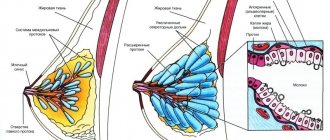
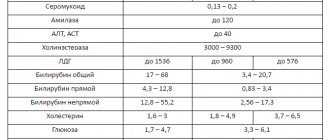
Nowadays, and especially in a metropolis, even a nutritious diet does not provide the expectant mother with the “set” of vitamins that are needed for the development of the baby and the normal course of pregnancy.
According to statistics, vitamin deficiency is observed in 7-8 out of 10 expectant mothers. You can protect yourself and your baby from problems associated with a lack of vitamins by taking vitamin complexes.
The main thing is to know what to drink, in what dosage and for how long.
What vitamins are especially useful during pregnancy for the expectant mother and fetus?
A balanced diet is the basis, and you cannot deviate even one step from a proper diet during pregnancy.
But the need for some vitamins in an expectant mother always increases, and not all of them can be obtained from foods (especially during toxicosis). Before buying anything that suits the occasion at the pharmacy, you should consult a doctor .
Only a specialist will be able to say exactly which vitamins will be superfluous and which ones you can’t do without. Remember that an excess of vitamins can be even more dangerous than a deficiency!
Especially useful vitamins - what can an expectant mother not do without?
In the 1st trimester:
- Folic acid. You should drink it already at the stage when you are just planning a baby. As a last resort - immediately after you see the long-awaited (or unexpected) “2 red stripes”. Timely intake of vitamin B9 is the prevention of hypovitaminosis, protection against accidental injuries to the baby’s spine, a “brick” in the construction of the psyche of the future baby. Lack of B9 is fraught with developmental defects. What foods to look for: beef and chicken liver, spinach and lentils, asparagus. Daily dose – 400-600 mcg. Important: green tea significantly reduces the absorption of B9!
- Pyridoxine. One of the main assistants in relieving nausea, reducing nervousness and eliminating muscle spasms and cramps. And from the 8th week of pregnancy, vitamin B6 is also needed by the fetus for the development of the central nervous system.
- Vitamin A . It is an important component for fetal growth, vision, skeletal and nervous system development. Important: exceeding the dose is fraught with heart disease and problems in the children's nervous system! What foods to look for: fish oil and liver, as well as vegetables/fruits in red/orange colors. Remember that vitamin A (as fat-soluble) should be taken with sour cream or yogurt.
In the 2nd trimester:
- Vitamin D. The child’s body is almost created, and for the rapid beginning growth of the fetus, substances for the growth of bone tissue and the heart, as well as for the prevention of rickets, are extremely necessary. In addition, this vitamin promotes the proper distribution of calcium and phosphorus. In the summer, it is quite possible to do without vitamin D (it is produced in the body independently), but in winter, with a lack of sunshine, taking it is mandatory. What foods to look for: fish oil, red fish, egg yolk, milk and butter.
- Tocopherol. This vitamin contributes to the correct functioning of the placenta, which, when it ages, often causes miscarriage. In addition, vitamin E is needed for metabolism and will not interfere at the planning stage to balance the monthly cycle. What foods to look for: oils, peas, rose hips, tomatoes.
- Iodine. It is usually prescribed in the 1st half of pregnancy, unless, of course, there is a history of thyroid disease. Iodine is needed for metabolism, prevention of rapid weight gain, weakness, brittle hair, etc. What products to look for: sea salt, seaweed (including dried), sea fish. Daily dose – 200 mcg.
In the 3rd trimester:
- And again pyridoxine. At this stage, the fetus grows rapidly, which contributes to the appearance of edema. Vitamin B6 will help prevent swelling.
- Iron. With its deficiency, a decrease in uterine tone, the appearance of muscle weakness and the development of anemia are observed. What foods to look for: veal, fish and chicken eggs, as well as pork and beef, turkey and rabbit meat. Less tea and coffee - they reduce the intensity of iron absorption. If you drink it with natural juice (vitamin C will speed up its absorption). Daily dose – 30 mg.
- Vitamin C. It is necessary in the 1st and 3rd trimesters for the full development of the placenta, protection of maternal immunity, and formation of fetal/egg membranes. What foods to look for: citrus fruits and sauerkraut, greens and potatoes, black currants.
- Calcium. Any mother knows about the need for this element - it is needed for the proper development of the kidneys and the child’s skeleton. You can, of course, load up on cottage cheese with sour cream and cabbage, but you still won’t be able to get as much calcium as you need - you should take it additionally. Important: coffee and carbonated drinks interfere with the full absorption of the element, switch to other drinks. Daily dose – 250 mg.
“Vitamin” educational program for pregnant women...
Vitamin B1 takes part in the development of the baby’s nervous system, its internal organs, and provides energy to the muscle and nervous tissues of the fetus.
If a pregnant woman feels constant weakness and gets tired quickly, she probably does not have enough vitamin B1.
Liver and kidneys, milk, rye and wheat bread, yeast, and egg yolk are rich in this vitamin.
Vitamin B2 protects against anemia and the formation of blood cells. If a pregnant woman has everything in order with this vitamin, then the baby is protected from congenital anomalies and is not in danger of premature birth.
Eat more liver, meat, dairy products, eggs.
Vitamin B6 is one of the most important for pregnant women. The need for it increases by 30%. Vitamin B6 is responsible for protein metabolism between a pregnant woman and the fetus, ensuring the development of important organs and systems of the baby. If pregnant women receive enough vitamin B6, they are not afraid of toxicosis.
If a pregnant woman suffers from nausea and vomiting, irritability, insomnia, and poor appetite, there is clearly not enough pyridoxine (vitamin B6). If you notice that your teeth have suddenly “flyed”, new foci of caries have appeared - it’s time to rely on vitamin B6!
Eat wholemeal bread, liver and meat, beans and buckwheat porridge.

Vitamin B9 (folic acid) is familiar to everyone. It is mandatory for all pregnant women to be prescribed it, and it is even recommended to take it for some time before conception.
Folic acid is needed by both the mother (for the regeneration of cells of the whole body) and the fetus (takes part in the formation of the brain, the synthesis of blood cells, and the development of all systems and organs of the child).
A lack of vitamin B9 can cause the birth of a premature baby, defects in its nervous system and other congenital abnormalities.
By eating buckwheat and oatmeal, legumes (soybeans, beans, peas), mushrooms, cottage cheese, hard cheeses, millet, wholemeal bread, liver, a pregnant woman can, to one degree or another, replenish the reserves of this essential vitamin.
Vitamin A is necessary for the formation of the placenta, organs and tissues of the fetus. With its deficiency, a pregnant woman may experience vaginal dryness, decreased immunity and a tendency to diseases of the respiratory system.
Eat carrots, butter, liver, cheese, eggs, apricots and dried apricots, rose hips, fish oil.
Vitamin C (ascorbic acid) is simply indispensable for strengthening the immune system and maintaining pregnancy. It is involved in the formation of the placenta and is needed for the formation of bone and cartilage tissue of the fetus. What is very important, vitamin C is necessary for the normal absorption of iron!
If pregnant women are worried about toxicosis, a constant feeling of fatigue, a vitamin C deficiency is clearly manifested.
Increase the amount of fruits and vegetables in your diet, especially citrus fruits, eat currants, raspberries, cabbage, red peppers, tomatoes, parsley.

Vitamin E is no less important for the fetus and the normal course of pregnancy. It helps strengthen the immune system, protects against anemia and stress, and affects the endocrine system. It is often prescribed when there is a threat of miscarriage, because... it is indispensable for maintaining pregnancy.
It is found in greatest quantities in vegetable oils. So more salads dressed with oil!
Vitamin D is responsible for the formation of bone tissue and the skeleton of the fetus, is needed for the functioning of the cardiovascular system, for the absorption of calcium and phosphorus, and is the prevention of rickets in newborns.
If a pregnant woman complains of frequent leg cramps, nervousness, or tooth decay, she probably doesn’t have enough vitamin D.
It will not be possible to eat it in the required quantity (it is found in very small doses in food), it is better to spend more time in the sun (but under no circumstances sunbathe on the beach for hours!).
x
Thanks for watching!
- Share on Facebook
- Share on VKontakte
Click here to watch the next video!
Remember, that…
- vitamin E until birth, as well as calcium and iron. But they should be taken separately.
- Vitamin C promotes better absorption of iron.
- Zinc and copper should not be taken together with iron.
- Vitamin D will improve calcium absorption.
And most importantly, do not prescribe vitamins for yourself! Contact your doctor and strictly follow the dosage regimen.

The healthiest foods for pregnant women - top 10 (from Ineta
It’s a fact that pregnant women have their own views on what’s tasty and what’s not, and sometimes they know how to combine completely incompatible foods. But let's look at the most useful products for pregnant women, which contain the maximum of useful things for the body of the expectant mother and her baby.
Yogurt
Yogurt contains much more calcium than a glass of milk. It will help you keep yourself in shape. It is best to replace fatty sour cream or mayonnaise in a salad with healthy yogurt. Another option is to add yogurt to your breakfast cereal. Well, besides, yogurt will help prevent various stomach upsets.
Oatmeal
This product is useful because it contains a large amount of fiber, iron and B vitamins. It can be consumed as an independent product in the form of porridge, or added to baked goods.
Avocado
Avocado is a mega healthy product for pregnant women, because it contains a large amount of folic acid. And, as we know, folic acid is necessary for the baby in the womb, because it helps the formation of the baby’s nervous system and brain. Plus, folic acid increases the chances of not losing a baby in the early stages of pregnancy. Avocado is also rich in vitamins C and B6. And B6 often saves pregnant mothers from morning sickness.
Broccoli
It also contains a lot of folic acid and calcium. It is easy to eat this healthy product, because it can be an excellent side dish for both fish and meat dishes.
Carrot
Everyone knows about the high content of vitamin A in it, which is important not only for the eyes of the expectant mother, but also for the eyes, teeth and bones of the baby.
Eggs
They are most useful when cooked. Fried eggs are less beneficial. But remember, pregnant women are strictly not recommended to eat raw or soft-boiled eggs.
Lentils
This legume product is more beneficial for the intestines than others. Lentils also contain a lot of iron, vitamin B6 and folic acid.
Mango
This delicious tropical fruit is rich in potassium and vitamin A. By the way, mango goes great with salty or sweet dishes. So, if you don’t want to eat it raw, try adding this healthy product to your favorite lunch.
Nuts
But nuts contain an unrealistic amount of useful minerals, which are also necessary for a pregnant mother and her baby. And walnuts are also good for the development of a child’s brain. The main thing is not to overdo it, because they are quite high in calories.
Spinach
Iron, vitamin A, folic acid, calcium - you agree, a healthy product. This healthy product for pregnant women can be used to prepare many delicious dishes - from soup to salad, or even just as a tasty side dish.
More details: https://www.happy-giraffe.ru/community/2/forum/post/82234/
More details: https://www.happy-giraffe.ru/community/2/forum/post/82234/
What else do you need to remember?
- Iodine will be prescribed to the mother separately. The norm is 200 mg.
- The maximum dose of vitamin A is 4000 IU. Exceeding the dose provides a toxic effect.
- Calcium is taken separately. And even at other times, so as not to disrupt the absorption of each drug.
- Avoid dietary supplements. The requirements for them are known to be underestimated, and the exact dosages of the substances present are not fully verified, so be careful!
In what cases is taking vitamin complexes recommended, or even mandatory?
- In the absence of adequate regular nutrition.
- For previous diseases that are associated with B12 or iron deficiency.
- For expectant mothers over 30.
- With low immunity.
- If the previous pregnancy was terminated or ended in miscarriage.
- For pathologies of the digestive or cardiovascular systems.
- If you have had a cold or an infectious disease during pregnancy.
- In case of multiple pregnancy.
- If there are any developmental anomalies in a previous pregnancy.

Summer nutrition during pregnancy: what you can, what you can refuse
In summer, a large number of fruits, vegetables, berries, and herbs appear. There is also a wide selection of soft drinks, including carbonated drinks, kvass, ice cream, village milk, cottage cheese, and cream. During pregnancy, it is important to know which of these foods and in what quantities are healthy to consume and which should not be consumed.
Prenatal vitamins
Vegetables and fruits are best consumed fresh. They are very rich in vitamins and microelements. Vegetables and fruits must be washed well under running water, even if grown in your own garden. It is unacceptable to eat vegetables and fruits directly from the garden, as their surface may contain pathogenic microorganisms. All these microorganisms reach the surface of vegetables and fruits from the soil. These are causative agents of helminthic infestations (for example, enterobiasis), as well as foodborne toxic infections (Proteus, Klebsiella, Enterobacteriaceae, etc.). When pathogenic bacteria enter the body of a pregnant woman, a picture of food poisoning develops: nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and fever. In such cases, medical attention is required.
Legumes (soybeans, peas, beans) can cause allergies in pregnant women, so it is recommended to include them in the diet no more than once a week. You should not get carried away with red, orange vegetables and fruits and black berries (for example, black currants). They contain natural salicylates, which in large quantities can cause allergic reactions.
Preference should be given to green and yellow fruits, such as apples, pears, etc. Beets or carrots are recommended in quantities of 1–2 pieces. per day, fresh or cooked in borscht. Wild berries are very useful: lingonberries, cranberries, cloudberries, blueberries. They are preferred over garden strawberries, which are a strong allergen. They must be washed thoroughly before use. You should not overuse peaches and apricots, since in addition to allergenicity, they stimulate intestinal peristalsis (contractions), which can cause an increase in uterine tone.
You can add fruit to porridge (buckwheat, rice, millet, corn). Due to the high calorie content, you should not get carried away with semolina and oatmeal. Fruits such as bananas, melon, grapes contain a lot of sugar, so consuming them in large quantities can lead to rapid weight gain, which is not desirable for the expectant mother.
Vegetables contain a lot of fiber - a substance that ensures normal intestinal activity and prevents constipation. Fiber is also rich in vitamins and microelements, which are necessary for the normal functioning of the entire body. It is found in large quantities in green vegetables (leeks, spinach, French beans). It is recommended to prepare vegetable salads seasoned with vegetable oil (sunflower, corn, olive). For vegetables, it is recommended to use zucchini, cauliflower, cucumbers, carrots, and beets. Vegetable casseroles, vegetarian soups, puree soups, borscht, and fresh cabbage soup are useful.
Greens (onion, parsley, dill) can be consumed in large quantities, as part of dishes or in pure form. It is advisable to eat vegetables and fruits in small portions 4–6 times a day, the total amount in the daily diet should be 500–600 g. However, you should not completely switch to vegetables and fruits during pregnancy; this is a fairly common mistake in the diet of expectant mothers in summer time. The diet of the expectant mother must contain animal proteins, which are the main building material for the fetus.

Nutrition for pregnant women: fermented milk products
Milk is a source of proteins and calcium necessary for the normal formation and growth of fetal bones and teeth. It must be remembered that dairy products should be chosen extremely carefully in the summer. This is due to a decrease in the shelf life of perishable products at elevated temperatures, especially in hot weather. When purchasing dairy products, you should always pay attention to the production date and expiration date. It is recommended to boil milk before drinking. Cow's milk protein is one of the strongest allergens, so the recommended amount of milk is no more than 500 ml per day. You should not consume milk “from the cow”, as it has a high percentage of fat content, and can also cause intestinal upset in a pregnant woman due to the content of pathogenic microorganisms in it. Healthy dairy products include: low-fat milk (up to 2.5% fat content, since consuming full-fat milk increases the load on the liver and pancreas), low-fat (up to 9?%) cottage cheese, fermented milk products (ryazhenka, kefir up to 2.5?% fat content), yoghurts without flavors and dyes. Cheeses are recommended mild and up to 45?% fat content), hard varieties, about 20 g per day. It is advisable to consume cottage cheese in the form of cheesecakes and casseroles in an amount of 50–100 g per day, since in the summer microbes can quickly begin to multiply in it and its consumption without heat treatment can lead to an intestinal infection.
Nutrition for pregnant women: fish and meat
Meat products and fish also need to be selected with special care, as they quickly deteriorate in the heat. For the same reason, it is recommended to abandon semi-finished and finished meat products. It is advisable to choose lean meat; chicken, turkey, lean beef, and rabbit are the most suitable. It is preferable to boil such meat or prepare steam cutlets, meatballs, and casseroles from it. When preparing soups, it is better to use secondary meat broths (after boiling, the water is drained and replaced with a new one). It is recommended to avoid traditional barbecue outdoors, as it may turn out to be poorly cooked. This is dangerous due to the risk of contracting toxoplasmosis. The causative agent of this disease, toxoplasma, causes severe fetal malformations when it enters the body of the expectant mother before 12 weeks of pregnancy. When infected at a later date, the risk of developing harmful consequences for the fetus is significantly reduced. For the same reason, pregnant women should not try raw minced meat. In addition, uncooked meat may contain pathogens of helminthic infestations (for example, trichinosis) and listeriosis (a disease that occurs in severe forms in newborns, with increased body temperature and damage to the nervous system). In pregnant women, listeriosis can in some cases lead to the development of premature birth and even intrauterine fetal death. It is also not recommended to eat charred kebab. In addition, as mentioned above, it is advisable for pregnant women not to consume fried meat. This can cause heartburn, indigestion, and put a serious strain on the liver and kidneys. Meat protein can cause allergic reactions, so meat is recommended in the amount of 150–200 g per day.
During pregnancy, low-fat varieties of fish (cod, navaga, catfish, sea bass) are useful. Fish is also recommended boiled or steamed, 1-2 times a week. The amount of fish eaten per week should not exceed 350 g. Eating sushi and other raw fish should be avoided due to the risk of contracting diseases such as listeriosis and toxoplasmosis, the dangers of which are mentioned above.

Nutrition for pregnant women: eggs
It is advisable to consume eggs only hard-boiled, no more than 2-3 eggs per week. Under no circumstances should you eat raw eggs, as there is a high risk of salmonella infection. This is a disease characterized by fever, malaise, headache, as well as nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea. The causative agents of this disease - salmonella - enter the body through the gastrointestinal tract along with raw eggs (especially duck and goose), as well as raw meat and milk. Before eating, it is recommended to wash eggs under running water and soap, since their surface may also contain pathogenic microorganisms (salmonella, E. coli, etc.).
Nutrition for pregnant women: bread
It is better to use bread made from wholemeal flour or with bran. This bread is rich in plant fibers, which have a beneficial effect on the intestines and prevent constipation in a pregnant woman. The total amount of bread should be 200–250 g per day.
In the summer, especially in the heat, you should not buy confectionery products (cakes, pastries) with cream, since the shelf life of these products at high temperatures is very short. In addition, in the summer, violations of the storage conditions of confectionery products are possible (for example, when refrigeration equipment breaks down or transportation conditions are violated), which can lead to poisoning.
Drinking regime during pregnancy
In the summer, you especially need to monitor the amount of fluid you drink per day. In hot weather, in the presence of nausea and vomiting due to toxicosis, the need for fluid increases. As for drinks, green tea is an ideal option; it has a tonic, diuretic, anti-inflammatory effect, does not contain caffeine, and quenches thirst well. In addition, fruit drinks, compotes, fermented milk products, still mineral water, and herbal teas are recommended.
Carbonated soft drinks should not be consumed as they can cause heartburn and belching. Sweet carbonated drinks are high in calories, which can contribute to rapid weight gain in a pregnant woman. In addition, most of them contain harmful flavors and dyes. In addition, in the summer, special attention should be paid to the temperature of the drinks consumed; they should not be too cold so as not to provoke throat diseases. It is advisable to remove drinks from the refrigerator 20–30 minutes before consumption or heat them for a few seconds in the microwave. The same applies to ice cream, which is recommended to be consumed no more than 50 g, in small portions, preferably melted. Ice cream should also not contain dyes or artificial flavors.
Spicy foods and spices provoke thirst, so it is recommended to exclude them from a pregnant woman’s diet. It is recommended to limit salt to 5–6 g per day. Salty foods increase thirst and promote fluid retention in the body, which can contribute to the development or intensification of edema and increased blood pressure.

Sample menu during pregnancy
In the first half of pregnancy, the calorie intake of a healthy woman is approximately 2500 kcal per day. It is recommended to compose the menu in such a way that breakfast accounts for 30?% of the total daily calorie intake, lunch - 40?%, afternoon snack - 10?%, and dinner - 20?%.
- Breakfast: egg (1 pc.) or omelet (150 g), green tea (200 ml), fresh fruit or berries (100 g).
- Lunch: fresh vegetable salad (150 g), borscht or vegetable soup with sour cream (200 ml), boiled meat or fish (150–200 g) with a vegetable side dish (200 g), compote (200 ml).
- Afternoon snack: kefir (200 ml), bun (30 g), fruit (100 g).
- Dinner: cottage cheese casserole or cheesecakes (100g), kefir or milk (200 ml).
In the second half of pregnancy , the fetus becomes larger and requires an additional 350 kcal per day (2850 kcal per day) for its normal development. Also, in the second half of pregnancy, meals should be taken more often and in smaller portions. This is due to the fact that the enlarged uterus puts pressure on the very full stomach, causing discomfort, belching and heartburn in the pregnant woman. Also, the evacuation of food from a very full stomach slows down, which negatively affects the digestion process.
- First breakfast: boiled egg (1 pc.) or omelette (150 g), green tea (200 ml), fresh fruit or berries (100 g).
- Second breakfast: fresh vegetable salad (100 g), steamed cutlet (50 g), tea with milk (200 ml), bread (20 g) with butter (15 g) and cheese (15 g).
- Lunch: vegetarian vegetable soup with sour cream (180 ml), boiled meat or fish (150 g) with buckwheat (50 g), compote (200 ml).
- Afternoon snack: cottage cheese (100 g), bun (30–50 g), kefir or other fermented milk drink (200 ml), fresh fruit or berries (100 g).
- First dinner: milk porridge (200 g), fresh fruits or berries (100 g), compote (200 ml).
- Second dinner: vinaigrette (200 g), kefir or other fermented milk drink (150 ml), baked apple (1 pc.). The last meal should be no later than 2–2.5 hours before bedtime.
What pregnant women should not eat
- Raw eggs.
- Unpasteurized soft cheeses: blue cheese, brie, camembert, feta, roquefort.
- Raw meat, fish, seafood.
- Snack meat and fish: ham, smoked sausage, smoked meat and fish, pates.
- Fatty meats and fish, lard.
- Pickles (pickles, herring, etc.).
- Unpasteurized milk and home-made purchased cottage cheese (market).
- Carbonated drinks.
- Unpasteurized juices.
- Hot sauces, spices and seasonings.
- Strong black tea and strong coffee.
- Any alcoholic drinks.