.
- Convulsions followed by coma.
It is possible to develop status epilepticus with subsequent disruption of the activity of brain stem structures that regulate vital functions (breathing, heart function). The processes of decortication and decerebration reflect destructive and atrophic changes in the nervous tissue. Symptoms of perinatal encephalopathy, which develops against the background of intracranial hemorrhage associated with hypoxia, depend on the degree of damage to the brain. With a mild form of the disease, the pathology may not manifest any signs.
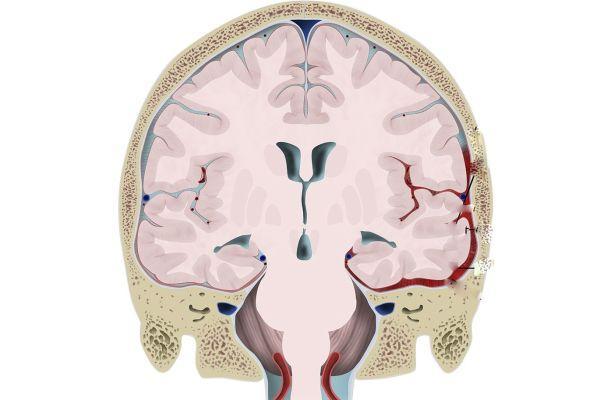
In a moderate form, signs are observed: shock, apnea (short-term stops in breathing), convulsive syndrome, confusion, depression of consciousness, development of a coma, increased intracranial pressure. Symptoms can be observed constantly or be transient (transitory) in nature. The appearance of hemorrhagic foci in the brain against the background of perinatal posthypoxic encephalopathy is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- Deterioration in general well-being, which manifests itself suddenly and leads to the development of a state of depressed consciousness, often alternating with periods of psychomotor agitation.
- Protrusion of the fontanel.
- Oculomotor disorders (abnormal movements made by the eyeballs).
- Thermoregulation disorder (hypothermia - hypothermia, hyperthermia - overheating of the body).
- Disturbances in the functioning of the autonomic system (frequent regurgitation, tachycardia - increased heart rate, tachypnea - rapid, shallow breathing, flatulence, stool upset).
- Pseudobulbar disorders (dysarthria - impaired pronunciation, dysphonia - decreased strength and sonority of the voice, dysphagia - impaired swallowing function, forced crying or laughter).
Posthypoxic encephalopathy, which occurs against the background of intracranial hemorrhages, is accompanied by anemia (hemoglobin deficiency), hypoglycemia (low glucose concentration), acidosis (a shift in the acid-base balance of the blood towards increased acidity) and other metabolic disorders. Often, somatic diseases - pneumonia, sepsis, heart failure - are associated with disturbances in the functioning of the central nervous system.
Severe clinical manifestations are a reason for inpatient treatment. If there are signs of mild damage to the brain, the child is discharged from the maternity hospital, he is at risk and is subject to medical supervision once a month. This approach often leads to a lack of therapy in the acute period. Treatment is carried out with a delay, during the period when complications of AEDs appear, which reduces the therapeutic effect.
Treatment of perinatal encephalopathy
Therapy for children with PEP differs depending on the period of the disease. First of all, treatment is aimed at maintaining vital organs and combating respiratory disorders. Such babies are often given oxygen therapy and tube feeding is prescribed.
Infusion therapy is carried out taking into account the needs and body weight of the child, and glucose-electrolyte solutions are administered intravenously. Drugs that reduce vascular permeability (kanavit, etamzilate), anticonvulsants (phenobarbital, diazepam), hormonal drugs (prednisone, dexamethasone), drugs that improve blood circulation in the brain (piracetam, cortexin, vinpocetine) are used.
The choice of medications for the treatment of the disease is carried out taking into account the prevailing symptoms and the severity of the clinical manifestations of the disease.
After the acute manifestations of the disease have been relieved, the doctor’s task is to restore brain function. Children with PEP are registered with a neurologist, who prescribes courses of medication and physiotherapeutic treatment. Of the medications, the specialist most often recommends the use of drugs that improve metabolic processes in the brain - nootropics; if there is increased excitability, sedatives are prescribed, and if the convulsive syndrome persists, anticonvulsants are prescribed.
Treatment with AEDs should be carried out by a neurologist, taking into account the clinical manifestations of the disease and the characteristics of the child. Incorrect therapy can worsen the baby’s condition and slow down the rate of recovery from illness.
Good results in the treatment of children with PEP are provided by massage, physiotherapy (electrophoresis, amplipulse therapy), swimming, and physical therapy. In case of developmental delays and speech disorders, classes with a speech therapist or psychologist are recommended.
The nervous system of children is characterized by plasticity and the ability to restore its functions. Therefore, treatment started on time, in the first months of life, increases the chances of normal development of the child in the future. According to statistics, complete recovery occurs in 20–30% of children; in other cases, the main syndromes may persist with the disease transitioning to minimal cerebral dysfunction, hydrocephalic syndrome. In severe cases, epilepsy and cerebral palsy may develop.
But the most important thing for forms of PEP of any complexity are gentle and drug-free methods of restorative treatment: reflexology, special therapeutic massage techniques, elements of therapeutic exercises, hydrotherapy with massage and therapeutic exercises in water of various temperatures and compositions, etc.
They require perseverance and great effort from the child’s parents - giving medicine is probably easier than doing a set of exercises every day - but they are very effective. This is explained by the fact that the injured brain, receiving the correct “information” through massage, swimming and gymnastics, recovers more quickly.
Reflexomassage (impact on active points) is first done by the hands of an experienced massage therapist, who then passes the baton of competent handling of the baby to the parents. Don’t forget: babies get tired quickly, all procedures should be carried out briefly, but often, at the height of positive emotions.
Early swimming of a child with mandatory diving is also a huge help in solving the neurological problems of the baby. What is painful and unpleasant to do on land can be done with a bang in water. When diving into the water column, the body experiences a baroeffect - gentle, soft and, most importantly, uniform pressure on all organs and tissues.
After emerging, the child receives a full, competent breath, which is especially important for babies born by cesarean section, who had hypoxia, etc. Water also helps with problems with intestinal colic - stool improves, spasmodic painful phenomena go away.
During the acute course of the disease, hospital treatment is indicated for newborns with pathologies of high or moderate severity, while treatment at home is indicated for newborns with a mild course of the disease.
An exceptionally friendly environment, full of love and care for the baby, should prevail in the house. This is extremely important for an infant with PEP symptoms. Often used as treatment methods:
- physiotherapeutic procedures;
- massages;
- baths with sea salt or with medicinal infusions and decoctions (pine needles, oregano, string, chamomile, oats).
Doctors recommend taking herbs and medications (“Novo-Passit”, “Elkar”, “Glycine”) with a sedative effect, vitamin and strengthening syrups. Also popular among doctors are drugs that activate cerebral circulation:
- "Hopantenic acid"
- "Piracetam"
- "Vinpocetine"
- "Actovegin"
- "Pyritinol."
Homeopathic and osteopathic treatment has a great effect.
For the syndrome of increased intracranial pressure, drugs with a diuretic effect are used (“Acetazolamide” together with “Asparkam”), it is recommended to slightly raise the baby’s head when he is lying down (put a special orthopedic pillow, put something under the mattress).
For symptoms of epilepsy, anticonvulsants are used. Severe forms of the disease require surgical intervention.
In the acute period, treatment of a child with perinatal encephalopathy is carried out in the neonatal pathology department. The child is prescribed a gentle regimen, oxygen therapy, and, if necessary, tube feeding.
Drug therapy is prescribed taking into account the prevailing syndromes of perinatal encephalopathy. To reduce intracranial hypertension, dehydration therapy (mannitol) is carried out, corticosteroids are administered (prednisolone, dexamethasone, etc.), and therapeutic spinal punctures are performed.
In order to normalize the metabolism of nervous tissue and increase its resistance to hypoxia, infusion therapy is carried out - the introduction of solutions of glucose, potassium, calcium, ascorbic acid, magnesium preparations, etc. To combat seizures, phenobarbital, diazepam, etc. are used. As part of the treatment of perinatal encephalopathy the prescription of drugs that improve blood circulation and brain metabolism (vinpocetine, piracetam, cortexin, deproteinized hemoderivative of calf blood, etc.) is indicated.
During the recovery period, treatment of a child with perinatal encephalopathy is usually carried out on an outpatient basis or in a day hospital. Repeated courses of drug therapy with nootropic drugs and angioprotectors, physical therapy, swimming, massage, physiotherapy (amplipulse therapy, electrophoresis), homeopathic therapy, herbal medicine, osteopathy are carried out.
For speech disorders - speech development disorder, alalia and dysarthria syndromes, corrective speech therapy classes are indicated.
Diagnostics
Immediately after birth, a physical examination of the baby is performed and an Apgar score is given. A poor prognosis correlates with persistence of an Apgar score of less than 3 points for more than 5 minutes. Unfavorable prognostic criteria: the appearance of seizures in the first 8 hours after birth, a persistent decrease in muscle tone.

Such children often subsequently develop cerebral palsy, epilepsy, and mental retardation. The diagnosis is made by a neonatologist or perinatal neurologist. Diagnostic examination and treatment are carried out in pediatric neurology departments. Basic instrumental examination methods:
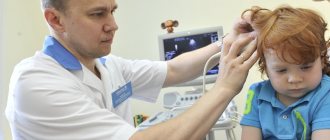
- Neurosonography (ultrasound examination of tissues of the central nervous system).
- Dopplerography (determining the state of the circulatory system that supplies the brain).
- MRI, CT (study of the morphological structure and features of the functioning of the central nervous system).
- Electroencephalography (study of bioelectrical activity of the brain).
Ultrasound diagnostics in DEG format shows signs of hypoperfusion (deterioration of blood flow through the nervous tissue). An MRI study shows the presence of focal damage to nerve tissue. In severe cases, a decrease in the density of the brain matter is detected. Perinatal neurology requires a thorough differential diagnosis.
For example, hypothyroid encephalopathy develops as a consequence of hypothyroidism - a decrease in the production of thyroid hormones. The disease is manifested by symptoms such as delayed physical and mental development, decreased muscle tone, lethargy, and refusal to eat. The baby retains a large diameter of the fontanel for a long time. Such symptoms can be mistakenly interpreted as signs of PEP of a different origin.
Consequences in adulthood
In adult life, the disease suffered at an early age can have residual severe consequences:
- Cerebral palsy.
- Epilepsy.
- Mental retardation.
- Violation of any body functions.
- psychoneurological diseases.
- Autonomic-visceral dysfunctions are disruptions in the functioning of any internal organs due to incorrect signals sent by the brain.
- Disorders of memory and consciousness.
But with proper care you can minimize possible risks:
- Hyperactivity syndrome and attention disorders.
- Headaches and tinnitus, dizziness.
- Physical weakness, fatigue and increased morbidity.
- Lack of activity and lack of initiative.
- Narrowed circle of interests.
- Absent-mindedness.
- Tendency to depression.
With minimal lesions or lesions of not too vital parts of the brain and a timely diagnosis, complete recovery from perinatal encephalopathy in newborns is also possible. Almost all sick children in adulthood are fully functional citizens who can take care of themselves.
Treatment
Modern medicine does not provide precise clinical recommendations regarding AEDs. For example, Dr. Komarovsky argues that a treatment protocol for perinatal encephalopathy cannot be developed because such a diagnosis does not exist in the civilized world. To eliminate the symptoms that appeared in a child during the postpartum period, you need to find out the exact causes of the disorders and carry out the correct therapy.
Treatment of posthypoxic encephalopathy in children and adults involves adherence to the regimen, including reducing exposure to light and sound stimuli, and organizing a nutritious diet. Regular measures are aimed at preventing hypothermia and overheating of the baby. If the newborn has no appetite, he refuses to eat, parenteral (via intravenous) nutrition is prescribed. Vital functions are constantly monitored.
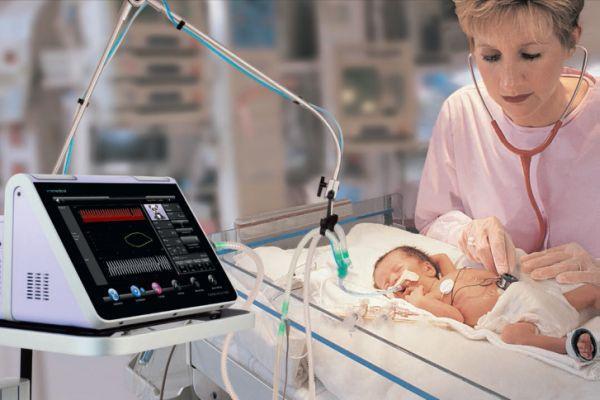
Newborns who exhibit cerebral edema and a comatose state are connected to a ventilator (hardware ventilation). They are prescribed Phenobarbital (has an anticonvulsant, antiepileptic effect). In the absence of intracranial hemorrhage, diuretics (Mannitol, Lasix) are indicated. If cerebral edema progresses, diuretics are combined with corticosteroids (Dexamethasone).
In parallel, antihypoxants (Piracetam, Cocarboxylase) and antioxidants (Alpha-tocopherol acetate) are prescribed. If there are movement disorders or changes in muscle tone after the end of the acute period, massage, therapeutic exercises, physiotherapy, and water procedures are prescribed. The duration of the recovery period is 1-12 months; in premature infants, the duration of rehabilitation can reach 24 months.