The significance of this indicator during pregnancy
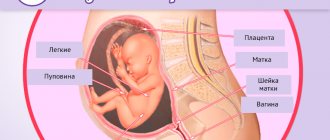
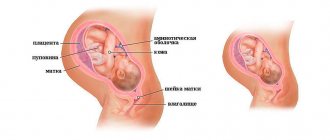
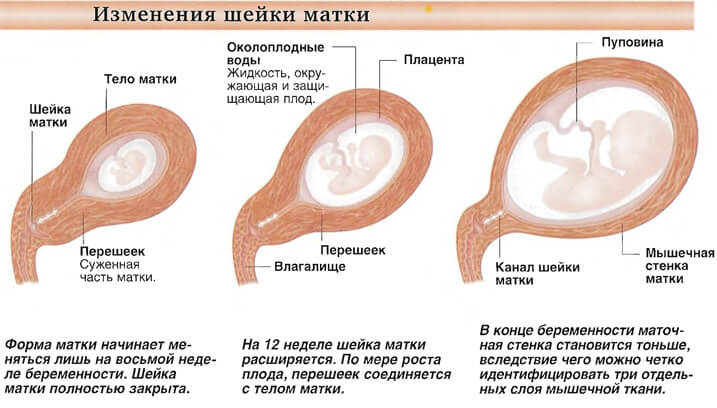
Cervix uteri is the Latin name for the lower part of a woman's reproductive organ. Inside the cervix is the cervical canal. Its upper part is icy with the body of the uterus itself, and the lower part descends into the vagina. The functions of Cervix uteri are as follows:
- Protection of the reproductive organ from various pathogenic microorganisms.
- The cervical canal is tightly closed with mucus, so it does not allow even sperm to enter the vagina at the wrong time.
- On the day of ovulation, the cervix opens and allows male reproductive cells to pass through. Thanks to this, pregnancy occurs.
After conception occurs, the Cervix uteri is again tightly closed with a mucus plug, reliably protecting the fetus from infection and other pathogenic microorganisms that can enter the reproductive organ through the vagina. Another important function of the cervix is to hold the baby as it develops in the womb.
If the Cervix uteri is weak, the woman is at risk of miscarriage or premature birth. That is why it is so important to monitor the condition of the cervix of the uterus throughout the entire period of gestation.
How does the measurement work?
These parameters are measured in medical practice in two ways. The first method is examination on a gynecological chair using a mirror and a colposcope. The second way is to conduct an ultrasound examination. During a gynecological examination, the doctor determines the condition of the external pharynx, the density of the cervix and the presence of dilation of the cervical canal. Ultrasound helps measure the length and obtain more accurate information about the condition of the internal pharynx.
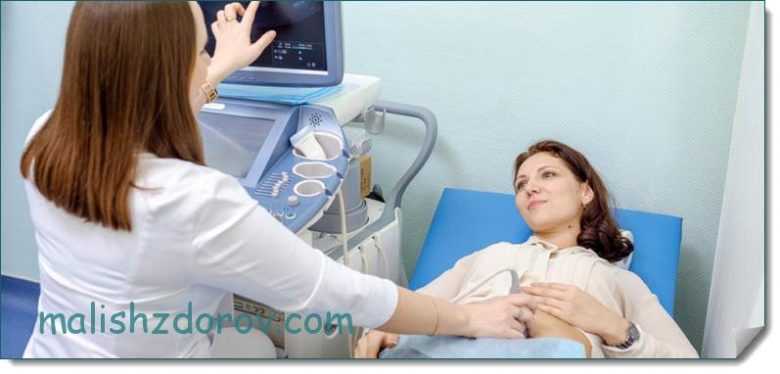
The length of the cervix is usually measured after the 20th week of pregnancy. In the first weeks, this indicator, as a rule, is not checked. This is explained by the fact that it is during this period that the baby’s active growth is observed.
Indicators dangerous for pregnancy
As a rule, the most dangerous deviations from the norm are considered to be deviations at a period of 14-22 weeks, these indicators include:
- a difference of less than 1 cm indicates the likelihood of a baby being born at 32-34 weeks of pregnancy;
- deviation from the norm by 1-1.5 cm - pregnancy can be maintained until 32-33 weeks of pregnancy;
- deviations from the norm by 1.5-2 cm - pregnancy can be maintained until 34 weeks;
- deviations from the norm of 2-2.5 cm - there is a high probability of giving birth to a baby at 36 weeks.
Popular articles:
|
Features of measurement in early and late stages
Normally, in a woman in the absence of various diseases, the length of the cervix should be approximately 3-4 cm and the width about 2.5 cm. These figures are not absolute and may be less or more depending on the individual characteristics of the girl’s body. If pregnancy has not occurred, Cervix uteri has a pink tint, a smooth structure and a somewhat shiny surface. After conception, the organ undergoes changes. Due to increased blood circulation in this area, its color becomes bluish or purple.

In addition, the process of maturation of the CMM begins. It will last all 9 months. At the same time, this part of the organ grows, becomes thicker and more elastic. This is necessary for normal labor. It is worth noting that in the early stages of pregnancy the Cervix uteri should deviate slightly towards the anus and close tightly. In the later stages, the doctor can assess by the condition of the cervix how close the woman is to giving birth. At the same time, this part of the uterus becomes softer, and the length of the cervix gradually shortens. On an ultrasound examination, you can see that the internal os is expanding, which indicates the imminent onset of labor.
You may be interested in reading an article on the topic of hCG in early pregnancy. All the necessary information is in this article.
Methods for determining the length of the cervical canal
How is the size of the cervix studied? Cervical length during pregnancy is determined in two main ways, namely:
- during a medical examination by a gynecologist, while the doctor examines by touch not only the length, but also the density of the cervix, its localization and expansion;
- cervicometry using ultrasound, which allows you to assess the extent and maturity of the cervix.
Colposcopy during pregnancy: features of the examination
From the twentieth week, the length of the cervix is recorded weekly, since it is at the 20th week that this parameter begins to change. It is necessary to study what is the normal length of the cervix during pregnancy. Sizes of the cervix at different periods of pregnancy
The normal length of the cervix during pregnancy in numerical terms depends on the period of gestation. The period after 20 weeks is more important (the length of the cervix at 20 weeks is 40 mm), but in the early stages of pregnancy it is also advisable to determine the value of the parameter. The weekly norm for different periods is disclosed in the tabular format below.
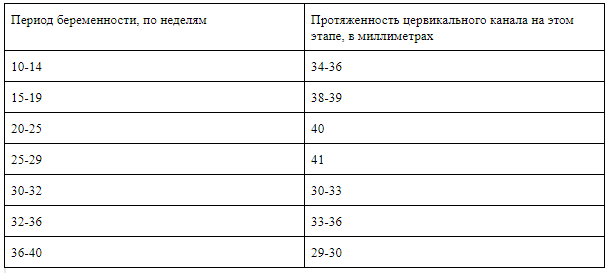
Table of norms for cervical length by week of pregnancy
Normal organ length by week
Timely diagnosis of abnormalities in the cervix allows you to take all measures to prevent negative consequences. In modern medical practice, various treatment methods are used to treat cervical cancer pathologies. These include both medications and special fixing devices to support the cervix. That is why doctors recommend that expectant mothers register in a timely manner and undergo Cervix uteri measurement at least four times.
You might be interested in: After what day after your period can you conceive?
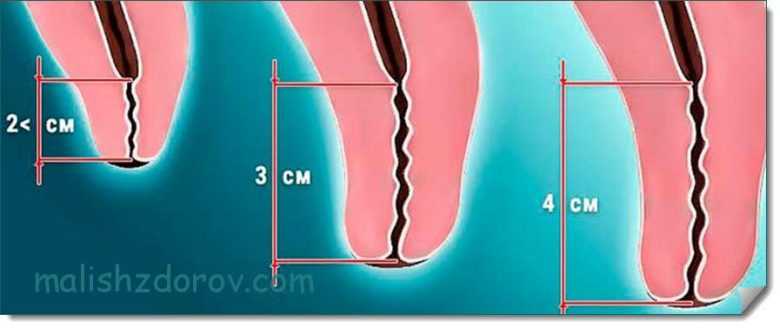
A routine examination of this indicator is carried out approximately at 20, 26-27 weeks, and then at 32-34 and 37-39 weeks of pregnancy. In the table you can see what the length of the cervix should be at different stages of gestation.
| Gestational age in weeks | Average values in mm | First pregnancy | Second and subsequent pregnancies | Standard size in mm | Deviation from the norm |
| 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16 | 35 | 35,2 | 35,7 | 23-45 | 5 |
| 17, 18, 19, 20 | 36 | 36,7 | 36,8 | 30-49 | 5,8 |
| 21, 22, 23, 24 | 40,4 | 40,6 | 40,7 | 33-45 | 4,8 |
| 25, 26, 27, 28, 29, 30 | 42 | 40,7 | 42,5 | 33-46 | 4,8 |
| 30, 31, 32, 33, 34, 35 | 36,7 | 35,9 | 36,4 | 36-43 | 3,9 |
| 35, 36, 37, 38, 39, 40, 41, 42 | 28,7 | 28,3 | 28,7 | 21-37 | 4,5 |
If in the first and second trimester the cervix is shortened or short, this indicates a threat of miscarriage or premature birth. In this case, the patient requires hormonal or other types of therapy. The prognosis for a woman is not very good even if the cervix is too long before the upcoming birth. In addition, it should be noted that in primiparous girls, the length of the Cervix uteri increases more slowly than in multiparous girls.
In case of twins, the length of the cervix may differ slightly from the indicators discussed above. However, it may be slightly shorter than with a singleton pregnancy.
Norms for cervical length during pregnancy
The cervix at the 12th week of pregnancy, at 13 weeks and up to the 15th week does not differ in length from the size of the cervix in a non-pregnant woman, provided she is in gynecological health. The size of the cervical canal of the uterus at 16 weeks and beyond begins to increase. The length of the cervix at 19 weeks is approximately 39 mm. The cervical canal should further increase, and the cervix at 21 weeks already has a length of 40 mm. The maximum length of the cervix is reached at 29 weeks.
Thus, until the 29th week, the length of the cervical canal gradually increases during pregnancy. For this reason, the answer to the question of whether the cervix can lengthen during pregnancy is clearly affirmative.
Preparing the cervix for childbirth
Changes in cervical length during pregnancy:
- after 29 weeks, the cervical canal shortens for a certain period - up to 32 weeks;
- the length of the cervix at the 31st week of pregnancy, as well as at the 30th week, should be in the range of 30-33 millimeters;
- the cervix at 32 weeks is approximately the same length;
- at 33 weeks and further up to 36 there is a slight increase in the length of the cervix;
- at 34 weeks and 35 weeks of pregnancy, the parameter value ranges from 33 to 36 mm.
The length of the cervix decreases at 36 weeks and further. The body is preparing for delivery, the pharynx opens, the structure of the cervical canal changes, and the cervix softens. The length of the cervix before childbirth is reduced to ensure timely opening of the pharynx and the onset of labor.
When is Ginipral prescribed for pregnant women?
Changes in the cervix during pregnancy
Thus, the normal, acceptable size of the cervix during pregnancy week by week helps to verify the parameter values obtained during the study and identify deviations from the norm. It is especially advisable to control the length of the cervix before childbirth.
By what indicators does the doctor judge the maturity of the cervix?
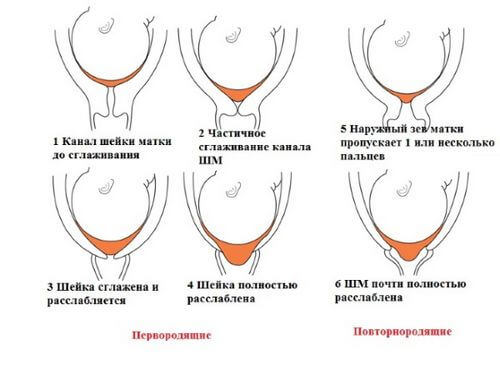
During a medical examination, not only the size of the cervix, its shortening or, conversely, lengthening are taken into account. Other criteria also indicate the degree of maturity of the organ. Let's look at them:
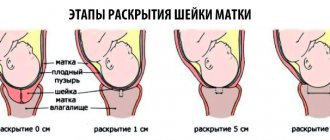
- Consistency of CMM. It is rated in points - dense - 0, soft - 1, soft - 2.
- Length. From 2 cm – 0, 1-2 cm – 1, less than 1 cm – 2.
- Location relative to other organs. Tilt back – 0, tilted forward – 1, in the center – 2.
- The degree of opening of the cervical canal. The doctor's finger does not pass - 0, one finger passes - 1, passes 2 fingers - 2 points.
Cervix uteri should be more dense to the touch in the early stages. In the second and third trimester, it becomes softer and smoother, which indicates that it is almost ready for childbirth. If any abnormalities are detected in the expectant mother, the doctor is obliged to inform the patient of the diagnosis and explain what to do to prevent dangerous complications.
You may be interested in: Chofitol during pregnancy

A soft cervix, for example, at 38-39 weeks does not mean that the expectant mother has some kind of pathology. This is a completely normal phenomenon before childbirth. It is much worse if the cervix is dense and immature at this stage.
Is lengthening of the cervical canal during pregnancy a pathology?
However, not only shortening of the cervix can lead to problems during pregnancy. The cervical canal may lengthen, and the reasons for this may include:
- congenital anatomical features of the cervix;
- frequent inflammation of the reproductive system;
- injury to the cervix;
- surgical interventions.
An elongated cervix can provoke disturbances in the processes of fertilization, bearing a baby, and labor.
The structure of the uterine os is disrupted, and the placenta may not attach correctly. There are often cases when a woman carries her pregnancy to term because the reproductive system is not ready for childbirth.
A long cervix is often characterized by a hard structure and is poorly extensible, which is why it does not mature by the expected date of birth.
How to prepare the cervix for childbirth
In addition, in this case, the duration of the period with contractions is prolonged, which weakens the female body and leads to a deterioration in labor. Most often in such situations, labor stimulation is required.
Possible deviations from this body
Measuring the length of the cervix during pregnancy makes it possible to timely suspect various pathologies in a woman. These disorders can cause serious problems, including fetal death and premature birth. Let's take a closer look at common problems.
Ectopic pregnancy in the cervix
It happens that in the early stages of pregnancy the cervix is too enlarged. In this case, the doctor may suspect such a dangerous condition as the attachment of a fertilized fertilized egg in this part of the genital organ. Under such conditions, the embryo lives for approximately 5-6 weeks, less often 6-7, after which it dies and is rejected.
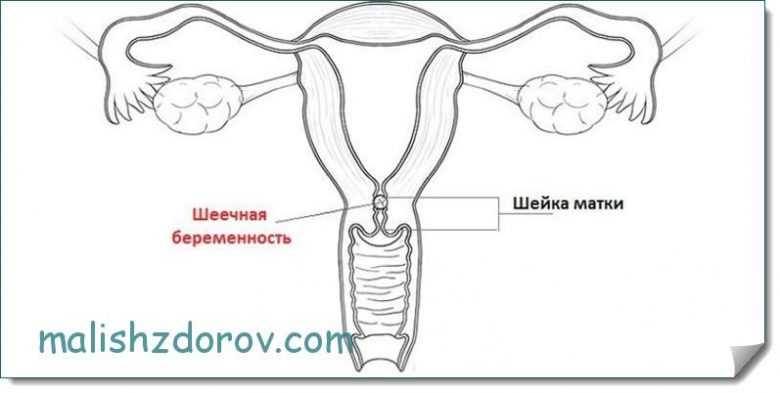
This type of pathology is considered quite rare and occurs no more often than in 0.01% of cases. Read more about ectopic pregnancy here.
Short neck
Shortening of this part of the organ can be either a congenital or acquired condition. In addition, it often happens that such parameters are observed in a woman due to the anatomical features of her body. Normally, the length of the cervix increases in the first and second trimester and shortens immediately before childbirth. If the length of the organ is too short, it will be difficult for it to support the growing fetus, which often leads to premature birth.
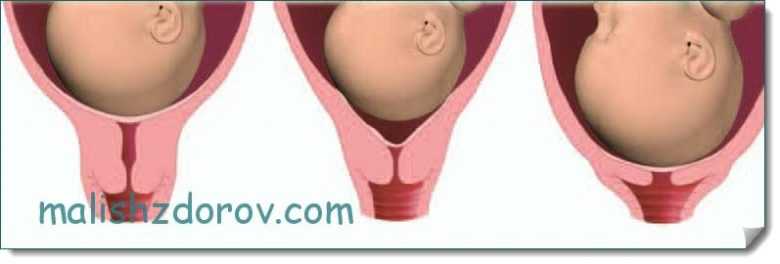
If such a condition is detected, the woman is subject to stricter medical supervision. Often, the expectant mother is offered to go to a hospital for preservation and completely limit physical activity. In addition, methods of treating this pathology include the installation of a pessary - a special ring that prevents the pharynx from opening prematurely. This device is removed before childbirth.
Extended neck
This disorder in women can also be a congenital feature of the body or develop as a result of various medical manipulations in this area, for example, after undergoing operations. This feature may cause some problems during conception. We can talk about, for example, improper attachment of the fertilized egg when it is implanted too low to the exit from the reproductive organ.
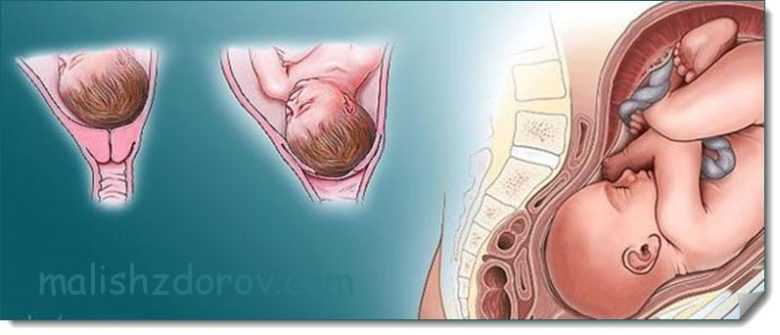
Childbirth is also complicated for women with this deviation. They are usually painful and protracted, and the risk of rupture increases.
Erosion
Sometimes the length of a woman’s cervix during pregnancy is normal, but a disease such as erosion may be detected. This disorder occurs among the fair half quite often, in approximately 60% of cases. Factors that provoke pathology include a wide variety of causes. These could be hormonal disorders, inflammatory processes in this area, and much more. Treatment of the disease is carried out using minimally invasive techniques such as cauterization and laser treatment. If erosion is diagnosed in a nulliparous woman, treatment is postponed to rule out problems with the resulting scar. At the same time, the expectant mother faces the threat of organ rupture and other dangerous complications.
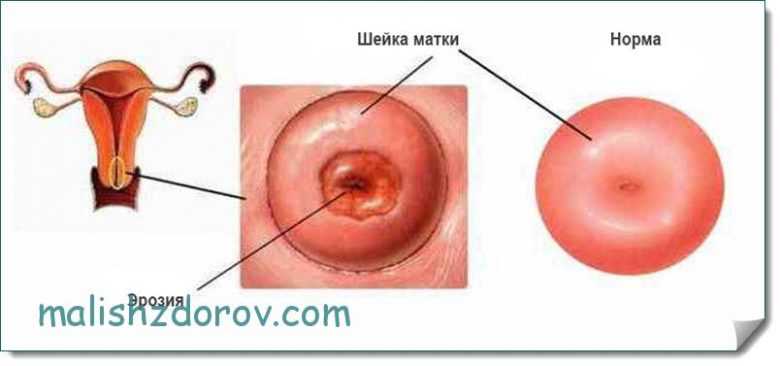
For many girls, after childbirth, erosion goes away on its own. The pathology does not affect the course of pregnancy itself.
Dysplasia
During colposcopy, another problem may be discovered in the patient - dysplasia. Pathology involves processes of change in the epithelium, which indicates precancerous conditions. In most cases, the disease is diagnosed in women aged 25 to 35 years. Timely treatment of pathology in the early stages allows you to cope with the disease without developing dangerous complications.
You might be interested in: Is it possible to get pregnant from the lubricant secreted by a man?

The causes of dysplasia include human papillomavirus. The risk group includes girls suffering from bad habits, as well as patients with weakened immunity and the presence of chronic inflammatory diseases. Another reason is the start of sexual activity too early and frequent changes of sexual partners. Treatment of the disease is carried out with medication or surgery.
Expert opinion
Ksenia Dunaeva
User experience expert and comment moderator. Higher medical education and more than 5 years of actual practice.
Ask Ksenia
A mild degree of dysplasia rarely degenerates into oncology, so this condition requires only medical supervision.
Ectopia
This concept means the same erosion, but with it part of the columnar epithelium is displaced into the vaginal area. During the examination, the gynecologist may see a red round spot that looks very similar to erosion. In this case, the patient may experience discharge with an unpleasant odor and uncharacteristic color. The causes of this pathology include mechanical damage to the reproductive organ, as well as various infectious diseases suffered by a woman in the past.
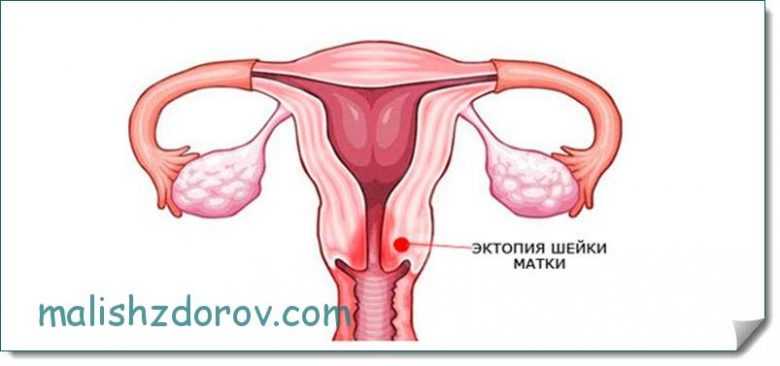
After bearing the baby and giving birth, changes in the form of ectopia observed in the patient, as a rule, go away on their own.
Recommendations for the expectant mother during pregnancy
The period of bearing a baby is a very important and responsible time in the life of every woman. At this stage of life, the expectant mother should be very attentive to her body, since now she has double responsibility. To prevent various complications and miscarriage, a girl should adhere to the following recommendations:
- Walk outdoors more often.
- Sleep and relax more.
- Properly organize working conditions and daily routine.
- Eat right, saturate your body with all the necessary vitamins and minerals.
- To refuse from bad habits. Smoking and alcohol negatively affect the health of the mother and fetus.
- Register in a timely manner and follow all recommendations of the specialist.
- Avoid heavy lifting and heavy physical work.
- Try to eliminate stress and excessive emotional disturbances.
- Devote more time to communicating with loved ones, read books, watch calm films.
If any alarming symptoms occur, you should contact your doctor immediately. All this will help maintain the health of mother and child, as well as prevent such dangerous pathologies as miscarriage, placental abruption and premature birth.

Do you want to know how to register during pregnancy? Then you should definitely read this article.