Physiology
Carrying a fetus causes changes in the female body. Hormonal imbalance occurs and organs and systems begin to function differently. This also applies to the muscle tissue of the uterus. It is partially replaced by connective cells, new collagen fibers are formed, which have elasticity and flexibility. This helps open the cervix.
Preparation of the organ for childbirth begins after 32 weeks of gestation. The outer side becomes soft, but the channel itself is still dense.
Completely softens by 36–38 weeks. It is at this time that the fetus moves into the pelvis, puts pressure on the uterus, which causes the pharynx to open.
First, the internal pharynx expands, and the tissue gradually expands to allow the baby’s head to pass through the birth canal. At the same time, the external os opens. This is how the cervix dilates during pregnancy at the beginning of the labor process. For women giving birth again, the procedure is accelerated.
Before the birth itself, the cervix shortens and widens. First, 2 fingers enter it, an opening of up to 12 cm is possible. This is the width of the channel that is necessary for the child’s head to pass through.
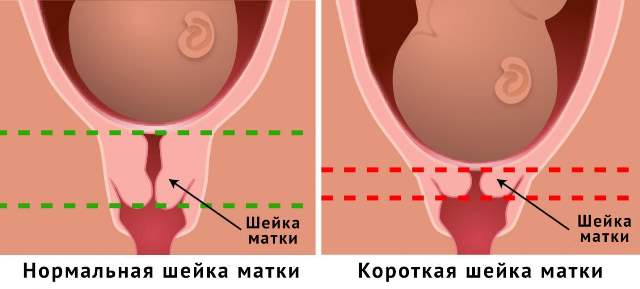
Short cervix
The main pathology of the cervix during pregnancy is its short appearance. This pathology is more common than the previous one. Its danger lies in the fact that shortening the cervix leads to miscarriage. This size is easy to detect both during normal viewing and during ultrasound.
In some cases, the cervix is naturally short, in which case it will be very difficult for a woman to bear a child, as threats will constantly arise. In other cases, the cervix becomes shorter and does not enlarge due to some reasons. They are based on previous abortions or severe gynecological inflammation. If a woman has scars on the cervix after treatment of erosion, then she is also at risk. Therefore, doctors often recommend giving birth to small erosions, and only then getting rid of it.
If the cervix is short, then it is difficult for it to support the weight of the child. She can open at any moment. A pathological cervix is not able to protect against infection as much as a normal sized cervix. During childbirth, this type of cervix can rupture, causing severe bleeding.
Signs of cervical opening during pregnancy
Disclosure does not always occur at the right time. In some cases it occurs much earlier. This is ICI or isthmic-cervical insufficiency. The pathology is dangerous because it causes miscarriage or premature birth. Therefore, the woman needs treatment.
ICI is diagnosed during examination - gynecological examination, ultrasound.
Symptoms of an open cervix during pregnancy are as follows:
- pain in the lower abdomen;
- bloody issues;
- length discrepancy relative to normal indicators;
- the amniotic sac is visible upon examination;
- feeling of spasms in the vagina.
In some cases there are no characteristic signs. Therefore, the woman does not feel that the cervix is open.
ICM
Cervical insufficiency during pregnancy is a fairly rare pathological problem. If this pathology is treated correctly, then there will be no threat to the life and health of the child.
Due to the large weight of the fetus and the large amount of amniotic fluid, the cervix in some cases cannot cope with the heavy load and there is a threat of not only miscarriage, but also premature birth. With such insufficiency, the bladder with the fetus descends into the uterine canal. As a result, the bubble easily bursts even from habitual movements, thereby endangering the child’s life.
Most often, such deficiency develops in the middle stages of pregnancy. Slightly less often, deficiency appears starting from the 11th week of pregnancy.
When making such a diagnosis, a woman must remain in bed, but even this cannot guarantee safety. In order to get rid of isthmic-cervical insufficiency, hormonal therapy is used. The woman will have to take hormonal medications for several weeks. After this, an inspection is carried out and further actions are decided.
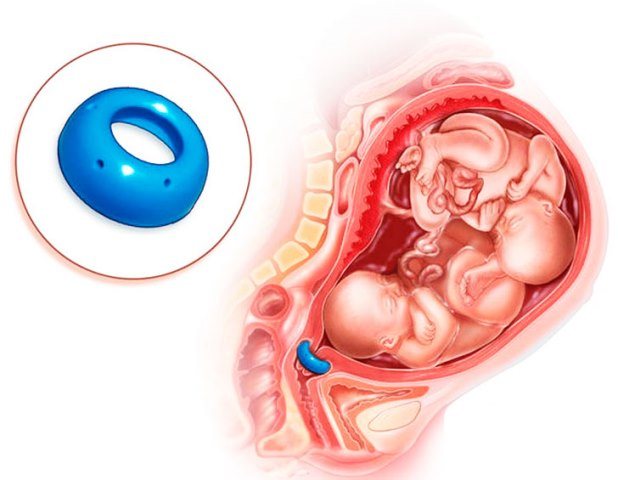
In order not to load the cervix, a pessary installation method is used. In another way, the pessary is called a gynecological ring. Such a device is necessary in order to avoid early birth. In general, a pessary can be installed at any stage of pregnancy, but most often it is installed in the middle or late stages.
Since the pessary is still a foreign device on the cervix, a woman with it requires more frequent monitoring by a doctor. The pessary must be installed by a qualified doctor, otherwise there is a risk of infection entering the vagina. In some cases, stitches are applied, but this method is more often used in the early stages.
What reasons
Dilation of the cervix prematurely, that is, in the early stages of gestation, often leads to miscarriage. An open throat cannot hold the fetus inside.
There are 2 types of isthmic-cervical insufficiency:
- Organic.
- Functional.
The first occurs as a consequence of injury as a result of:
- miscarriages, history of abortions;
- treatment of erosion, polyps;
- diagnostic curettage.
Due to such manipulations, the cervical tissue loses its elasticity and scars appear on it. The organ loses its ability to contract, as a result the fetus cannot stay in the uterus.
Causes of functional ICN:
- pathology of the uterus;
- polyhydramnios;
- hormonal imbalance.
Women with diagnosed deficiency are at increased risk.
On the video about changing the length
Isthmic-cervical insufficiency
Examination of the cervix can detect pathological conditions. An alarming sign is a shortened section. The length of the cervical canal 3 cm is dangerous. In this case, the doctor prescribes an ultrasound examination to determine the degree of threat to the pregnant woman.
If the length of the cervical canal is 2 cm, a diagnosis of isthmic-cervical insufficiency is made. A cervix that is too short and soft cannot support the weight of a developing baby. As it grows, the external pharynx will expand and infection will penetrate into it. Pathogenic microorganisms can cause disruption of the integrity of the amniotic sac and rupture of amniotic fluid. If the opening of the external pharynx occurs rapidly, the fertilized egg may fall out.
Is treatment required?
When a diagnosis is made, a woman is prescribed a course of therapy. For functional ICI, hormone-containing drugs are recommended. Taking them restores the necessary hormonal levels. The woman is recommended to rest in bed. Any physical activity is prohibited.
Other methods:
- Conservative therapy includes installation of a pessary or Meyer ring on the cervix. This is a plastic product that restrains fetal pressure. Indication – small opening for a period of 28 weeks. The ring distributes the baby's weight and pressure evenly.
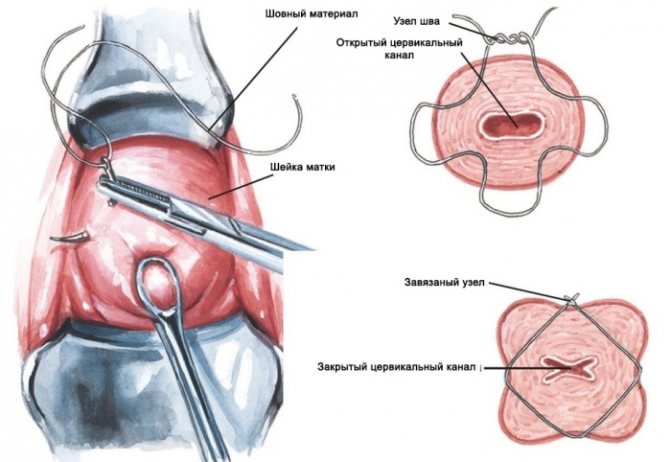
- If dilation occurs in the early stages, surgical intervention can be performed - suturing. Stitches are placed on the cervix to prevent further opening until labor begins. The suture material is removed at the onset of labor when the membranes are opened.
Additionally, antibacterial treatment is prescribed, which is necessary to prevent the development of infection. To enhance effectiveness, you can take antispasmodics.
We recommend reading the article about uterine tone during pregnancy. From it you will learn about the pathology, its causes and symptoms, why hypertonicity is dangerous, how it is diagnosed and whether treatment is required, as well as preventive measures.
During pregnancy, the cervix is hard or soft
Most women undergo an examination by a gynecologist once a year, unless there are any abnormalities in their health.
If you suspect pregnancy, you should consult a doctor. This must be done after the delay occurs. Until this moment, many ladies worry and wonder whether conception has occurred. The cervix looks different before menstruation and during pregnancy. A woman will not be able to see the changes on her own, but it is quite possible to feel them. How this diagnostic method is used, its advantages and disadvantages should be considered in more detail.
Cervix and its condition
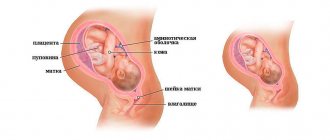
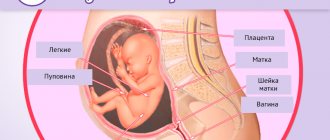
The lower part of the uterus is called the cervix. It looks like a tube connecting the vagina and the cavity of the reproductive organ. The average length of this section is 4 cm, and the length is 2.5 cm.
Changes occurring in this organ make it possible to diagnose early pregnancy, as well as the period of ovulation or regular menstruation. A gynecologist can observe its changes and determine its consistency: there is a hard and soft cervix.
This organ also makes it possible to determine whether there are any pathologies in the functioning of the female reproductive system.
An experienced gynecologist will be able to evaluate various conditions of the cervix.
If it is not possible to visit a doctor frequently, a girl has the opportunity to determine some conditions on her own. This must be done correctly.
A woman can only assess what the cervix looks like at different periods by comparison, as well as by theoretically knowing its parameters.
Cervix during menstruation
From the first day of the cycle, the uterus begins to reject the overgrown endometrium. To do this, the cervix opens slightly. This happens a few days before the start of the critical days. The position of the uterus becomes lower.
When the organ opens slightly, infections should be avoided in the vagina. To do this you should:
- Observe personal hygiene rules.
- Do not visit the pool.
- Do not swim in bodies of water.
- Wipe the anus away from the vagina.
- Do not insert foreign objects or fingers into the vagina.
- Don't douche.
Small discharge from the cervical canal that appears at this time is designed to protect the internal environment from infection. But it's not worth the risk.
Cervix after menstruation
A healthy cervix in the first phase of the cycle prepares for future conception. Her channel is narrowing. The bleeding stops. The uterus is pulled high, and the endometrium begins to grow in it.
After your period ends, your cervix becomes dry and hard. The cervical canal is closed. This position of the organ allows you to avoid infection getting inside.
The cervix feels firm to the touch. To conduct an examination at home, a woman should compare tactile sensations over two, or preferably three, cycles.
Ovulation period
A soft cervix is determined upon examination when it is time for ovulation. During this period of the cycle, the gynecologist can determine that the pharynx of the organ is open. This is called the pupil sign.
You can feel your cervix at home during ovulation and note its increased humidity. During this period, it rises a little.
If during the examination the cervical canal is open, abundant mucus is released from it with a soft surface, it means that the egg is preparing to leave the ovary. The uterus is ready to receive sperm.
After this, either conception occurs, or the body begins to prepare for the next menstruation. If fertilization does not occur, on the 16th–17th day of the cycle the canal closes and the organ takes a different position.
The period preceding menstruation
The cervix is low before menstruation. It is dry and hard to the touch. During examination, the gynecologist will note tight compression of the cervical canal. This means that the uterus is not ready to receive sperm.
By the last days of the cycle, after the absence of fertilization of the egg, the organ also undergoes a number of changes. The cervical canal enlarges.
The cervix before menstruation, the day before it begins, looks a little like what it looks like during ovulation. Only this time it opened not to accept sperm, but to tear away a layer of endometrium.
Cervix during pregnancy
The uterus undergoes a number of changes during pregnancy. In the early stages, even an experienced gynecologist will not be able to accurately diagnose the conception that has occurred. After examination, the doctor can determine what changes have occurred in the organ.
First, hidden changes within are observed. They cannot be seen so easily. In the early stages, before the delay, it looks almost like the uterus before menstruation. However, visible changes will appear very soon.
You can feel a tight cervix with a soft uterus. The pregnancy begins to appear. It is difficult to determine how many days the body will need for this. In the early stages of pregnancy, the uterus changes in the following parameters:
When fertilization has occurred, the color of the cervix begins to change. It can be described as cyanotic. There are objective reasons for this condition of the mucous membrane. They consist of increasing blood flow.
Source: https://nashi-malyshki.ru/pri-beremennosti-shejka-matki-tverdaja-ili/
Is it possible to prevent pathology
The prognosis for the pregnant woman and the unborn child with premature opening depends on the degree of the disease.
If the pathology is not diagnosed in time, pregnancy often ends in miscarriage. This happens in 20% of cases. If the necessary medical care is provided, there is a chance of reaching birth.
Prevention measures include:
- timely treatment of gynecological and endocrine diseases before conception;
- maintaining a rest regime after conception, eliminating unnecessary physical activity.
If characteristic symptoms, pain, or bleeding appear, the expectant mother should immediately consult a doctor to rule out ICI.
Symptoms of pathology
Hypertonicity is difficult to detect. A hard uterus does not have pronounced symptoms. In some cases, the expectant mother feels some tension and discomfort in the abdomen, but she is unlikely to be able to make a correct diagnosis on her own, without an examination in a gynecological chair.
As for the loose uterus, the disorder has a number of specific symptoms. Reasons for visiting a specialist to clarify the diagnosis may be:
- aching pain in the lower abdomen, accompanied by bloating;
- discomfort that occurs during sexual intercourse;
- unpleasant sensations in the vagina (unsystematic, sharp, but short-lived);
- too much mucous vaginal discharge (often mixed with blood).
How do pathologies manifest themselves?
Doctors identify several risk groups, which include women with certain pathologies. In order to assess this risk, anamnesis is very important. If a woman had abortions, especially complicated ones, before conceiving a baby, then in this case more careful monitoring of her pregnancy is required.
The use of obstetric forceps and other auxiliary medical instruments during previous pregnancy contributes to the fact that the cervix may be damaged.
Hormonal imbalance only contributes to the fact that a woman’s progesterone level significantly decreases. In this situation, doctors, as a rule, prescribe special hormonal drugs to pregnant women.
Expectant mothers carrying twins or triplets also have a higher risk of developing various cervical pathologies. Such pathological conditions appear during multiple pregnancy already in its earliest stages.
Low placenta previa very often leads to the development of various pathologies of the cervix. Typically, this pathology develops towards the end of the first trimester of pregnancy.
The lack of full medical control over the development of this condition can contribute to the development of extremely dangerous pathologies for both the expectant mother and her baby.
Women in whom doctors have identified cervical erosion before or in the early stages of pregnancy are at increased risk for the development of various pathologies. In this case, careful monitoring and selection of monitoring tactics for the expectant mother is necessary.
If by the end of the first trimester a woman’s doctors suspect isthmic-cervical insufficiency, she is referred for additional examination. For this purpose, she undergoes an ultrasound examination. In some cases, this may lead to the doctor referring the woman to hospitalization.
Isthmic-cervical insufficiency can be suspected already in the very early stages of pregnancy. In this case, the cervix opens too early. Usually it opens significantly by 8-12 weeks of pregnancy. This pathology is fraught with the possibility of spontaneous miscarriage.
Isthmic-cervical insufficiency can also lead to infection of the fetus and internal female genital organs. hormonal therapy is usually prescribed More invasive procedures are used somewhat later.
If the pathological condition is severe, then sutures may be required. This procedure is already carried out in a hospital setting. In this case, sutures are placed on the cervix. They are removed closer to childbirth.
It is important to note that isthmic-cervical insufficiency is not an absolute contraindication for natural childbirth. If the stitches are placed on time and the treatment tactics are chosen correctly, then a woman can give birth to a baby on her own without a cesarean section.
Even cervical pathologies that occur early in pregnancy and are detected in a timely manner can be controlled and effectively prevented.
For information on the norms for cervical length during pregnancy, see the following video.
Many girls are interested in what signs gynecologists use to determine pregnancy during an examination, and how this can be done at home. To have an idea of the processes occurring in the female body after fertilization, it is necessary to know the features of the location and functioning of the reproductive system.
Cervicitis in pregnant women
During examination of the cervix in early pregnancy, acute or chronic inflammation of its mucous membrane (endocervicitis) may be detected. If the mucous membrane of the cervical canal is simultaneously affected, cervicitis is diagnosed.
The inflammatory reaction is caused by pathogenic microorganisms that have settled on the mucous membrane of the cervix. The presence of inflammation is indicated by severe redness and swelling. There may be an ulcer and serous-purulent discharge on the surface. Smears from the vagina and cervical canal help identify the causative agent of the disease.
Cervicitis causes uterine tone, loose membranes, spontaneous abortion, premature birth, purulent-septic complications, as well as the development of oxygen starvation of the fetus and its intrauterine infection.
When diagnosing cervicitis, a pregnant woman is prescribed therapy directed against the causative agent of the disease (antibacterial or antifungal).
- The role of cervicitis in obstetric and gynecological pathology, Candidate of Medical Sciences Yu.I Tirskaya, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor, E.B. Rudakova, I.A. Shakina, O.Yu Tsygankova, Omsk State Medical Academy, Omsk, BUZOO “KMHC-MZOO”, Omsk, magazine “Attending Doctor”, No. 10, 2009.
- Isthmic - cervical insufficiency with various risk factors, L.I. Kokh, I.V. Satysheva, journal “Siberian Medical Review”, No. 2, 2008.
Healthy intrauterine development of a baby is impossible if the expectant mother has any pathologies of the female genital organs. During pregnancy, doctors regularly evaluate the condition of the cervix. It is especially important to carry out such diagnostics at the earliest stages of pregnancy.