Features of admission in children under 3 years of age
When using antibiotics in such children, it is necessary to strictly adhere to all the doctor’s wishes, and most importantly, give the drug only as prescribed.
Amoxicillin
Belongs to the group of penicillins. Has a wide range of influence. This antibiotic is prescribed for sinusitis, pneumonia, pharyngitis. For small children there are granules for teaching suspension.
Amoxicillin for children
They just need to be diluted with boiled water. If the child is under 2 years old, the dose will be ¼ teaspoon. But for children under 5 years of age, take 5 ml
It is also important to know how many days to take Amoxicillin.
Augmentin
This is a powder for obtaining a suspension, which has a wide range of effects. It has similar indications as Amoxicillin. Do not give to babies under 3 months. May cause allergies.
Augmentin for children
Zinatsef
This medication belongs to the 2nd generation cephalosporins. Has a wide range of effects. But they are used in the treatment of sinusitis, pneumonia, otitis media, tonsillitis. It is used in the form of injections.
Zinatsef
For children, the amount of the drug is 30-100 g per 1 kg of weight.
Zinnat
This is another 2nd generation phephalosporin. Produced in the form of granules to obtain a suspension. The medication is used in the treatment of ailments of the upper and lower respiratory tract. Cannot be used in patients under 3 months of age.
Zinnat for children
There are 10 ml of the drug per 1 kg of patient weight.
Ceftriaxone
This medication belongs to the group of 3rd generation cephalosporins. Produced in the form of injections for injection into a muscle or vein. Cannot be used by children with jaundice. The dosage for newborns is 20-50 mg per 1 kg of weight, but for older children - 20-75 ml per 1 mg.
Ceftriaxone for treating children's colds
The course of therapy lasts 4 days. The injections are painful, so the baby will have to be patient. Here's how to use the antibiotic Ceftriaxone for sinusitis, and how effective this remedy is.
Features of treatment for colds in children under 12 years of age
There are a number of drugs that can be used by both adults and small children. The above antibiotics can also be used in children under 12 years of age. But there are also drugs that are designed specifically for this age category.
Suprax
The presented drug belongs to semi-synthetic drugs of the phephalosporin type. The main component is cefixime. Its action is aimed at stopping the main substance of the bacterial cell wall. Under the influence of Suprax, it is possible to destroy enzymatic bacteria, which include strempotococci and Escherichia coli. Salmonella.
Suprax for treating children's colds
This antibiotic is often prescribed for a child’s cough. Available in the form of capsules and granules to obtain a suspension. Children from 5 to 11 years old take 6-10 ml. It is necessary to dilute the granules with water in two stages. At the same time, shake the product thoroughly each time. The drug is effective in the treatment of cough and runny nose. The drug is also used in stepwise treatment. First, the doctor prescribes a drug from the group of 3rd generation cephalosporins, and then Suprax. But this information will help you understand how to use Suprax for tracheitis in a child.
You cannot use an antibiotic if you are individually intolerant to its components. Children with chronic kidney disease should treat colds with caution.
Sumamed
This antibacterial drug successfully copes with cough. The main component is azithromycin dihydrate. It has a wide range of influence. And the drug suppresses bacteria due to the synthesis of microbial protein. Under its influence, the growth and development of pathogenic microorganisms is inhibited.

Sumamed for children
For children from 3 to 12 years old, the dose depends on body weight. You can give the drug in the form of syrup, taking into account 10 mg per 1 kg of body weight. To prepare 20 ml of suspension, you will need to dilute the powder with 12 ml of water
It is forbidden to take it due to hypersensitivity to the ingredients of the medication. It is also contraindicated for children with liver and kidney pathologies. It cannot be used to treat cough in tandem with Ergotamine and Dihydroergotamine. But how a sore throat is treated with Sumamed is described in great detail in this article.
How to take it correctly
To prevent taking antibiotics from harming the child’s developing body, parents should know a few basic rules for taking these drugs:
- The course of antibiotic treatment is a minimum of 5 days, a maximum of 14 (in severe cases). Even if the child feels much better even on the 3rd day of treatment, under no circumstances should you stop treatment for at least another 48 hours. If drugs are taken incorrectly (unauthorized dose reduction, non-compliance with the dosage regimen or an incomplete course of treatment), only the weakest microorganisms die, although a temporary improvement in health is noted. The remaining bacteria mutate, adapt to the previously taken medicine and no longer respond to it. You have to look for a replacement, increase the dose, or try a completely different antibiotic.
- The antibiotic should be taken at the same time every day. If you need to take the medicine 2 times a day, then this should be done exactly every 12 hours.
- If the drug is given to young children in the form of a suspension or drops, then the contents of the bottle are thoroughly stirred until the liquid becomes homogeneous and all the sediment has dissolved.
- Almost all antibiotics should be taken during or immediately after meals, with plenty of water (not tea, compote, milk, juice or mineral water).
- To maintain a normal level of intestinal microflora and avoid the development of dysbiosis in a child, bifidobacteria or lactobacilli should be taken in parallel (prescribed by a doctor).
- While taking antibiotics, it is advisable to keep the child on a diet: exclude fatty, fried, smoked foods, and sour fruits. The use of antibiotics itself greatly inhibits liver function, and heavy meals significantly increase the load.
- Any antibacterial drugs are prescribed only by a doctor. The dosage is calculated based on the severity of the disease, the characteristics of the body and the general condition of the child.
- If there is no improvement within 48-72 hours after starting antibiotics, you should immediately consult a doctor to adjust treatment. The same actions should be taken by parents if an allergic reaction is detected in the child or other side effects occur.
- It is always necessary to write down when, what medications, in what course were taken previously, and whether there were any allergic reactions or other side effects in children.
Features of reception in children after 12 years
At this age, children may be prescribed medications that are approved for use by adults. Here the antibiotic can be used not only in the form of a suspension, but also in the format of tablets or injections.
A-Klav
This drug is intended for systemic use. Refers to a number of penicillins. In case of infection of moderate severity, take 1.3 ml per 1 kg of weight every 8 hours.
If the pathology is severe, then the dosage is maintained, but only the interval between doses will be 6 hours.
Telithromycin
This medication should be used in the treatment of colds such as pneumonia, bronchitis, acute sinusitis, tonsillitis. Take 800 mg once a day. The course of therapy is 7-10 days. Why a child coughs without signs of a cold can be found in this article.
Roxithromycin
With this medication you can treat infections of the upper and lower respiratory tract, skin and soft tissues. Before prescribing this medicine to a child, the doctor must accurately determine the sensitivity of the microflora to it, which influenced the development of the disease.
Roxithromycin for the treatment of colds in children
Children 12 years of age and older take the drug 0.15 g 2 times a day. Side effects such as vomiting, abdominal pain, and diarrhea may occur.
Today, the choice of antibiotics for treating colds in children is quite wide. It should only be prescribed by a doctor after the cause of the development of the pathological process has been accurately determined. In addition, he decides on the dosage and duration of treatment. If after the specified time there is still no relief, he will change the drug to a more effective one.
What are antibiotics
In medical reference books, antibiotics are a group of very strong substances that inhibit the development of certain microorganisms or provoke their death. They can be of natural, synthetic or semi-synthetic origin. A characteristic feature of these drugs is the effect on both pathogenic and beneficial microflora, but at the same time the vital abilities of bacteria are suppressed gradually and in small concentrations.

Did you know? Pear is a natural antibiotic. Herbalists recommend these fruits for people with chronic inflammatory processes, as well as for cancer.
Antibiotics have an effect only on a certain type of pathogen, which is determined by the results of a culture test of the patient’s blood or urine. But, despite the effectiveness of these tablets, they should not be considered omnipotent. An incorrectly selected medicine will only harm the body, and even more so a child’s body. Therefore, under no circumstances do you self-medicate or test the entire contents of your first aid kit on your child.
When do children need antibiotics?
In modern pediatrics, it is practiced to prescribe antibiotics for children with a temperature that lasts more than 3 days, as well as in cases of acute forms of severe diseases such as meningococcal infection, viral pneumonia, sinusitis, sinusitis, and otitis media.
Doctors draw the attention of parents to the aggressive effects of such drugs on the digestive tract. By destroying “bad” cells, they have the same effect on “good” bacteria
Therefore, it is strictly forbidden to give your baby antibiotics when he has a runny nose or a sore throat. If you are taking such medications, you should also take medications to restore your intestinal microflora. It could be “Linex”, “Yogurt”. If your attending physician “forgot” to prescribe such therapy for you, then there is reason to doubt his qualifications.
Important! The average course of antibiotic therapy cannot last less than 5 days. Typically, medications are recommended to be taken for 7 to 10 days.
In special cases, when the patient has serious complications of the disease, he is prescribed treatment for up to 3 weeks or longer.
The main types of antibiotics for colds for children
Antibiotics for colds for children should not cause complications or side effects. Instead of tablets, children are given medicine in the form of a sweet suspension or syrup. When necessary, intramuscular injections of drugs are prescribed.
The list of antibiotics for colds is opened by antibacterial agents from a number of penicillins: Augmentin, Amoxicillin, Solutab, Flemoxin. Among macrolides, Sumamed forte is used.
During bacterial infections of the upper respiratory tract, first and second generation cephalosporins can be used to treat children: cephalexin, cefadroxil, cefaclor, cefuroxime. During a severe cold, children are given tablets of Zinnat, Cephalexin, Duracef, Ceclor.
In case of complications or severe colds, injectable antibiotics are used; the most common names are Azithromycin, Augmentin, Amoxiclav.
The most effective antibiotics for colds are drugs that are determined based on the results of bacterial analysis and act selectively on the causative agent of the inflammatory process.
The variety of medications in tablets makes it possible to significantly reduce the prescription of injections. They also use a treatment regimen when, in the first days, they begin to treat the baby’s serious condition with injections, and then switch to therapy with medications in tablets.
Medicines contraindicated for children
Antibiotics are not recommended for children with colds:
- chloramphenicol;
- tetracyclines – tetracycline, minocycline, doxycycline;
- fluoroquinolones;
- fourth generation cephalosporins;
- aminoglycosides.
Tetracycline destroys the liver, affects protein synthesis, and disrupts the formation of tooth enamel. Aminoglycosides are ototoxic compounds that cause deafness and hearing loss because they affect the auditory nerve.
In pediatric practice, the most popular aminoglycoside is gentamicin; the prescription of this drug is not justified due to the lack of sensitivity to pneumococci and the ototoxic effect.
Tetracyclines and aminoglycosides are not prescribed to children under 7 years of age. In children, treating colds with lincomycin for bacterial complications is not justified. This drug interacts with other antibiotics and is incompatible with heparin, calcium gluconate, and ampicillin.
There is no need to use ampicillin injections for children, just like lincomycin; this antibiotic promotes the appearance of dysbacteriosis and is one of the most dangerous for intestinal flora.
Levomycetin begins to disrupt hematopoiesis. Levomycetin affects the central nervous system and liver in children under three years of age.
In young children, antibiotics from the third generation cephalosporins (ceftriaxone) can cause dysbiosis with almost complete replacement of their beneficial intestinal flora by fungal microbiota, pathogenic and bacterial.
Fluoroquinolones drugs disrupt the formation of cartilage tissue in joints and are prohibited for children and pregnant women, and not only during colds, but also during systemic diseases.
List of antibiotics for children in suspension
Currently, the pharmaceutical market offers many antibiotics in suspension form. The most popular of them are the following:
- "Suprax".
- "Pancef".
- "Klacid."
- "Cefalexin".
- Azithromycin.
- "Macropen".
- "Azitrox".
- "Augmentin".
- "Amoxicillin."
- "Amoxiclav".
- "Ospamox".
- "Zinnat".
- "Hemomycin."
- "Sumamed."
Next, let's look at each of them in more detail.
List of antibiotics for children
The most popular antibiotics for children should be known to any competent mother:
- Amoxicillin is a group of penicillins with a fairly wide spectrum of action. They are used for pneumonia, otitis media, sore throat, pharyngitis and sinusitis, as well as cystitis or urethritis. Granules are convenient for preparing a suspension/syrup; they are diluted with boiled water. For children under 2 years old - a quarter of a teaspoon, for children under 5 years old - half. Price on average 150 rubles.
This drug is suitable for very young children.
- Augmentin (amoxicillin + clavulanic acid) - powder for suspension, thanks to the acid, the spectrum of action is wider. Indications are the same as for amoxicillin. Prohibited for babies under 3 months. May cause an allergic reaction. Price from 150 to 250 rubles depending on the dosage. Augmentin's analogue is Amoxiclav.
- Zinacef is a 2nd generation cephalosporin, a wide range of effects, indications: otitis media, pneumonia, frontal sinusitis, sinusitis, tonsillitis, cystitis. For injection only. Children are prescribed 30-100 mg per 1 kg of weight per day. Diluted with water for injection. Costs from 130 rubles.
- Zinnat is a 2nd generation cephalosporin; granules are convenient for preparing a suspension. Indications: diseases of the upper and lower respiratory tract, ENT organs, genitourinary infections. Not recommended for children under 3 months. Dosage: 10 mg per 1 kg of baby’s weight, given twice a day. Cost from 200 rubles.
Zinnat should not be given to children under 3 years old!
- Sumamed - the active substance azithromycin, belongs to the azalides, has a wide spectrum of action on bacteria. Indications: sinusitis, otitis, pharyngitis, tonsillitis, pneumonia. Contraindicated for babies under 6 months of age. Shake the bottle before use, and after swallowing, give it a drink of water to swallow all the granules. Dosage 10 mg per kg of child’s weight, given once a day, course of treatment - 3 days. The price of the drug is on average 230 rubles.
- Suprax is an active antibiotic cefixime, a 3rd generation cephalosporin. Treatment of infections of the ENT organs, bronchitis, otitis, infections of the genitourinary system. Prohibited for children under six months old. From 6 months to a year - from 2 to 4 ml per 1 kg of weight, over 2 years - 5 ml. Divide the dosage into 2-3 doses. Dilute the granules with boiled water at room temperature. The medicine costs about 500 rubles.
- Flemoxin Solutab is the active ingredient amoxicillin, an intestinal antibiotic. Indicated for diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, in particular bacterial intestinal infections. Children 1-3 years old: 250 mg of medication twice a day or 125 mg three times. For children under one year of age, the dose is 30 mg per 1 kg per day, divided into 2-3 times. The price is about 250 rubles.
- Ceftriaxone is a 3rd generation cephalosporin, available in injections for intramuscular and intravenous administration, and is contraindicated in premature and newborn infants. Newborns up to 2 weeks - 20-50 mg per 1 kg of baby's weight per day, older - from 20 to 75 per kilogram. The course is at least 4 days, depending on the pathogen. The injections are very painful. The cost is around 19 rubles per ampoule.
Popular means
Keep in mind! Common antibiotics for colds in childhood are drugs from the following list:
- Amoxicillin. A drug from the category of penicillins of semi-synthetic origin. It has a wide spectrum of action and can be used from the age of two , on which the form of the drug depends. So, starting from the age of 12, you can give your child up to three amoxicillin tablets per day, depending on the symptoms. This is explained by the fact that this remedy can be used to treat various infectious viral diseases, including influenza. For young children, the dosage is calculated based on age, and the drug is given in the form of a suspension. Children under two years of age are given the drug based on a dosage of 20 milligrams per kilogram of the drug, from 2 to 5 years and from 5 to 10 years - 125 and 250 milligrams of the drug per day, respectively. From 10 to 12 years, depending on the symptoms, give from half to one tablet per day.
- Flemoxin solutab . Another semi-synthetic penicillin, which is prescribed for severe forms of infectious colds , including influenza. It is recommended that children be given tablets containing 125 milligrams of the active substance. From one to three years the dosage is three tablets per day, from three to 10 years - three tablets twice a day, starting from 10 years - 3-4 tablets three times a day.
- Azithromycin. The macrolide antibiotic, which is also used for colds and flu, is often prescribed for diseases with an atypical or complicated course . Given the high toxicity of the drug, treatment with such a drug for longer than one week is not practiced. Tablets are prescribed to children only from 12 years of age (or earlier if the child weighs more than 45 kilograms). The dosage is 1 tablet per day, and often a three-day course is enough to completely eliminate pathogenic microflora.
- Suprax . The drug is suitable in cases of resistance to penicillins in pathogenic flora. Children from six months to 11 years are prescribed the drug in the form of a suspension. The dosage for children up to six months is up to 4 milliliters per day, then 2 to 4 years old - 5 milliliters, up to 10 years old - 10 milliliters.
- Amoxiclav . Indicated for many respiratory diseases of infectious origin . Children are prescribed in the form of syrup starting from the age of three months (in such cases, up to one year, the drug is given three times a day, half a teaspoon). Up to seven years of age, the dosage is a teaspoon three times a day; at the age of 7-14 years, the dosage is doubled. From the age of 14 you can switch from suspension to tablets (three tablets per day at regular intervals).
- Sumamed Forte . A medicine based on azithromycin, which not only eliminates pathogenic microorganisms, but also prevents the development of new ones. Depending on the child’s body weight, the dosage of the drug per day is 2.5 milliliters (10-14 kilograms), 5 milliliters (15-24 kilograms), 7.5 milliliters (25-34 kilograms), 10 milliliters (35-44 kilograms) and 12.5 milliliters for children weighing 45 kilograms and above.
- Ofloxacin. A fluoroquinolone antibiotic, which is used mainly in the development of pathogen strains that have developed resistance to drugs of other groups . The average dosage is 7.5 milligrams of the drug per kilogram of weight. Taking into account that one tablet contains 200 or 400 milligrams of antibiotic, depending on the form of release.
- Cefotaxime. A cephalosporin antibiotic, which is used in the most severe cases and is administered intramuscularly and intravenously. Therefore, this remedy is not very relevant for home treatment. Children weighing less than 50 kilograms in a hospital setting are administered from 50 to 180 milligrams of the drug per kilogram of weight at a time. The number of injections can be from 2 to 6 times a day. For larger weights, the dosage is calculated individually.
Antibiotic for children with cough and runny nose
Cough and runny nose are most often the result of the activity of pathogenic microorganisms that have settled on the mucous membranes of the nose and nasopharynx. Usually, for such diseases, the doctor does not prescribe antibiotics to the child, but uses antiviral supportive and restorative therapy. But sometimes it is not enough.
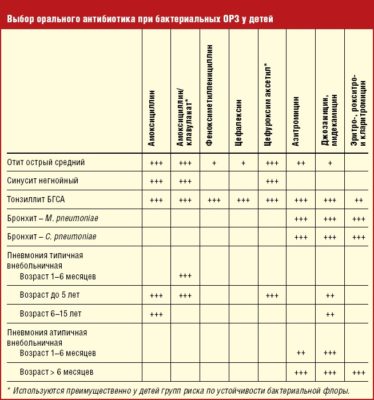
By releasing toxins into the blood, pathogenic microorganisms reduce the body's resistance to viruses and microbes, and lead to a protracted form of the disease, a complication of which can be the development of bronchitis, pneumonia, sinusitis and other bacterial complications. In this case, antibiotics must be prescribed.
The most common antibacterial drugs that a doctor can prescribe to a child for a cough and runny nose are:
- Amoxiclav
- Augmentin
- Flemoxin Solutab
They are used for dry barking and wet coughs, when sputum is not released from the bronchi and lungs. In this case, antibiotics protect the airways from the development of an inflammatory process. In addition to these medications, the child needs medications that thin and remove mucus.
Cephalosporins (Cefataxime, Cefuroxime and others) can be prescribed to a child for cough and runny nose if he has already been treated with penicillins no later than 3 months ago, as well as if penicillins are intolerant or if their use is ineffective.
Macrolide antibiotics are also prescribed to children for persistent coughs and runny noses. This includes:
- Azithromycin
- Sumamed
- Clarithromycin
Indications for use and use are similar to the previous groups of drugs.
Features of application
Experts have compiled a number of recommendations that parents must follow when treating children with antibiotics:
- If the doctor confirms the presence of a bacterial infection in the child’s body, he himself prescribes the appropriate treatment. Never self-medicate, especially with such serious drugs! This can lead to dire consequences;
- therapy is carried out strictly at a certain time, without violating the regime;
- in order to wash down a tablet or syrup (suspension), only plain non-carbonated water is used;
- Be sure to simultaneously take a course of probiotics - drugs that strengthen and restore the microflora of the gastrointestinal tract. Another condition: take vitamins for several days after finishing taking antibiotics;
- if tests show that the infection is not bacterial, treatment is stopped immediately;
- If the child’s condition worsens or if therapy does not work, treatment must be adjusted as soon as possible. Also, this is important when serious side effects are identified or a pathogen has been identified;
- Never combine antibiotics with antihistamines, immunomodulators and antifungal agents.
With the right treatment tactics, the child should feel better 2–3 days after the start of the course. But do not stop taking the medicine yourself - you need to drink as much as the doctor prescribed.
For cough and runny nose
A runny nose and cough can be accompanying symptoms of diseases such as:
- tuberculosis;
- bacterial bronchitis;
- pneumonia;
- pleurisy;
- angina;
- chlamydia or mycoplasma in the respiratory tract;
- purulent tracheitis.

Some products have an antibiotic effect
First of all, make sure that the disease is indeed bacterial. If you have a severe cough, submit sputum for clinical analysis for correct further treatment. If your health has deteriorated significantly, you should definitely take a broad-spectrum antibiotic approved for children.
Medicines are selected depending on the age category and weight of the baby. For a runny nose and cough, the following medications may be prescribed:
- if a child has not only a runny nose, but also a dry or wet cough, penicillins are used: Amoxicillin, Flemoxin, Amoxiclav, Augmentin, Ospamox;
- macrolide category: “Sumamed”, “Rulid”, “Azithromycin”, “Klacid”, “Clarithromycin”, “Macropen”;
- Cephalosporins are prescribed as a last resort if penicillins have not helped: Cefixime, Cefuroskim, Suprax or Cefotaxime.
At high temperature
It is worth remembering that most often a high temperature rises precisely during ARVI. But there are serious exceptions:
- a bacterial disease can be suspected if the baby had a cold, but the symptoms soon returned;
- persistent elevated temperature lasts more than 3 days. It cannot be brought down either by antipyretic or antiviral drugs;
- The first symptom is discomfort in the throat. The second is a runny nose. Third, the temperature rises. If the symptomatic picture is observed gradually, it is most likely that the nature of the disease is bacterial.
If the body temperature rises, the following may be prescribed:
- "Ampicillin";
- "Sumamed";
- "Klacid";
- "Cefotaxime";
- "Augmentin";
- "Suprax";
- "Clarithromycin";
- "Cefix";
- "Flemoclav Solutab";
- "Azithromycin";
- "Cefazolin";
- "Ceftriaxone".
Pros and cons of antibiotics
With the creation of antibiotics, completely new perspectives in the treatment of diseases opened up for doctors. The effectiveness of the drugs allows you to cure numerous childhood diseases and avoid complications. Medicines act on bacteria in different ways: some stop the growth of bacteria, others completely destroy their cells. This is the main advantage of antibiotics: effective treatment for bacterial infections.
However, in addition to the advantages, taking antibiotics also has a number of disadvantages that are inevitable during treatment. Any antimicrobial agent, even the best and most modern, can boast of a large list of consequences.
- "Healed immunity." This is a popular, but absolutely accurate name for the phenomenon when antibacterial drugs are used so often that they no longer work. If you give your child antibiotics for any cold, the bacteria adapt to their action and stop reacting to them. The child begins to get sick even more often, and treatment no longer helps: more and more powerful drugs have to be prescribed each time.
- Dysbacteriosis. This problem is much more common than others, since when the antibiotic enters the body, it does not divide bacteria into “good” and “bad”. First of all, this concerns the favorable microflora that populates the children's intestines. However, there is a way out while taking antimicrobial drugs, even new generation drugs from the fluoroquinolones group; the pediatrician prescribes probiotics. They allow you to avoid many negative consequences and minimize the risk of dysbiosis. After treatment, you should also take medications that restore intestinal microflora. Dysbacteriosis most often appears after taking broad-spectrum drugs - Sumamed, Suprax, Augmentin, Zinnat and others.
- Acquisition of immunity to antibiotics in bacteria. This occurs when the drug is incorrectly selected, the dosage is incorrect, or when the course of medication is interrupted. Often, at the first improvement, parents stop giving their children pills, which leads to bacteria mutation. If the course is completed to the end, then all pathogenic bacteria will die.
- Drug toxicity. The effect of taking antibiotics is their cumulative effect. But at the same time, accumulating, they poison the body due to their toxicity. If there is no improvement in the first 3 days, then the medicine should be changed. An ineffective antibacterial drug only weakens and poisons the body.
- Allergic reaction. Modern children are increasingly susceptible to diseases such as allergies. Moreover, the reaction can occur to a variety of products, including medications. Allergies most often manifest as a skin rash. In this case, there are two possible options: changing the medication to a drug from a different group or taking antihistamines. Tavegil or Suprastin are prescribed as additional antihistamine therapy. List of antibiotics to which allergies usually occur: Cedex, Flemoxin Solutab, Fluimucil.
- Thrush. This side effect mainly affects girls. Thrush especially often bothers children when treated with drugs such as Zinnat, Fluimucil, Macropen, Ceftriaxone. For prevention, the pediatrician can immediately prescribe the medications Linex or Biovestin.
Names of children's cough antibiotics
The doctor prescribes the medicine based on the respiratory system infections common in the region. Recommends a class of substances that are safest in childhood, with a wide spectrum of activity. The dosage of the drug is selected taking into account the symptoms, the general condition of the baby, its weight and age.

Correction of treatment is carried out 2-3 days later or after receiving the results of bacterial culture. The analysis reflects which bacteria caused the disease and how sensitive they are to individual antibiotics.
Suspensions
This dosage form is ideal for treating children 2–4 years old. It is a suspension of powder in a liquid medium. Thanks to flavorings and flavoring additives, the bitterness and specific smell of the main active ingredient are hidden. It is easier for a child to swallow the suspension. In dispersed (crushed) form, the bioavailability of the active component increases.
Sumamed
The active ingredient is azithromycin, belongs to the group of macrolides.
An antibiotic popular in pediatrics for any cough due to its good tolerability and reduced risk of developing allergies and other side effects. Prescribed for coughs caused by bronchitis, pneumonia, as well as bacterial rhinitis and sore throat. The suspension is used for patients from 6 months to 6 years. The doctor calculates the dosage based on the child’s weight. The drug is given once a day, an hour before or 2 hours after the main meal. The course lasts from 3 to 7 days.
Amoxiclav
A combination of amoxicillin (a substance from the penicillin group) and clavulanic acid, which expands the spectrum of antibiotic activity. The drug of choice for children with cough and high fever, as well as bacterial rhinitis, sinusitis, and sore throat. The suspension form can be used from 2 months. The daily dose is calculated by weight (20/5 mg per 1 kg), divided into 3 doses. For optimal effect, the drug is given to the child at the beginning of the meal. The prepared suspension is stored in the refrigerator for 7 days.
Ospamox
Semi-synthetic antibiotic (amoxicillin) has a wide spectrum of action. First-line drug for bacterial infections of the upper respiratory tract, as well as ENT organs in children. Prescribed even to the youngest patients.
Take twice a day, a single dose is selected individually:
- up to one year - 125 mg;
- 1–3 - 250 mg;
- 3–6 - 250-375 mg;
- 6–10 — 500 mg per dose.
For complicated infections, your doctor may prescribe higher doses. The prepared suspension is stored at room temperature for no longer than 14 days. The course of treatment is extended by 3–5 days after the symptoms of the disease have completely disappeared.
Augmentin
Contains amoxicillin enhanced with clavulanic acid. Prescribed to children from birth with bacterial lesions of the respiratory system and ENT organs. Cough syrup with an antibiotic is dosed for children by weight (20/5–60/15 mg per 1 kg of body weight per day), given 3 times a day with an interval of 8 hours. The suspension is stored in a cool place for a week.
Cephalexin
A second-line antibacterial drug for children from improved generations of cephalosporins.
Prescribed when penicillins are ineffective. Prescribed for persistent cough and runny nose, with or without fever. The dose is calculated based on the child’s body weight, focusing on the severity of symptoms and the location of the infection (25–50 mg/kg). The daily volume is given 2–4 times, regardless of meals. The suspension is stored at a temperature of 20–25 0C for up to 2 weeks. The course of treatment lasts 7–10 days.
Bactrim
Combined agent of the sulfonamide group. Contains co-trimoxazole and trimethoprim. Prescribed as a last resort if the cough is caused by a combined or multi-resistant infection. The dosage is calculated based on the child’s weight (30/6 mg per kg of body weight). The drug is given 2 times a day, with an interval of 12 hours. The suspension is indicated for children from 2 months to 12 years. The course of treatment lasts 7–10 days.
Antibiotics in tablet form
Substances that inhibit bacteria are unstable in the external environment. This is why suspensions need to be stored in the refrigerator. As an alternative to heat-labile syrups, your doctor may recommend tablets. These forms of antibiotics are better stored. It is important to consider whether a small patient can swallow the pill whole, because not all medications are allowed to be chewed and dissolved.
Flemoxin solutab
Amoxicillin tablets. Prescribed for cough and fever caused by bacteria. Can be used among children of any age. The daily dose is selected according to body weight (30–60 mg per kg). It is divided into 2-3 doses. The tablets can be chewed, crushed, or mixed with water.
Erythromycin
One of the first macrolide antibiotics. Not very popular due to the large number of side effects and high risk of an allergic reaction. For children from 3 years of age, 500–700 mg per day is recommended. The course of therapy is 10–14 days. Therapy is extended for another 2 days after the symptoms disappear.
Biseptol
Combined tablets containing sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim. Prescribed rarely, for persistent bacterial bronchitis or pneumonia. The drug is recommended for children over 6 years of age.
Zinnat
Antibiotic from the cephalosporin class. It is well tolerated and therefore popular in modern pediatric practice. Used to treat cough in children with bacterial sinusitis, pharyngitis, tonsillitis. The dose is selected by weight. For children over 2 years of age, the drug is prescribed 1 tablet (250 mg) 2 times a day. The course of treatment lasts 7–10 days.
Injections
Cough is treated with antibiotic injections only in case of serious complications, often in a hospital setting. Sometimes they are prescribed for outpatient treatment of sore throat.
Cefuroxime
Used in children older than 3 months. Doctors prefer the suspension form of fluoroquinolones. However, if the patient’s condition is serious, an antibiotic is administered intramuscularly.
Ceftriaxone
Prescribed to children of any age for bacterial pneumonia, which is accompanied by a severe cough. The injections are painful, so it is recommended to mix the injection powder with anesthetics (Lidocaine or Novocaine). Due to the risk of allergies, the dose of the drug and the solvent are chosen by the doctor.
Ampicillin
Prescribed to children from 1 year of age for bacterial infections of the respiratory tract and ENT organs. Due to the risk of microbial resistance and allergies, it is used in hospital settings. Therapy is carried out for 7–14 days.
Features and benefits of the suspension
Antibiotics in the form of a suspension are the most popular antibacterial drugs for children today. They have their own advantages:
- The dosage of the active substance in the suspension for children is usually reduced. Thanks to this, the drug has a gentler and more gentle effect on the body.
- These medications are absorbed faster than similar medications in tablets.
- The suspension is much easier to give to both infants and schoolchildren. After all, even at 6-7 years of age, children are not always able to swallow a whole tablet. Injections are a great stress for any child, and the suspension is a more gentle alternative. In addition, most suspensions have a pleasant fruity taste. The baby will not have to drink bitter medicine, and parents will not have to force him to do it.
When prescribing antibiotics for children, check with your doctor whether it is possible to replace drugs in the form of injections or tablets with a suspension.
How the suspension is prepared
Children's antibiotic suspension is a powder of small granules. The solid substance is ground or crushed in the factory, after which the finished product is placed in a container. The drug must first be prepared following the instructions included in each package.
There is a special mark on the bottle to which you need to add water. It is located close to the neck and is clearly visible. The water should be potable and at room temperature. The first portion of water is added to half the required volume, after which the bottle should be shaken thoroughly so that the powder is evenly distributed in the water. After 30-40 seconds, add the remaining volume of water and shake the suspension thoroughly again. You can prepare the drug in three steps for more thorough mixing.
The prepared suspension is stored in the refrigerator. Before giving it to your child, you need to shake the bottle thoroughly, since the powder does not dissolve in water, but forms a suspension that settles at the bottom. The bottle can be placed in a cup of warm water for a few minutes to slightly warm the medicine
A measuring syringe or measuring spoon is required with each drug in order to correctly measure the required dose.
Important! The concentration of the active substance in the drug may vary. Be sure to check the dosage when purchasing an antibiotic
How to prepare the suspension instructions
It is very simple to prepare a suspension from a drug purchased at a pharmacy. Each package contains instructions along with the bottle, according to which you can easily prepare the mixture for treatment.
On the bottle with the drug powder there is a little graphic located closer to the neck. At this mark you need to pour liquid into the bottle to dilute the powder. It is best to use boiled, chilled water. You cannot pour boiling water into the antibiotic, as this may worsen its properties. But in order for the suspension to acquire a uniform consistency, it is not recommended to pour in the entire volume of liquid at once.
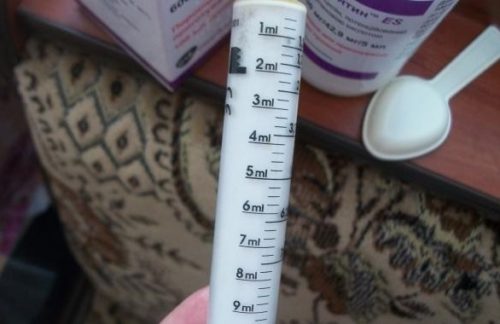
First, pour a third of the total volume of water into the bottle, screw the lid on the bottle and shake the contents well. Then add another third of the water and repeat the manipulations. This is necessary so that there are no lumps left in the mixture. After this, it remains to add the remaining volume of liquid. The prepared suspension should be stored in the refrigerator, and before use, slightly warm the bottle in a cup of warm water.
When are antibiotics prescribed for a cold?
As a result of interviewing parents and examining the child, the pediatrician will decide to prescribe antibacterial drugs if the following facts are present:
- After treatment with antiviral drugs, after 3 days there was no improvement in the patient’s condition.
- On the contrary, an imaginary improvement occurs, after which on the 5th-6th day the temperature rises again and hardly drops (or does not drop at all).
- The cough becomes severe, sometimes accompanied by shortness of breath.
- Urine loses transparency (cloudies).
- Lymph nodes enlarge.
- The pain in the chest and throat intensifies, and “shoots” in the ears.
- Severe nasal congestion, yellow or green thick discharge without response to topical medications.
- The general condition worsens, weakness and weakness appear.
These signs are a direct indication of a developing bacterial infection, and it is no longer possible to neglect the prescription of antibiotics here. Otherwise, the disease will become chronic or another, more serious disease.
Individual prescription, difficult choice of doctor
You can often hear from parents that doctors at the site prescribe antibiotics as a safety net when the baby’s temperature does not drop for several hours. Yes, there are recommendations that if you have a fever for more than 5 days, there is a high chance of a secondary microbial infection, which requires taking antibiotics, but all cases are individual, and you need to approach the use of antibiotics thoughtfully and carefully.
Important! Against the background of influenza, severe acute respiratory viral infection and in weakened, often ill children with foci of chronic infection, the use of antibiotics will be justified, since many different microbes may be in a dormant state in the child’s body.
If a decrease in immunity occurs against the background of such provocations (colds, flu), an exacerbation of the microbial process is quite likely, and the body, against the background of weakness, may not suppress the activity of these microbes itself, then secondary complications are formed - tonsillitis, otitis, pneumonia, bronchitis. Then millet cannot be avoided without antibiotics; such processes can be dangerous to health and life.