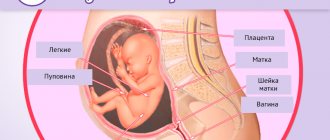
Disturbance of uteroplacental blood flow: danger and signs of pathology, diagnosis and treatment
Any disturbances in hemodynamics during pregnancy pose a threat to the development and future health of the fetus.
Pathologies of blood circulation along the vascular communication of the uterus and placenta are among the most common pathologies of pregnancy, significantly worsening the condition of the mother and baby. Therefore, it requires the maximum exclusion of all risk factors that can cause changes in blood flow through the vascular system connecting the mother, placenta and fetus, and if disorders occur, a quick start of therapeutic measures is important.
Diagnostics
The most accurate and informative research method in case of circulatory disorders is Dopplerography . With its help, it is possible to detect even minor changes in the blood flow of veins and arteries, study the hemodynamics of the fetus and obtain a graphic color image. That is, thanks to this method, it is possible to determine the prognosis of a real pregnancy and prescribe adequate therapy.
Less accurate methods are ultrasound and CT, which detect indirect signs of hypoxia: pathologies of the placenta and lack of fetal weight.
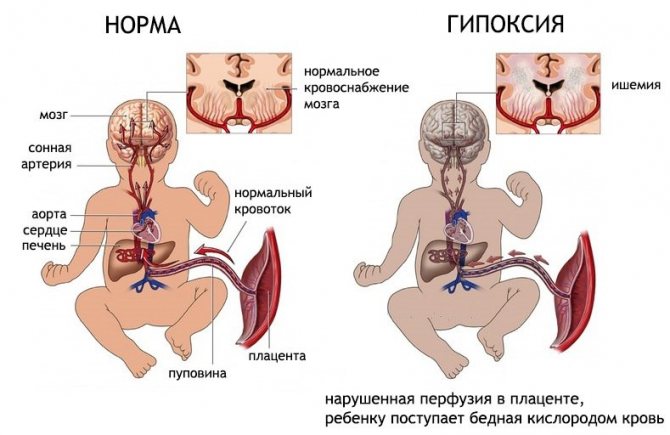
Violation of the uteroplacental blood flow of the fetus: how dangerous is it?
Changes in blood circulation in the vascular bed connecting the uterus with the placenta are considered a rather dangerous condition, due to the fact that it can lead to a number of complications:
- Hypoxia, leading to a delay in the formation and development of the fetus.
- Infection of a child in the womb.
- Formation of child development anomalies.
- Fetal death, especially when disorders appear after the first trimester, when the pathology ends in spontaneous miscarriage.
Treatment of uteroplacental blood flow disorders
It is worth noting that treatment of utero-fetal circulation disorders is required in all cases. Conditions with the first degree of violation are considered the most harmless. But a critical violation of fetoplacental blood flow requires immediate treatment. The faster measures are taken to eliminate critical changes affecting blood flow, the higher the chances of saving the baby’s life.
The main directions of treatment of fetoplacental circulatory disorders are as follows:
- blood pressure control;
- normalization of the lifestyle and diet of a pregnant woman;
- therapy with antibiotic and antiviral drugs in cases where intrauterine infection occurs;
- in case of Rh-conflict pregnancy, plasmapheresis is very successfully used;
- use of magnesium preparations;
- use of antispasmodic medications;
- taking vascular medications.
If acute hypoxia occurs due to blood flow disorders that can be classified as second or third degree, early delivery is used. This measure is resorted to in situations where conservative therapy does not produce any results.
Causes
The etiology of disturbances in blood flow through vessels in the combined system of the uterus and placenta includes many factors, which are divided into endogenous (internal) and exogenous (external). Among the endogenous causes of pathology:
- Low attachment of the placenta in the uterus, which is accompanied by insufficient blood flow to the fetus.
- The development of late toxicosis, affecting small-caliber vessels in the uterus and disrupting microcirculation.
- Anemia in a pregnant woman, causing increased blood flow, lack of oxygen and tissue nutrition.
- Conflict of Rhesus between mother and fetus, causing anemia and disorders in the child’s immune system.
- Pathological development of the umbilical arteries.
- Multiple pregnancy, when the fetus lacks nutrients.
- Malformations of the uterus that threaten to compress the fetus and the vessels feeding it and the placenta.
- Endocrine pathologies such as diabetes mellitus that damage blood vessels.
- Diseases of women with a gynecological profile, such as endometriosis or uterine fibroids, requiring appropriate therapy during the period of preparation for conception.
- Diseases of the vascular system in the mother, such as hypertension.
- The woman has venereological diseases.
- Genetic defects.
In turn, external factors that can lead to hemodynamic disorders are presented:
- Infections of bacterial and viral origin that can penetrate the placenta.
- Exposure to adverse factors: stress, excessive physical exertion, ionizing radiation, certain medications.
- The mother has bad habits.
There are also several social and everyday factors that can lead to the formation of pathological changes in blood circulation through the communicating vascular system of the uterus and placenta:
- A woman's age is more than 30 years or less than 18 years.
- Nutritional deficiency.
- Occupational hazards.
- Psycho-emotional overload.
Management of childbirth
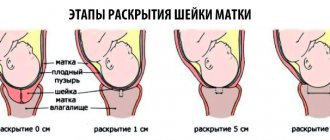
Delivery through the natural birth canal is carried out in the presence of a favorable obstetric situation, a mature cervix and compensated placental insufficiency. Childbirth is recommended to be performed with pain relief (epidural anesthesia). If weakness of labor occurs, stimulation is carried out with prostaglandins, and in the second period, obstetric forceps are applied or vacuum extraction of the fetus is performed.
Early delivery (up to 37 weeks) is indicated in the absence of positive dynamics according to ultrasound (fetometric indicators of the fetus) and Dopplerography after 10 days of therapy, as well as in cases of diagnosed fetal malnutrition. If the cervix is immature, delayed fetal development with disorders of its functional state is diagnosed, as well as a complicated obstetric history, age 30 years or older, a cesarean section is performed.
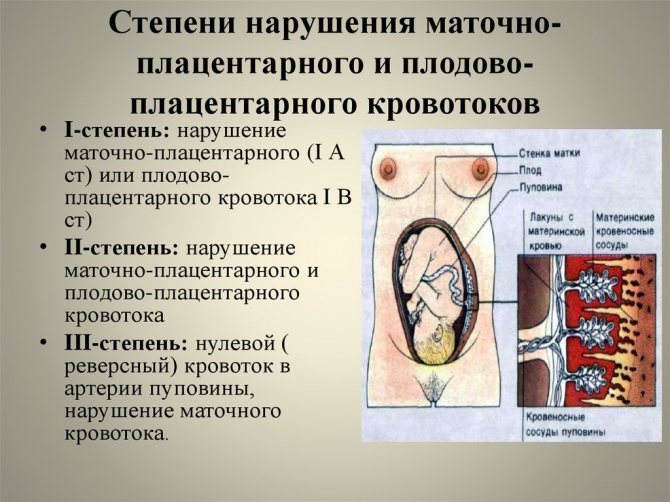
Classification by severity
The main classification of changes in blood flow along the vascular bed of the uterus and placenta divides pathology according to severity, guided by the localization of changes in the vessels.
1st degree
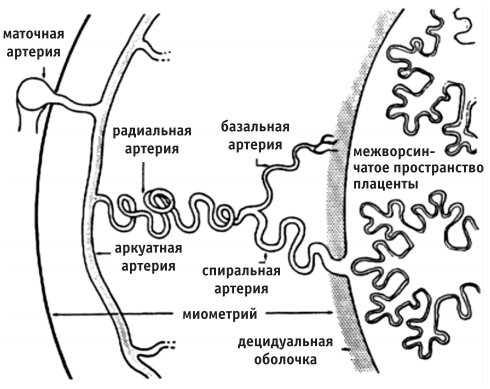
It is divided into 1a and 1b. A – corresponds to a hemodynamic disorder in one uterine artery, with no changes in the remaining vessels. This condition is not accompanied by serious disturbances in the child’s nutrition in the womb. B – affects blood flow in the umbilical vein, without changes in the uterine arteries.
2nd degree
In this case, the entire system of communication between the blood vessels of the fetus, placenta and mother undergoes changes, but the lack of oxygen for the child is not very pronounced.
3rd degree
This is a critical degree when hemodynamic parameters deteriorate sharply. The fetus does not receive the required oxygen concentration and the level of incoming nutrients decreases. This pathology can lead to death for the fetus in the womb or spontaneous abortion.
Degrees of disturbance of uteroplacental circulation
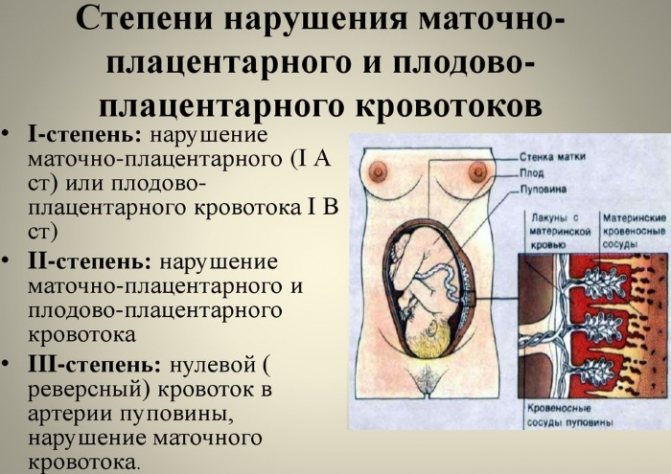
There are three main degrees of disturbance of utero-fetal blood flow:
- The first degree implies the presence of minor violations and contains the following varieties:
- 1a - at this degree, disruption of the uteroplacental blood flow occurs in the uterine artery system, while the fetoplacental blood flow remains normal.
- Degree 1b violations - here there are no violations of the uteroplacental blood flow (this blood circulation is preserved), and pathologies affect the post-placental level, which may be evidence of a violation of the fetoplacental fetal blood flow.
- In grade 2, disruption of uteroplacental blood flow is observed at two levels at once: feto-placental and uteroplacental. At the same time, there is no critical deterioration, which suggests that there is no serious threat to the development of the fetus in the near future. The danger is that negative changes can happen at any time. Therefore, this condition requires close attention from a doctor.
- The third degree means the presence of critical changes in the feto-placental blood circulation, while the uteroplacental blood flow can be disrupted or preserved. This type of violation requires immediate medical care and constant monitoring of the expectant mother until the condition is completely stabilized.
Depending on the degree of the disorder, the tactics for managing the pregnant woman and the type of treatment measures used are selected.
Types of disturbances in blood flow through the uteroplacental system
In accordance with the period of gestation of the child, a change in blood circulation between the uterus and placenta developed, 2 types of pathology are distinguished.
Primary
It is typical for the first trimester. The causes of the changes are pathologies of implantation, formation or attachment of the placenta in the uterus.
Secondary
It can appear at any time after the 16th week of embryonic development. Its appearance is facilitated by the influence of external factors or certain diseases of the mother, for example, high blood pressure, diabetes or other pathology that affects the vascular bed.
Degrees of blood flow disturbance
1st degree: the violations are compensated and concern only the uteroplacental blood flow, there is no threat to the fetus. The child's development is within normal limits. According to the level of changes, there are:
- disturbance of uteroplacental blood flow of 1a degree: disturbances occur only in one of the arteries of the uterus, hemodynamics are stable, there are no deviations from the norm, that is, disturbance of blood flow of type 1a has a favorable course;
- disturbance of fetal-placental blood flow of 1b degree : damage is detected at the level of the umbilical cord vessels, the uterine arteries provide adequate blood supply, that is, disturbance of blood flow of 1b degree during pregnancy has a favorable prognosis.
Clinical picture of blood flow disorders
The symptoms of blood flow disorders depend on how pronounced the changes in the vascular bed are. On the part of the pregnant woman herself, there may be no signs of pathology at all or only gestosis. Often, hemodynamic disorders are detected due to the fact that a woman is undergoing examination due to the threat of miscarriage or premature onset of labor, which manifests itself:
- Pain in the abdomen and groin area.
- The appearance of bloody-mucous discharge from the genital opening.
Often in pregnant women with a similar pathology, colpitis appears or worsens during gestation.
As a complication of pathologically altered blood flow in the uterus and placenta, colpitis can lead to intrauterine infection of the child.

On the part of the fetus, the symptoms of hemodynamic disorders are more pronounced. With the development of hypoxia, the frequency of the child’s movements decreases. During examinations at an appointment with an obstetrician-gynecologist, a specialist may pay attention to an increase or decrease in the child’s heart rate. The doctor may also note that the volume of the abdomen and the height of the uterine fundus are not correlated with gestational age.
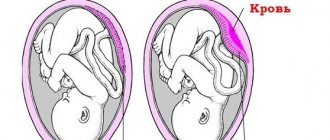
Pathology of blood circulation between the uterus and placenta along the united vascular bed can cause the formation of premature placental abruption, regardless of its location. This is one of the reasons why it is important to pay attention to the slightest signs of pathology.
Diagnosis of disorders at different levels of severity
To identify the pathology of the uteroplacental blood flow, 3 methods are used, regardless of the degree of development of the changes:
- Laboratory analysis of blood serum of the expectant mother.
- Ultrasound diagnostics (ultrasound).
- Cardiotocography (CTG).

A study of enzymatic activity is also carried out - oxytocinase and thermostable alkaline phosphatase are assessed. Ultrasound helps the specialist determine the size of the fetus and how well it corresponds to the gestational age. Rate:
- Where is the placenta located, what is its thickness, does its maturity correspond to the existing period of gestation of the child.
- Volume of amniotic fluid.
- Is the umbilical cord formed correctly?
- The presence or absence of pathological components in the placenta.
All these characteristics help to identify the presence or absence of pathologies in the bloodstream, as well as inhibition of fetal development processes.
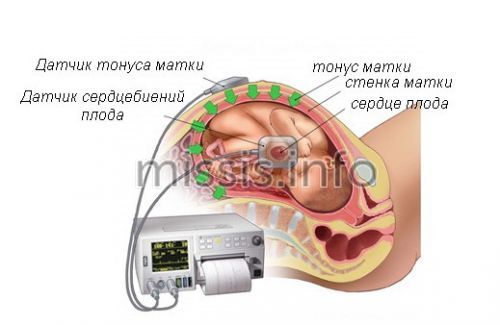
CTG is used to assess the functioning of the heart and the entire vascular system of the child in the womb. Compared to listening to the heartbeat using an obstetric stethoscope, this option is more accurate. It allows you to quickly identify tachycardia or bradycardia caused by hypoxia
In doubtful situations and the necessary equipment is available, the doctor may prescribe Doppler measurements. This is an analogue of ultrasound, which allows you to obtain detailed information about the blood flow in each of the vessels that make up a single system between the mother, placenta and fetus.
Diagnosis of placental insufficiency
To diagnose placental insufficiency, the following are used:
- Assessment of fetal cardiac activity. In addition to simple listening with an obstetric stethoscope, the most accessible and common method for assessing fetal cardiac activity is cardiotachography, which is based on recording changes in fetal heart rate depending on uterine contractions, the action of external stimuli or the activity of the fetus itself in the period after 28 weeks of pregnancy.
- Ultrasound examination (ultrasound) . At the same time, the size of the fetus and its correspondence to the gestational age are determined, the location and thickness of the placenta, the correspondence of the degree of maturity of the placenta to the gestational age, the volume of amniotic fluid, the structure of the umbilical cord, and possible pathological inclusions in the structure of the placenta are assessed. In addition, the anatomical structure of the fetus is studied to identify abnormalities of its development, as well as the respiratory and motor activity of the fetus.
- Doppler . This is a variant of ultrasound examination, which evaluates the speed of blood flow in the vessels of the uterus, umbilical cord and fetus. The method allows you to directly assess the state of blood flow in each of the vessels in the second half of pregnancy.
- Laboratory methods . They are based on determining the level of placental hormones (estriol, human chorionic gonadotropin, placental lactogen), as well as the activity of enzymes (oxytocinase and thermostable alkaline phosphatase) in the blood of pregnant women at any stage of pregnancy.
Based on a comprehensive examination, a conclusion is made not only about the presence or absence of placental insufficiency, but also about the severity of such a disorder. The tactics of pregnancy management for different degrees of severity of placental insufficiency are different.
Choosing the time and method of labor
If a woman is diagnosed with 1st degree of change in blood flow, regardless of whether it is subtype A or B, the pregnancy is prolonged and childbirth is subsequently carried out through the natural birth canal.
With grade 2 pathology, the condition is considered borderline and requires constant monitoring. If possible, they try to prolong pregnancy for as long as possible so that the respiratory system of the fetus has time to form and the surfactant necessary for the breathing of the newborn is produced.
If the therapy is ineffective or the pregnant woman is diagnosed with stage 3 disorders, the choice of specialists is on urgent surgical delivery.
How to help the body?
Treatment of uteroplacental disorders should be started in a timely manner to avoid negative consequences. If a woman is at increased risk of developing this pathology, then she should visit the gynecologist more often. The treatment method depends on the reasons that provoked this phenomenon. In most cases, medications that relieve uterine tone or improve blood clotting help improve blood circulation.
When the first signs of changes in blood circulation in the pelvis appear, a pregnant woman should immediately consult a doctor.
If a woman is diagnosed with a violation of the fetal-placental blood flow, she is immediately hospitalized at 36 weeks
. She will have to stay in the hospital until she gives birth. It should be noted that labor activity with such pathology requires special care. If a woman did not take any medications during pregnancy, she is prescribed a cesarean section, which means that a natural birth is impossible.
What emergency situations may arise?
In case of pathology of the communicating vascular system of the uterus with the placenta of 2-3 severity, situations may arise that require the emergency initiation of therapeutic measures:
- Acute fetal hypoxia.
- The formation of heart defects or other anomalies in a child that are incompatible with life or jeopardize the life of the newborn.
- Detachment or premature aging of the placenta.
- Death of the fetus in the womb.
Each of these situations is decided in accordance with the condition of the woman and child, gestational age and the degree of threat to the fetus and mother.
Severity
The severity of hemodynamic deviation from the norm in gynecology depends on the localization of pathological manifestations.
Degrees of hemodynamic disturbances during pregnancy
Hemodynamic disturbance of 1a degree during pregnancy is accompanied by an imbalance of blood exchange between the placenta and the uterus, while the normal transit of nutritional components is not changed and the child receives them in sufficient quantities.
With impaired hemodynamics of degree 1b, a deterioration in the blood supply between the child and the placenta is recorded.
In case of circulatory disorders of the 2nd degree, changes already affect three components of the “woman-placenta-fetus” circle, while the fetus experiences a slight lack of oxygen.
Hemodynamic impairment of the 3rd degree during pregnancy is characterized by a dangerous imbalance of hemodynamic parameters and increases the risk of fetal death, as well as spontaneous miscarriage.
Prognosis for the child
With a primary change in blood circulation between the vessels of the uterus and placenta, fetal death in utero or spontaneous miscarriage often occurs. If a blood flow disorder was detected in a timely manner and therapeutic measures were started, then the pregnancy is prolonged until the 37th week and this allows the woman to give birth to a healthy child.
Surgery

If the blood flow disturbance is pronounced, emergency delivery is performed. If conservative treatment fails, even in the case of a mild disorder, a decision is made within two days. A caesarean section is usually performed. If it is planned at a gestational age of less than 32 weeks, then the condition of the fetus and its viability are assessed.
Prevention
Preventive actions begin with preparation for conception and continue until childbirth. They include:
- Proper preparation for pregnancy, including the elimination of extragenital and gynecological pathologies, transferring chronic diseases into remission, registering the expectant mother with an obstetrician-gynecologist to monitor the condition and receive appropriate recommendations.
- Throughout the entire gestation, the expectant mother should receive adequate nutrition, maintaining the proportions of proteins, fats and carbohydrates, supplemented with vitamin therapy. If necessary, the diet should be supplemented with nutritional supplements such as the drug laminolact.
- The use of drugs to maintain balanced tissue metabolism and redox processes if the expectant mother is at risk. Antioxidants and hepatoprotectors can be used.
- When severe swelling occurs, a woman is advised to maintain fluid intake at 1-1.5 liters per day, but not less.
- If a woman experiences abnormalities in the functioning of the nervous system, which is most often present in asthenics with high levels of anxiety, she is recommended to take nootropic drugs and mild sedatives.
- Frequent sleep disorders in pregnant women are corrected with the help of various complex herbal remedies, based on lemon balm.
- If a pregnant woman has vegetative-vascular dystonia, which is of the hypotonic type, then adaptogens are recommended for her.
- Throughout the entire period of bearing a child, a pregnant woman should exclude any contact with infectious patients.
Women who use tobacco or alcohol products, or narcotic drugs are included in the risk group for the formation of pathological changes in the hemodynamics of the uterine vascular system with the placenta. Therefore, the elimination of any bad habits is included in the period of preparation for bearing a child.
Pathology of the uteroplacental blood flow is a serious complication of pregnancy that cannot be cured at home, without the help of a specialist. A pregnant woman needs constant monitoring by a doctor to increase the chances of giving birth to a healthy newborn naturally. In case of untimely detection, violation of specialist instructions, or refusal of therapy, the risk of developing dangerous diseases of the fetus and newborn or even death for the child increases significantly.
Normal uteroplacental blood flow
Pregnant women often do not even suspect the existence of Doppler ultrasound
. This study helps determine the volume and strength of blood flow using ultrasound radiation. Usually Doppler testing is carried out in the third semester of pregnancy, but in some cases this study can be carried out earlier.
With the help of Dopplemetry, it is possible to identify any pathologies of blood vessels in the uterus or placenta in the early stages. It also helps to identify abnormalities in the fetal carotid and cerebral arteries. Based on the results, the doctor will be able to determine whether the baby is experiencing a lack of blood flow or not.
If a woman’s uteroplacental blood flow is disrupted, her fetus is in constant deficiency of oxygen and nutrients.
Doppler ultrasound examination
, which helps determine blood flow in the pelvis. It can also be used to determine the resistance index, compliance with which is necessary for the normal functioning of the fetus. Having received accurate data from such an analysis, doctors use special mathematical formulas to calculate the speed and volume of blood flow. Based on the results, it can be concluded whether the woman suffers from BMD violations or not.