What can cause premature birth?
Primarily an infection
2. Normally, the uterine cavity is sterile. Any inflammatory process makes the uterine wall defective, so pregnancy continues as long as the uterine wall can stretch, and then the body tries to get rid of the embryo.
That is why there is no need to spare money, time and effort to be examined for the presence of infection. Every woman - ideally even before pregnancy - should be examined for the presence of infectious diseases, especially those that are often asymptomatic (carriage of chlamydial, ureaplasma, mycoplasma, toxoplasma infections, herpes simplex virus, cytomegalovirus). Women with a history of chronic and acute inflammation of the uterine appendages and endometrium (the mucous membrane of the uterine body), intrauterine interventions (abortions, diagnostic curettages), as well as cases of spontaneous abortion should deserve special attention. If there is an inflammatory process, it naturally needs to be cured. Medicines and procedures selected by your doctor will help expel the infection from the body even before conception. If for some reason the necessary tests were not done before conception, then when diagnosing pregnancy you should definitely undergo an appropriate medical examination, and in the future you should not neglect regular examinations. The sooner the presence of microbes in a woman’s body that can cause premature birth or are potentially dangerous to the fetus is detected, the better. Modern medicine has a significant arsenal of tools to reduce the risk of miscarriage and fetal infection.
The second common cause of premature birth is isthmic-cervical insufficiency
, ICN (isthmus - “isthmus”, the place of transition of the uterine body into the cervix, cervix - “uterus”), that is, the inferiority of the muscular layer of the cervix, which, during a normal pregnancy, plays the role of a kind of sphincter (retaining ring) that does not allow the embryo to " leave the uterine cavity. ICI can be congenital (very rare) or acquired. What can cause the development of ICI? The reasons are quite banal: injuries to the isthmus and cervix during abortion, especially when terminating the first pregnancy, deep ruptures of the cervix in previous births (this can happen, for example, during the birth of a large fetus, the application of obstetric forceps), gross forced expansion of the cervical canal during diagnostic manipulations in the uterine cavity (hysteroscopy, i.e. examination of the uterine cavity using a special device - a hysteroscope; endometrial curettage), that is, any injury to the muscular layer of the cervix.
Very often, ICI is formed due to hyperandrogenism - an increased level of male sex hormones in the blood, which are produced in the adrenal glands of the mother, and later in the fetus.
Infections and isthmic-cervical insufficiency are the main, but not the only factors causing premature birth. Endocrinopathies often lead to premature birth
- mild dysfunction of the endocrine glands - the thyroid gland, adrenal glands, ovaries, pituitary gland (with severe disorders, women, as a rule, cannot become pregnant on their own).
Premature birth can also occur when the uterus is overstretched.
caused by multiple pregnancy, polyhydramnios, large fetus.
Hard physical work
, a chronic
stressful situation
at work or at home, any
acute infectious disease
(influenza, acute respiratory infections, tonsillitis, pyelonephritis, especially with increased body temperature, etc.) can also provoke termination of pregnancy.
Causes of childbirth at 36 weeks of pregnancy
Childbirth at 36 weeks of pregnancy can be caused by 4 main reasons:
- infectious and inflammatory processes (25-40% of cases) of cervical-vaginal localization or in the urinary tract;
- activation of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal system;
- uterine bleeding caused by abruption or placenta previa; decreased blood flow in the placenta and uterus;
- overstretching of the uterus as a result of physical exertion.
Infections can be descending, that is, spread from other organs, for example, with periodontitis. Therefore, it is important to eliminate bacterial foci in the oral cavity before pregnancy or in the first months.
The triggering of premature birth in infectious diseases is carried out indirectly, through the activation of the production of prostaglandins - mediators of inflammation, as well as enzymes that lead to the destruction of the intercellular substance.
They increase uterine contractions and destroy the membranes, resulting in the release of amniotic fluid. Bacteria and inflammation are also found in the amniotic fluid in 80% of caesarean sections, which are performed on women before the membranes rupture after the onset of labor.
The following factors increase the risk of preterm birth:
- hormonal pathologies (thyroid disease, diabetes mellitus and others);
- bleeding disorders;
- the age of the pregnant woman is under 18 or over 34 years old;
- stress (the risk increases by 2 times);
- multiple pregnancy (15-20% of all premature babies);
- smoking, since nicotine has a strong vasoconstrictor effect, leading to a deterioration in placental blood flow;
- alcohol consumption;
- overheating;
- polyhydramnios and oligohydramnios;
- placenta previa;
- obesity;
- surgical interventions on the abdominal organs during pregnancy;
- history of miscarriages, abortions and premature births;
- injuries;
- poor nutrition, leading to deterioration of immunity and resistance to infections;
- insufficient body weight, which is associated with a low volume of circulating blood, leading to disruption of uterine and placental blood flow.
What to do if premature labor begins?
If alarming symptoms appear: abdominal pain, leakage of amniotic fluid, urgent hospitalization is necessary. Only in a hospital can doctors choose the right tactics for each specific case.
Before the ambulance team arrives, you can take 2 tablets of No-shpa or, if a woman is taking Ginipral, an additional tablet of this drug.
As a rule, in a hospital they try to preserve the pregnancy, since every day spent in the womb increases the child’s chances of survival.
What do doctors do to stop premature labor?
In case of premature onset of contractions, first of all, topolytic (that is, reducing the tone of the uterus) drugs are prescribed - partusisten, ginipral. First, these drugs are administered intravenously, and when contractions stop, a switch to tablet forms is possible. These medications are usually taken until 37 weeks of pregnancy. Magnesia sulfate, a 10% solution of ethyl alcohol and some other drugs are also used as agents that reduce the tone of the uterus.
At the second stage of treatment, they try to eliminate the very cause of premature birth. When an infection is detected, antibacterial drugs are prescribed (depending on the type of infection), sedative (that is, calming) therapy - in order to break the vicious circle: in addition to the objective factors that increase the tone of the uterus, the fear of losing a child is added, which, in turn, further increases the tone uterus
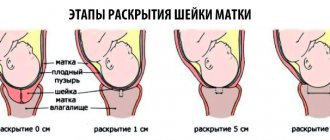
When ICI develops up to 28 weeks of pregnancy, “tightening” sutures are placed on the cervix, which prevent the fertilized egg from “falling out” of the uterus. Sutures are placed under short-term intravenous anesthesia, using drugs that have minimal effect on the child.
At a period of more than 28 weeks, if the cervix is defective, a special supporting Golgi ring is inserted into the vagina: without narrowing the cervix, it holds the presenting part of the fetus, not allowing it to put pressure on the cervix. In this case, if the contractions have stopped, further opening of the cervix does not occur.
The treatment complex always includes the hormonal drug dexamethasone (microdoses of this hormone are prescribed, so side effects are practically excluded). Its action is not aimed at preventing premature birth, but at stimulating the “maturation” of the baby’s lungs (so that he will be able to breathe on his own if he is still born prematurely).
A woman must comply with bed rest, and in a hospital setting. In nutrition, it is better to avoid irritating, spicy, fatty, and difficult-to-digest foods.
The situation is more complicated with premature rupture of amniotic fluid. During pregnancy up to 34 weeks, if labor has been suppressed, the condition of the woman and fetus is normal, there is no increase in body temperature, no inflammatory changes in the blood, it is possible to maintain and prolong pregnancy with the obligatory prescription of antibacterial drugs to prevent infectious complications. (The fact is that the breaking of water indicates a violation of the integrity of the fetal bladder. This means that the vagina is now communicating with the uterine cavity, that is, the path of infection is open, and taking antibacterial drugs is a vital measure.)

Doctor's advice to give birth to a healthy baby
The probability of a mature woman becoming pregnant is determined by the organization of her life. By following simple principles of caring for the body, you can prolong youth and prepare the body for menstruation and fertilization to occur:
- avoid stressful situations and unpleasant moments;
- go to bed before 10 pm;
- if the body requires it, sleep during the day;
- give up tobacco before conception;
- avoid drinking alcoholic beverages;
- take a course of vitamin complex;
- eat healthy foods;
- watch only positive TV shows and movies;
- tune your thoughts to the positive;
- take a walk in the fresh air every day;
- get tested for worms;
- Examine your body completely for preventive purposes.
Do doctors always try to stop premature birth?
No not always.
There are situations that require early delivery due to the woman’s threatening condition. In severe forms of late toxicosis (preeclampsia), chronic diseases of internal organs, doctors often induce premature birth to save the life of both mother and fetus.
At a period of more than 34 weeks, when the waters break, the pregnancy is also not maintained, but they try to carry out the birth very gently and carefully.
What happens to a woman after premature birth?
The course of the postpartum period3 with premature birth, as a rule, is no different from that after a timely birth. It happens that a woman is detained in a maternity hospital longer than expected, but in most cases this is due to the condition of the child, and not the woman herself.
It is advisable for all women after premature birth to undergo a comprehensive examination, including tests for the presence of infectious diseases and carriage of infectious agents, and a study of hormonal status. In case of ICN, it is necessary to perform hysterosalpingography (x-ray examination of the uterus and fallopian tubes after the introduction of a radiopaque substance into their cavities); in case of severe somatic diseases, be examined by appropriate specialists. Naturally, if violations are detected, you need to undergo a course of treatment.
During subsequent pregnancies, hospitalization in a maternity hospital during the so-called “critical periods” is advisable. The greatest concern is the timing of termination of the previous pregnancy. In addition, the following are considered critical periods: the first 2-3 weeks (fixation of the fertilized egg in the uterine mucosa); 4-12 weeks (placenta formation); 18-22 weeks (intensive increase in uterine volume); days corresponding to menstruation.
Medical aspect
The opinion of doctors regarding late pregnancy is still ambiguous. Some do not see any obstacles to having a child at 35–37 years old, others, on the contrary, intimidate a woman with all sorts of problems.
Often, gynecologists are particularly persistent and even dissuade the expectant mother from late pregnancy, citing serious risks to the health of the woman and child.
Risks
Pregnancy after 35 years is different from that at 22–26. First of all, it is fraught with the following medical problems:
- More complex flow.
- Exacerbation of chronic diseases.
- Exchange disorders.
- Gestational diabetes mellitus.
- Chromosomal abnormalities in a child.
- Violation of labor.
- Difficult postpartum period.
This does not mean that every woman after 35–36 years will encounter these problems. Some, on the contrary, endure the hardships of pregnancy much easier than twenty-year-old girls. However, you still need to know about possible dangers in order to pay attention to problems in your health in time and consult a doctor.
Difficult flow
The difficult course of pregnancy at the age of 37–40 years cannot be explained by any one reason. A combination of negative factors that the expectant mother has to face throughout her life plays a role here.
Obviously, at 20–25 years of age, health is much stronger, there is more strength, activity is increased, and any difficulties are perceived differently. While excess load after 35 years can cause fatigue and apathy, severe fatigue and even depression. Sometimes the body can react to an unexpected load with various diseases.
Older pregnant women often experience severe toxicosis and gestosis, high and low water levels, premature aging of the placenta, and pathological labor.
Exacerbation of chronic diseases

According to doctors, carrying a baby has a negative impact on chronic diseases. Even if they were previously in a state of long-term remission, pregnancy can provoke exacerbations. The older a woman is, the more luggage she has of various pathologies - respiratory and digestive systems, diseases of the endocrine organs.
Frequent colds and acute respiratory viral infections against a background of weakened immunity lead to the activation of opportunistic microflora. The result of this is a recurrent runny nose, sore throat, enlarged lymph nodes - exacerbation of chronic tonsillitis, adenoiditis, pharyngitis.
The previously compromised digestive system during pregnancy makes itself felt with cholecystitis and pancreatitis, irritable bowel syndrome, and dyspeptic symptoms.
If a woman had problems with the thyroid gland before pregnancy, the disease will most likely progress during pregnancy, which can lead to its decompensation.
That is why gynecologists strongly advise their patients to visit specialized specialists before conceiving and treat existing diseases.
Exchange disorders
As a woman ages, she loses valuable microelements such as calcium and iron. Calcium metabolism is extremely important for the normal functioning of the musculoskeletal system. In addition, the correct development of the child depends on it. The older a woman is, the more likely she is to have an underlying calcium deficiency. This means that during pregnancy she may experience problems such as:
- brittle nails;
- hair loss;
- multiple caries;
- bone pain.
Lack of iron leads to a decrease in the amount of hemoglobin and the development of anemia. Usually this trace element is lost during menstruation. If menstruation is heavy or iron loss is not replaced with food, iron deficiency develops over time.
The likelihood of anemia is directly related to age. The older the expectant mother, the more likely this disease is.
In order to prevent metabolic disorders, doctors prescribe special vitamins and iron supplements.
Gestational diabetes mellitus
This disease is associated with disruption of the pancreas, or more precisely, its insular apparatus. A characteristic feature of the disease is that it occurs only during pregnancy. After childbirth, diabetes mellitus may disappear without a trace, although in some cases the pathology of carbohydrate metabolism persists until the end of life.
The risk of gestational diabetes increases with age. It is impossible to predict its occurrence, as well as to carry out preventive treatment. As a rule, this disease debuts at the end of the second or third trimester.
The consequences of diabetes include:
- The birth of large children, which can seriously complicate childbirth.
- Decrease in sugar levels in babies in the first days of life.
- The child is lagging behind in intellectual-motor development.
- The risk of developing type 2 diabetes in the future.
Currently, at 24–28 weeks, all pregnant women undergo a screening test of blood sugar levels - a glucose tolerance test.
Fetal chromosomal abnormalities

Doctors are unanimous regarding this problem. The risk of having a baby with a chromosomal abnormality directly depends on age. And there is an explanation for this.
Unlike sperm, a woman does not form new eggs, and their number does not increase throughout life. However, over the years, mutations accumulate in them. This is due to the influence of unfavorable factors on the female body, the negative consequences of which are stored in the germ cells and can be passed on to offspring.
The older the woman, the higher the likelihood of participating in the conception of such a defective egg. That is why, after 35–37 years, the risk of having a child with trisomy - Patau, Edwards and Down syndrome - increases sharply.
For example, the probability of trisomy 21 by the age of 40 is 1:365 versus 1:1000 at the age of thirty.
There is no way to prevent chromosomal damage. In developed countries, all patients over 35 years of age are offered invasive diagnostics - amniocentesis. It allows you to identify genetic pathology before the birth of the child and terminate the pregnancy. However, this option is not suitable for all parents due to ethical and religious beliefs.
The number of children with chromosomal abnormalities born from late pregnancy remains significant.
Disturbance of labor
Childbirth is the final stage of pregnancy, a complex and responsible process. During this period, a woman can face various dangers, and their likelihood is higher the older the woman in labor is.
Problems during childbirth include:
- Pathological preliminary period. These are irregular painful contractions, the intensity of which increases in spurts, causing real agony to the woman, but does not lead to adequate dilatation of the cervix.
- Primary and secondary weakness of labor.
- Weakness during the period of pushing.
- Perineal ruptures due to a large fetus or improper management of labor.
- Bleeding.
Of course, even at 20–25 years of age, childbirth can be accompanied by these complications. But still, the compensatory capabilities of a young organism are much higher. Often, at 35–40 years old, the process of childbirth itself is much more difficult for a woman. But, as a rule, this is typical for the first pregnancy.
If a second or third or fourth child is expected, then there is another danger. Childbirth can be very fast - rapid. And this is also not good for the baby.
Difficult postpartum period
The postpartum period can be problematic at any age, but after 37–40 years of age this likelihood increases.
If a woman has had stitches, the healing and recovery time may be longer. This is due to a decrease in the regenerative abilities of the skin and mucous membranes.
In addition, the risk of postpartum depression and neuroses increases with age. A woman gets more tired and has a harder time with lack of sleep and physical activity.
The capabilities of the immune system are also reduced. The body's defenses are restored much more slowly. This means that there is a higher risk of developing colds or acute respiratory viral infections.
If chronic diseases worsen, then at 37–40 years old it is more difficult to cope with them than at 22–25.
We should not forget that with age, the number of anovulatory cycles increases and the ability to conceive a child naturally decreases significantly.
Benefits of Late Pregnancy
But still, late pregnancy is not only disadvantages. It also has its advantages. Very often, expectant mothers note a surge of strength, increased activity, and increased performance during pregnancy. Carrying a baby forces the body to rebuild itself and restart its work.
In addition, for many women, pregnancy and childbirth after 35 years is a conscious and desired event. They allow you to eliminate depression associated with a midlife crisis and get rid of stress by switching to the anticipation of motherhood.
Positive emotions force the body to produce hormones of joy and pleasure, which has a positive effect not only on a woman’s health and well-being, but even on her appearance. It is not without reason that many people notice that pregnancy and childbirth after 35–37 years rejuvenate a woman.
What happens to the baby after premature birth?4
Currently, it is possible to nurse children whose body weight at birth is more than 1 kilogram, but, unfortunately, such low birth weight babies survive only in 50% of cases. Sometimes children with a body weight of 500 to 1000 grams are nursed, but this happens extremely rarely, in addition, it is a very, very expensive process. Children born weighing more than 1500 grams are easier for pediatricians to care for, since all their organs are more “mature.”
At the second stage of nursing, premature babies are often sent to children's hospitals.
1
Preterm birth is usually diagnosed after 28 weeks of pregnancy.
Spontaneous termination of pregnancy between conception and 28 weeks is called spontaneous abortion (miscarriage). For more information about the threat of termination of pregnancy, see: A. Koroleva, “Threat of termination of pregnancy” / No. 1 -2001. 2
For more information about infectious diseases, see: Zh. Mirzoyan “You need to know the enemy by sight.
TORCH infections - what is it?”/No. 4-2001; S. Gonchar “Treatment is light, and non-treatment is darkness. Diseases that threaten intrauterine infected fetuses”/No. 5-2001. 30
during the postpartum period, see N. Brovkina’s article “The Fourth Trimester” in this issue of the magazine.
4
The subject of this article is premature birth, so literally a few lines are devoted to nursing premature babies. Detailed material on methods of caring for premature and low birth weight babies will be published in one of the upcoming issues of our magazine.