By the way the baby moves in the stomach, you can determine his well-being. Tremors are a physiological norm, because during the process of embryonic development, the skeletal muscles and nervous system begin to function in the fetus. To maintain normal muscle function, he begins to actively move. In addition to natural needs, movements occur as a reaction to external and internal stimuli.
First movements
The embryo begins to move at 7-8 weeks, but during this period of intrauterine development it is characterized by its small size. Therefore, his activity goes unnoticed.
The tremors become more noticeable at 16-20 weeks of pregnancy if the woman is hypersensitive or thin.
In 74% of cases, women feel a slight movement of the baby at the 23rd week of embryonic development. In the early stages, movements are rare, they appear 1-2 times in 24-72 hours.
Why is the baby pushing?
In the second trimester of pregnancy, intense fetal movement is observed. The embryo turns over freely or extends its limbs. The tremors and their pace are individual for each fetus. The baby in the tummy takes a more comfortable position, so the woman feels movements inside herself.

Ultrasound examinations revealed that the child was swallowing amniotic fluid. On an ultrasound, the expectant mother can see the movements of the embryo's arms and legs, grasping reflexes with the umbilical cord, and head turns. In 25% of cases, a child may push after eating sweet foods. In addition, movements appear in response to irritation:
- from loud sounds;
- votes;
- sources of light and noise.
Strong movement begins when there is a hormonal imbalance or emotional shock to the mother.
Babies need movement too
To maintain skeletal muscle tone, a person must constantly move. This happens at the level of reflexes. A similar situation is observed in the embryo. Prototypes of muscles - somites - appear at the 4th week of pregnancy. By the end of the 8th week, the nervous system is finally formed, which begins to stimulate muscle contraction and set it in motion.
Reflexes develop by 9-10 weeks, when the baby actively swallows amniotic fluid. From the 18th week, a grasping reflex appears when the embryo holds on to the umbilical cord.
At the same time, a motor reaction to stimuli appears, which is necessary for the mother to assess the well-being of the fetus.
How and what to do to make the child move
An embryo is a future person whose body increases physical activity after eating food. In particular, the intensity of movements increases when consuming high-carbohydrate foods: desserts, baked goods, candies and other foods high in sugar.

When eating sweets, the plasma concentration of glucose in the mother’s blood increases, which, after passing through the umbilical cord, begins to circulate in the embryo. Its cells actively consume energy, and its excess amount manifests itself in the form of tremors. Therefore, sweet foods help provoke movement.
In some cases, the baby moves while the mother is resting. At rest, the amniotic fluid does not create vibrations that could put the embryo to sleep. In such a situation, the fetus is pushed. If the baby in the stomach does not move, he may also be sleeping.
Intrauterine movements can be recorded during walking or when the mother is in a good mood. It is important to remember that the mother’s hormones enter the fetus’s body through the blood. Therefore, high dopamine levels can affect the intensity of his movements.
Temperature changes can make the embryo move in its tummy during sleep or increase its physical activity. To do this, you need to direct a stream of cold water onto your stomach for 5 seconds.
Baby, how are you?
Studies have shown that in utero a child reacts to external sounds and brightness of light. Their strength affects the intensity of his movements. It is also known that its activity is influenced by both the mental and physical state of the mother. The state of wakefulness and rest can change in the fetus within every hour. This occurs in accordance with the physiological rhythms of its intrauterine development, which are different for everyone. Some babies may be more mobile in their mother's belly, while others may be calmer. Their intrauterine life follows its own laws, which have not yet been fully studied.
Even in the mother's womb, children have days of special activity and periods when they want to rest and behave calmly. Sometimes fetal movements can be caused by the body touching the inner wall of the fetal membrane, from which it moves away. Perhaps not enough oxygen is supplied to him through the blood through the umbilical cord. When it moves, its position changes, blood flow increases and oxygen supply increases.
The fetus makes breathing movements, sighs, and sometimes hiccups. At times, the expectant mother feels cramps in her stomach from his hiccups. In the fetus, as in the newborn child, this does not cause any particular inconvenience. With some babies this happens every day, or even several times a day, while others do not hiccup at all.
The number of fetal movements increases as pregnancy progresses. Rhythmic beats in some cases become regular and are repeated at constant intervals, while in others the fetus pushes spontaneously and variedly. The greater activity of the fetus in the mother's womb does not mean at all that after birth it will be more restless than those babies whose movements were less intense.
D. Pearson's test "Count to ten"
On a special card, the number of fetal movements is recorded daily from 28 weeks. Counting starts at 9:00 and ends at 21:00. A small number of movements (less than 10 per day) may indicate oxygen deficiency in the fetus and is a reason to consult a doctor.
The influence of the environment on fetal behavior
The child reflexively reacts to changes in the world around him. Movements are provoked by the following factors:
- touching the belly of the expectant mother;
- light stimuli;
- emotional state of a woman;
- sound;
- smells;
- bright light.

From 24 weeks, tremors can be felt if you put your hand on the belly of a pregnant woman. The embryo reacts to the first touch with calm. If you do not remove your hand, the fetus will adapt to the new sensations and continue to move.
Often the baby pushes the uterus hard in response to a strong noise or unpleasant odor.
This behavior is provoked by irritation - the fetus gives a signal to the mother about danger.
Hormonal imbalances also cause a negative reaction in the child.
The influence of odors
Strong odors can increase fetal activity in the uterus. The most irritating effects are caused by chlorine, acetone and other strong odors of synthetic compounds. When the mother inhales, volatile substances pass through the lungs into the blood, which passes to the embryo. Toxic components provoke an inadequate reaction of the child, who warns the mother about the intoxication of the body. She must get rid of the unpleasant odor in order to protect the body of the unborn baby from the negative effects of toxic compounds. The latter can provoke the development of intrauterine anomalies.
A similar reaction can be observed when a pregnant woman smokes. Salts of heavy metals, when released into the blood, reduce the level of hemoglobin, which is why the child begins to hit the walls of the uterus.

Your baby will start moving before you feel it.
The first movements begin at the 8th week of pregnancy, when impulses begin to be transmitted through the nerves to contract and maintain the tone of the skeletal muscles. The rudiments of muscles and nervous tissue must create movement for the normal functioning of other organs and systems. Activity is necessary for normal blood supply to tissues. With increased physical activity, intracellular metabolic processes intensify, and the rate of tissue differentiation and growth increases.
Under conditions of physical inactivity, normal fetal development is impossible, because in the absence of movement, metabolism is disrupted and circulatory disorders occur. Low mobility causes muscle tissue atrophy and provokes the development of nervous system abnormalities.
When the baby starts pushing
For the first time, you can feel the tremors of the embryo at 17-18 weeks of pregnancy. At the initial stage, it is felt inside the abdomen. A woman may confuse the tremors with abdominal cramps or peristalsis of the digestive tract. Starting from the 5th month of intrauterine development, the fetus moves more actively. Pregnant women feel strong kicks or blows from the unborn child. If a woman notices this feeling ahead of schedule, this is normal. This phenomenon is typical for girls with thin or sensitive uterine endothelium.

From the 24th week, the fetus already communicates with the mother through movements
Intrauterine movements indicate normal well-being of the embryo. From 18 to 20 weeks, its activity is low and does not appear every day. It is recommended to record kicks from the beginning of the 6th month of pregnancy, when the fetus can move its limbs or move in the uterine cavity. The child moves chaotically in response to external stimuli or the emotional state of the mother. With the help of tremors, the fetus informs the pregnant woman about its well-being. The frequency of movements may vary depending on the behavior or emotions of the fetus.

If the baby kicks, that's good
If a child kicks in the stomach, this indicates his good health and normal intrauterine development. High activity is observed from 24 to 32 weeks. With the help of pushes, the child communicates his mood or changes in it.
Is it possible to determine the position of the fetus in the womb by its movements?
Some mothers wonder whether it is possible to understand how the baby lies in the stomach by its movements? Yes, by assessing the baby's movements, it is possible to guess his position. With a cephalic presentation, the kicks will be more pronounced in the upper part of the tummy, while with a pelvic position of the baby, the kicks will be felt more in the lower tummy. It is important to understand that during the entire pregnancy the baby turns over in the womb several times.
You might be interested in: Anti-nausea pills during pregnancy
If mommy feels that the little one is lying head up, there is no need to panic. Most likely, closer to childbirth, he will roll over into the correct position.
If there are no movements, the baby can just sleep
At week 24, the mother notes 10-15 movements of the embryo in 60-80 minutes. If the embryo calms down for 3-4 hours, young women wonder why the baby is quiet. If this happens once a day, then you should not worry. The fetus should fall asleep for 4 hours to relax the muscles and slow down the rate of metabolic processes in the developing body. This time is necessary to normalize cellular metabolism and remove unnecessary substances.
What determines the frequency of fetal movements?
The baby in the placenta is constantly moving, making up to 200 kicks at 20 weeks of pregnancy. In the period from 28 to 32 weeks, their number increases to 600. After this time, the activity of the embryo gradually decreases, which is associated with its growth and reduction of free space in the uterus. After 7 months of intrauterine development, the baby pushes up to 8-10 times per hour of wakefulness.

The child is most active from 7 pm to 4 am. The sleep period in 85% of cases occurs from 4 to 9 am.
The frequency of movements for each embryo is strictly individual. It depends on the woman’s diet, her activity, exercise and hormonal levels. The room in which the pregnant woman is located plays an important role. Sources of light and noise can irritate the embryo, which increases its activity as a sign of dissatisfaction.
Let's take a closer look at how a baby breathes in the womb
How does a baby breathe in his mother's belly? Such questions may arise when you see a pregnant woman. Let's figure it out in order.
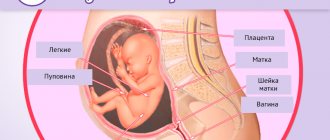
Placenta
The question arises: how does a child breathe in the womb, since he swims in water? The placenta provides “transport of oxygen and carbon dioxide.” This unique temporary organ is specially conceived by nature and is formed only for the fetus. The placenta is responsible for the life and nutrition of the embryo; even in cases of lack of nutrients in the mother’s body, it receives them.
The outer membrane of the placenta prevents the blood of mother and baby from mixing. Therefore, the blood types of the child and mother may not match.
Umbilical cord
Let's consider how a child breathes in the womb with the help of the umbilical cord?
The fetus is connected to the mother's body by the placenta and with the help of vessels that connect to form the umbilical cord. This organ is formed from the 2nd week of embryonic development and increases as it grows. At birth, the umbilical cord is the same length as the overall height of the baby.
The organ is responsible for providing the fetus with all nutrients. The umbilical cord is also responsible for removing products resulting from metabolism.
It is based on two arteries and a vein. These vessels are a tourniquet well protected from rupture and compression. Arterial blood, saturated with nutrients and oxygen, enters the fetus through a vein, and waste blood from the vein enters the placenta, which has the ability to be cleansed. The umbilical cord can bend in different directions and provides a comfortable position for the baby in the mother's womb.
Why fresh air is necessary

To understand what a baby breathes in the womb, you need to know that modern medicine strongly recommends that a pregnant woman move more and more actively, breathe clean air and be outside as often as possible.
Oxygen from the mother's blood flows to the fetus, which is why the woman is so sensitive to its lack and may lose consciousness. In the last weeks, it is better for a pregnant woman to protect herself and walk with someone close to her.
The expectant mother should know that oxygen deficiency occurs because the woman leads an incorrect lifestyle. You should exclude from your life during pregnancy:
- Alcohol.
- Drugs.
- Tobacco products.
- Stressful situations.
- Medicines.
What is he like inside?
Any woman is interested in what a child looks like in the womb as it grows. From the very first weeks of the fetus’s life, all internal organs and systems are formed.
The second month is characterized by the development of the nervous and cardiac systems, the eyes, ears, nose and mouth are determined, as well as the formation of muscles and the spine.
Already from the 16th week, the placenta is functioning, and at the 20th week, the mother can feel the baby’s tremors as he moves or changes his position.
How does a baby breathe in the womb in the 2nd half of pregnancy? There is a rapid pace of development. You can already determine the sex of the baby. He begins to actively gain weight and height, reacts to his mother’s voice, performs his first breathing movements, and his skin thickens.
At week 32, the immune system is formed, which is responsible for the baby’s health after birth.
At the 9th month, he is rapidly gaining weight, and by the 38th week the head drops down, that is, the baby is ready for birth.
In total, 40 weeks are needed for full intrauterine development. Childbirth from 38 to 40 weeks is considered timely, and the newborn weighs about 3 kg or more, with a height of 50 cm.
Now you know how a baby breathes in the womb, and you can safely enjoy your pregnancy!
How to properly check movements at home. 2 special tests
In the third trimester of pregnancy, a woman should keep a calendar of fetal movements. In it, the expectant mother records the number of kicks over a period of time. To assess the activity of the embryo, there are 2 tests:
- Count to 10. In this case, on a special form you need to mark the number of embryo movements every day. A woman should count her kicks for 12 hours. If the number of movements during this period is less than 10, she needs to see a doctor.
- Sadowski's method. After the evening meal, the pregnant woman should lie on her left side and count the movements of the embryo. Normally, he should push the uterus about 10 times in 60 minutes. If the number of movements is less than normal, counting continues for the next hour. In the evening, due to an increase in serum glucose levels, fetal activity increases 3-4 times, so during this period pathologies can be diagnosed in time.
Changes in the body at 17 weeks of pregnancy
The fifth month of pregnancy is a time when a woman’s condition is much better than in the first trimester, but toxicosis can still occur in the seventeenth week (as a rule, it ends during this period). Toxicosis manifests itself not so much in nausea and vomiting, but in severe swelling; the woman begins to notice that she can hardly put on shoes, not to mention rings. If severe weight gain is noticed along with swelling, it makes sense to consult a doctor.
At the 17th week, the woman feels well, the terrible nausea has passed, vulnerability and irritability have been replaced by calm and happiness from the knowledge that a new life is developing in the womb.
Among the unpleasant factors are such as excessive sweating and excessive vaginal discharge, the cause of the phenomena is a pronounced hormonal background.
Discomfort can cause pain in the lower abdomen with sudden movement, if the unpleasant symptoms quickly pass, there is no need to worry, this reaction of the body occurs due to stretching of the uterine ligaments. By the way, a dark stripe has appeared on the stomach, from the navel to the pubis, there is nothing dangerous about it, there is no need to worry.
A pregnant woman's breasts have become very rounded, the process of their enlargement has stopped, there is no pronounced sensitivity, which caused a lot of trouble in the first months, at the same time, the nipples have become dark in color.
Fetal movements may be slightly painful
If the baby moves a lot in the stomach, the expectant mother may feel pain. In such a situation, the pregnant woman is recommended to change her body position. If the pain does not go away for a long time and the child remains active, you should immediately consult a doctor. The symptom may indicate oligohydramnios or hypoxia.
In the third trimester, mothers feel pain in the hypochondrium, which is within the physiological norm. The uterus rises high during pregnancy, so the baby reaches this area and can strongly push the placenta in this area.
Can kicks be painful?
Normally, fetal kicks should not cause discomfort in a woman, but in practice this is still possible. Most often this happens due to an uncomfortable position of the woman, for example, if she lies on her back or sits bent over. If discomfort occurs, you need to change your body position. Try lying on your side and relaxing. Breathing should be calm and uniform. This is usually enough to calm the baby.
There are also pathological causes of painful sensations during jolts. Let's look at them in a little more detail:
- Pain with jolts in the right hypochondrium may indicate liver and gallbladder diseases.
- If there is discomfort in the upper abdomen, it is important to exclude gastric pathologies, in particular, a diaphragmatic hernia.
- Pain in the lower abdomen often indicates the presence of an inflammatory process in the bladder area - cystitis.
- It is imperative to consult with a specialist if the mother has a scar on the uterus after a Caesarean section.
Some women talk about the phenomenon of pulsation in the abdominal area. This is a sign of blood moving through the umbilical cord. If this phenomenon is not permanent, there is no need to worry.
You might be interested in: Femitest - pregnancy test
Smart kid. Why are fetal movements too active?
If the child moves very much, you need to calm down. An inadequate reaction of the embryo is observed when there is a sharp change in the psycho-emotional state of a woman. In addition, from the 20th week, when the cartilage tissue of the hearing aid begins to harden, this reaction is typical in response to loud sounds.
What to do if your baby pushes a lot
If your child is pushing in his stomach, you should talk to him. It is easier to detect fetal movements in a calm environment. When the mother's body is in motion, the activity of the embryo decreases. This is caused by fluctuations in the amniotic fluid, which calms the unborn baby. Therefore, if there are strong and painful tremors, it is recommended to go for a walk or turn on soft music in the room.
What baby activity should cause concern?
The child can move very actively. If intense movements suddenly stop, it is necessary to immediately exclude the possibility of embryo hypoxia. Oxygen starvation can lead to fetal death.
If the unborn child feels that the concentration of hemoglobin in the blood entering him decreases and oxygen stops flowing, he begins to push hard for a long time. Mothers need to pay attention to this. If the situation is not corrected, the child may lose consciousness or die. As a result, the tremors stop abruptly.

At what rate of baby's movements should you contact a doctor?
At the end of the 6th month of embryonic development, the intensity of fetal movements may decrease for a long period. From 26 to 28 weeks of pregnancy, the expectant mother can feel up to 10 kicks in 3 hours. In some cases, a fetal activity calendar should be kept, which will help record fetal movements. This is necessary in order to diagnose the pathological process in time and seek medical help. Women with Rh-conflict, people with chronic diseases and injuries are at risk.
If an active child has stopped moving for a long period, it is necessary to walk or eat a confectionery product.
If there is no reaction, it is recommended to consult your doctor. If the movements cause pain, the child may be in an awkward position and cannot change his position. In this case, in order to reduce the risk of developing oxygen starvation of the fetus, it is necessary to change the position so that the vessels are not compressed.

The importance of fresh air in the breathing process
To provide for her body and that of the baby, a pregnant woman needs to spend a lot of time in the fresh air, since a lack of oxygen can cause not only dizziness and loss of consciousness in the mother, but also hypoxia in the fetus, which negatively affects its development.
Therefore, to understand the importance of fresh air, you need to know how a baby breathes in the womb. A photo of the fetus in the womb makes this process more visual and understandable.
Since the child’s lung tissue matures only at the 34th week, after exposure to a special substance - surfactant. If a child is born premature, he is connected to a ventilator until the lung tissue in the baby’s body matures. Modern medicine has learned to synthesize surfactant, allowing the maturation of the lungs and giving the child the opportunity to breathe independently.
The way a baby breathes in the womb is significantly different from the process of spontaneous breathing, which requires the opening of the alveoli of the lungs. Therefore, a pregnant woman needs to walk enough in the fresh air and try to spend as little time as possible in stuffy rooms in order to avoid the development of oxygen starvation and premature birth.
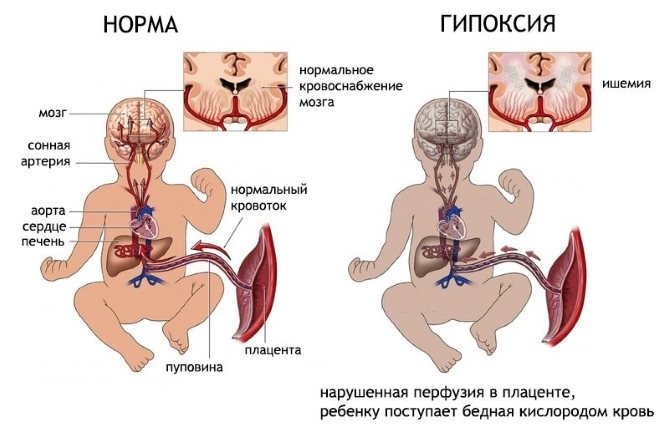
How is oxygen starvation of the fetus expressed?
Increased activity of the embryo for a long time indicates its oxygen starvation. However, strong tremors are not the only symptom. Increased frequency and intensification of movements is observed only at the initial stage of hypoxia. If the serum hemoglobin level does not rise for an extended period, the frequency and activity of movements weaken and stop. Therefore, a pregnant woman should immediately seek help from a doctor if she feels less than 10 kicks per day or weak movements of the embryo after 30 weeks.
Increased fetal activity after prolonged sleep warns of hypoxia. To accurately determine the condition of the embryo, cardiotocography and ultrasound are performed, the speed of blood flow in the fetal aorta and its cerebral circulation are measured.
How to find out that hypoxia has begun
In stationary conditions, the following instrumental methods allow you to monitor the movements and condition of the fetus:
- Ultrasound screening;
- auscultation of the fetal heartbeat using an obstetric stethoscope;
- cardiotocography (CTG);
- Doppler and blood flow velocity measurements using electrodes.
Women with bad habits or Rh conflict with the fetus are at risk. A pregnant woman should seek advice from an obstetrician-gynecologist if she does not notice embryo movements within 24-48 hours. After taking a history, the doctor listens to the fetal heartbeat using a stethoscope. Normally, the child should react to the touch of a cold device with a push, but under conditions of hypoxia no movement is observed.
If the fetal heartbeat is normal, the doctor will recommend that the mother walk more in the fresh air and not sit for a long time in an uncomfortable position.
To prevent oxygen starvation, a pregnant woman should balance her diet and breathe deeply.
If there are pathological noises or a low pulse rate, the gynecologist prescribes an ultrasound. An ultrasound examination will allow you to find out the exact size of the fetus, assess the formation of internal organs and systems, and detect movements. During the procedure, the doctor determines the amount of amniotic fluid and the condition of the placenta in order to exclude detachment of the placenta and oligohydramnios. If hypoxia is suspected, the doctor focuses on the thickness of the placenta, the position of the umbilical cord and the size of the fetus.
Doppler or Doppler ultrasound is necessary to assess the blood circulation between the mother and the embryo. During an instrumental examination, it is possible to timely detect entanglement or compression of the umbilical cord by a child. With Doppler ultrasound, information is recorded on a disk, while Doppler ultrasound does not allow recording the results obtained. The latter technique is used only as an emergency diagnostic measure.
Cardiotocography must be performed after 33 weeks of pregnancy. The device's sensors allow you to detect the baby's breathing, heartbeat and movements. The resulting tape with the results visually resembles an ECG curve. During the study, the doctor determines how the increase in uterine tone affects the breathing of the embryo.
As the tone increases, the uterus begins to contract intensively, and the pregnant girl feels severe cramps. She is tormented by severe nagging pain. Frequent contractile movements can lead to oxygen starvation of the embryo and fetoplacental insufficiency. With an increase in the tone of the smooth muscles of the uterus, the woman’s anxiety increases and the activity of the fetus increases. The embryo feels the compression of the contracting uterus and feels a decrease in free space.
Despite the alarming symptoms, increased embryonic activity does not 100% indicate that the child is struggling with hypoxia. Each fetus develops an individual sleep and wakefulness pattern. You should consult a doctor only when the embryo’s sleep period has passed or strong, uncharacteristic changes in its behavior are observed. As a preventative measure, expectant mothers are advised to take walks in the fresh air to maintain high hemoglobin levels, maintain a positive mood and avoid stressful situations.
Ways to help move your baby's tummy
It is necessary to monitor the baby’s movements in the womb at any stage, no matter whether it is 20, 22 or 30 weeks. If the tremors have become passive, you can try to rouse the little one using simple and safe methods. So, let's look at a few techniques.
Listening to dynamic music
Sometimes cheerful music helps to increase the baby's activity. There is no need to turn it on too loud, the main thing is that it is dynamic.

If you have headphones, you can put them on your tummy. This helps to wake up the baby, after which he will begin to push.
Use your fear
This method should be used very carefully. If, for example, mommy is afraid of spiders, you can play a video about them or look through a book with their image. The release of adrenaline into the blood will make the baby move too. It is important to understand that this technique should only be used as a last resort.
Talking to a child
A baby's hearing in the womb begins to develop at 16 weeks, and by 22 weeks the baby can hear you and all surrounding sounds well. You can try to stir up the baby by talking. At the same time, you can stroke your tummy.
You might be interested in: Dysfunctional uterine bleeding

This will also help to form a close bond between mommy and her little one during pregnancy.
Take a horizontal position
When a pregnant woman walks or does something, it creates conditions for the baby similar to rocking in a cradle. The experience of some women shows that as soon as they lie down, the baby begins to actively push. Try lying on your back for a few minutes, then roll over to your right or left side. Within a few minutes the little one will certainly make itself known.
Sweets to the rescue
When the level of glucose in the blood increases, the baby’s body reacts in the same way as the woman’s body. Try eating a piece of chocolate, cookies, dried fruit, banana or other treat. You can wash everything down with sweet natural juice or tea.

Practice shows that the baby's movements increase when the blood sugar level increases.
Physical exercise
The motor activity of the mother herself will help to stir up the little sleepyhead. Do a few squats, walk around the room, and do a few gentle bends. This usually causes the baby in the tummy to wake up and make itself known.
Tummy jiggling
Many mothers have noticed during an ultrasound examination that the doctor can give a small push to the tummy or slightly show it. After this, the little one begins to move.

It is important to remember that you should rock your tummy very carefully so as not to harm your baby.
Exposure to light
Babies in the womb see a bright light that passes through the tummy. You can try to rouse the baby using a regular flashlight. Turn it on and place it on your stomach. After just a moment, you will feel the baby’s kicks, because the light will undoubtedly wake him up.
How does a baby move just before birth?
Before labor, from 32 to 36 weeks, the following changes are observed:
- the child reduces activity;
- the kicking stops, the embryo prepares for birth, contractions begin;
- During uterine contractions, the fetus actively moves, but these sensations are overshadowed by severe pain.

To track the dynamics of movements and evaluate the heart rate of the embryo, doctors connect a CTG machine.
Norms and control over the child’s movements
A woman may not feel fetal movements for up to 3-4 hours, which normally means the fetus is asleep. If this period has passed, the pregnant woman can stimulate the activity of the embryo. To do this, you need to direct cold water to your stomach or hold your breath. In the latter case, the level of hemoglobin in the blood will drop and the child will begin to move, becoming concerned about the sudden changes.
To determine whether the embryo is moving within normal limits, the timing of the tremors should be recorded and each movement should be monitored. It is necessary to record the time of every 10th fetal movement, which should occur over the last 2-3 hours.
Why may a child move little or stop doing so?
If a pregnant woman feels less than 10 kicks per day, or the baby does not move for about 3-4 hours, you should consult a doctor. In most cases, a sharp decrease in activity indicates the development of fetal hypoxia, in which embryonic movements may be absent for 12 hours. If the pathology is not detected in time, the fetus freezes.

Physiological reasons
A child may reduce activity for the following reasons:
- the woman is in a noisy room, loud sounds can frighten the embryo;
- the fetus is in a state of sleep;
- a pregnant woman goes in for sports - with active movements, vibrations of the amniotic fluid are created, and the child may fall asleep;
- childbirth is approaching.
2-3 weeks before birth, the embryo reduces physical activity. At the same time, there are movements.
Starting from week 28, the fetus increases in size, occupying free space inside the placenta. It becomes difficult for him to move and roll over. The cramped space limits his activity.
Symptoms
The alarming clinical picture begins with the appearance of sharp and severe pain in the lower abdomen after 12-24 hours from the moment the fetus freezes. The pain syndrome is caused by increased peristalsis of the uterus, which seeks to get rid of the dead embryo. Other symptoms include:
- increased body temperature above +39°C;
- weakness;
- pale skin;
- increased sweating;
- uterine bleeding;
- thready pulse and drop in blood pressure;
- at a later stage, the breasts return to their natural size.
If your general health worsens, you should consult your doctor for a diagnosis.

Diagnostics
Cardiotocography and ultrasound with Doppler measurements allow hypoxia to be diagnosed in a timely manner. CTG helps to count the number of heartbeats of the embryo and record them in the form of a graph. Cardiotocography additionally determines the tone of the uterus. The procedure lasts about 20-40 minutes, during which the woman presses a button when she feels the embryo kicking.
To clarify the diagnosis, the doctor performs Doppler sonography, with which he establishes the speed of blood flow in the arterial vessels of the uterus and umbilical cord. Ultrasound allows you to evaluate the movements of the embryo, the volume of amniotic fluid, and the muscle tone of the uterus. If the data obtained indicates a serious condition of the child, the doctor decides to initiate premature labor or hospitalize the woman.
Causes for concern
The first cause for alarm is the absence of tremors for 2-3 hours. If movement does not resume after 6 hours, you must call an ambulance. The baby should move at least 10 times in 3 hours before the 26th week of pregnancy. At later stages, up to 12 shocks per day can be considered normal activity. If the movements do not correspond to the norm, it is necessary to undergo an instrumental examination.
Causes of low movements
Sometimes women notice that the fetus in the womb has become less active. Don't immediately panic and run to the doctor. The causes of this condition can be both pathological and normal physiological in nature.
Physiological reasons
You should listen to the baby’s movements, as this indicator indicates the normal development of the baby in the womb. If mommy notices that the tremors have stopped for a while, she needs to remain calm. Perhaps the baby is just sleeping. If there are no tremors for more than 3 hours, you should try to rouse the baby. You can drink sweet tea, eat chocolate, go up the stairs, and lie on your left side for about an hour. Such actions usually help to wake the baby.
In addition, it is important to remember that a few weeks before birth, the baby’s movements are no longer as intense as before. In the later stages, there is no longer enough space in the mother’s womb. Although the baby moves as before, the woman no longer feels these movements as much.
If there is no movement for more than 3 hours, and not one of the methods to move the little one, you should definitely consult a doctor.
Pathological conditions
Reduced activity of a child often indicates the development of hypoxia. If the mother notices that the baby’s activity has become less pronounced during those hours when the baby was usually kicking and awake, you should definitely consult with your doctor. Research methods such as ultrasound and CTG (cardiotocography) help determine hypoxia. If hypoxia is confirmed, the woman is prescribed special treatment.