Why do moles appear in newborns, and what could be their danger?
When moles appear on a child’s clean body, parents may become concerned, because harmless spots tend to degenerate into malignant tumors. There is also concern that the baby may accidentally scratch or injure the nevus.
Therefore, with the appearance of moles in children, many questions arise - what was the impetus for their formation, how dangerous they are, and whether it is worth getting rid of them in childhood or is it better to postpone them until they grow up.
Moles and age spots on a baby’s body are formed from melanocytes. These pigment cells are present in the body of every person, regardless of age. The place of their localization is the space between the outer and inner layers of the epidermis. Thus, the presence of pigment cells is not a deviation; it is normal for childhood.
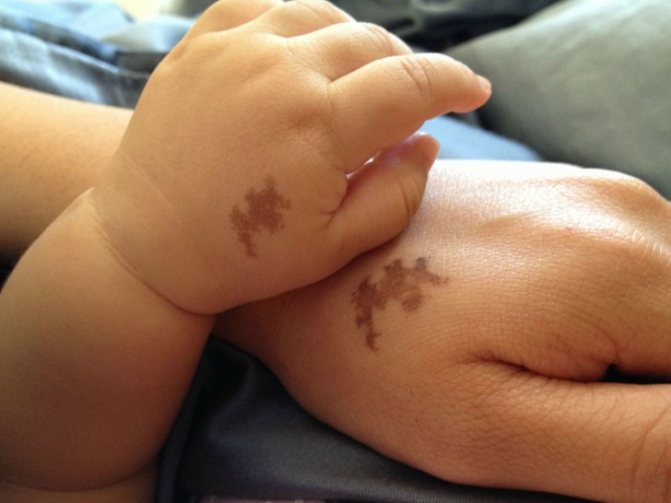
The photo shows nevi that can pop up on a child’s body. Most often they are small in size and have a light brown color. It is impossible to feel them with your finger.
If such moles have formed in multiple numbers, there is no need to worry. But formations with a diameter of more than 1.5 cm with unclear edges and uneven tonality require consultation with a pediatrician or dermatologist. Modified nevi are dangerous due to possible degeneration, so it is important to take timely measures to prevent or remove the problem area.
It happens that a mole disappears on its own and suddenly. If a small pale spot takes its place, the child should be shown to a doctor. Such unexpected behavior of a nevus may signal the beginning of the development of a skin disease.
Pigment cells fill a small organism during intrauterine development. Scientists say that the appearance of nevi is possible immediately at the moment of human birth. But these are such rare cases that it is not worth focusing on them. But by about 4 years old, children can already notice specific spots on their bodies.
If a child has many moles during the transition period, these changes in the body are identified with changes in the hormonal balance of the teenager. Over the course of several years, formations can form very actively. In the third decade, there are already many moles on the human body, then the process slows down.
It is impossible to answer unequivocally when moles appear in children. The mechanism of their development depends on the specific organism, and only attentive parents can know exactly at what point in the baby’s life path this or that element appeared.
In general, the process of formation of nevi depends on several factors:
- frequency of sun exposure;
- stage of active child development;
- hereditary predisposition.
Why do moles appear in a child? Genetics is one of the main reasons that determines the age at which nevi appear. Doctors believe that if a person’s moles appear in adulthood, then in children of this individual they will also form late. Dermatologists say the same thing about the multiplicity of formations. The more moles the parents have, the more of them there will be on the child’s body.
Medical statistics have recorded an early age for the appearance of moles - 1 - 2 years. Such children are already taken on country and beach holidays, where they are exposed to ultraviolet radiation. Short-term street walks that expose a child’s body to sunlight can cause the formation of new nevi.
All moles in newborns are classified as follows:
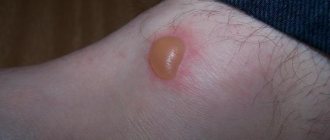
- Borderline nevi are nodules with clear boundaries, the color of which is not only brown and black, but also dark purple. The elements rise above the skin and do not cause pain when pressed. Hair does not grow on the surface of such moles, which distinguishes them from other types. The diametrical size of border nevi varies from a few millimeters to 1 cm. Occasionally they grow up to 5 cm. The danger lies in possible malignancy.
- Experts classify intradermal moles in infants as ordinary birthmarks and indicate their shape. It can be either a speck spread on the skin surface and having a diameter of several millimeters, or a large folded formation similar in appearance to a blackberry. In some children, the intradermal nevus has a characteristic stalk. Its color can be red, black, pale brown or natural flesh.
- Complex, also known as mixed form, is a transitional type between the types described above. A dense neoplasm with a spherical or dome-like shape is characterized by a dark brown, dark red and black color and a size of about 1 cm in diameter. Complex nevi are distinguished from epidermal moles by the presence of hairs. Their risk of transformation into melanoma is minimal, but they still require increased attention.
- Congenital nevi are a common phenomenon. Doctors link their formation to a disruption in the mechanism of transformation of cells that were originally the skin of the embryo into melanin. A congenital mole is immediately noticeable and attracts the attention of doctors even in the maternity hospital. The risk of malignancy of such a birthmark is determined by its position relative to the epidermal layers.
Giant nevi of the congenital type are very rare in newborns. They develop more often in girls than in boys. Moles grow with a child's body and stabilize in size as a person grows older.
According to an old saying, a child who has many moles will definitely be happy. Many believe that by the location and number of these spots on the body one can judge a person’s future and his character.
However, emerging moles in children are often a cause of concern for parents. It is worth saying that worrying about whether these marks are safe is indeed not without merit.
Many are convinced that we had spots on our body even when we were born. But that's not true. Very few babies have them at birth.
When does a child get moles? These spots, which develop from nevus cells, are transmitted genetically. Moles can be congenital. They are popularly called birthmarks. Such a mole grows with the child along with him. And this phenomenon is natural.
The question of when a child gets moles may sound incorrect. Nevi in newborns can be clearly visible. It is possible that there are barely visible spots on the baby’s body. At first it is just a lighter area of skin.
You can notice it with the naked eye. Over time, the spots become darker in color. Parents see that moles have appeared on the child’s body. They approach this phenomenon differently. There are people who are proud of their birthmarks; they look forward to the appearance of the same spot on their baby.
Causes of nevus
Why does a child get moles? There are several reasons for this. First of all, moles in children arise due to genetic predisposition. For example, one of the parents has the same dark spot located in almost the same place on the body. It is impossible to get rid of this phenomenon. Even if a mole does not decorate the baby, surgery to remove it is not worth doing. There is a high probability that the nevus will reappear.
When a child develops moles, one can hypothesize a hormonal cause for this phenomenon. However, as a rule, this does not occur in infancy.
One of the reasons for the appearance of moles is ultraviolet rays. But babies are not usually taken to the beach to sunbathe. That is why the rays cannot have a harmful effect.
With a high degree of agreement, it is possible to predict in advance the presence of a congenital nevus in an infant. Most often, birthmarks at birth are observed in the following cases: - in fair-skinned children; - in girls (four to five times more often than in boys); - in premature babies.
Nevi in a child
When do moles appear in children? This process is individual. It depends on the child's maturation, the amount of time he spends in the sun, and also on genetics.
In the case when the first moles appeared late on the father or mother, then they will probably not appear too early on their child. If a child has a lot of moles, then most likely his parents also have a large number of these marks.
In order for the child to be protected from the formation of new moles, he should be protected from exposure to sunlight. Under no circumstances should you allow your baby to get sunburned. In the summer season, the child must wear a Panama hat on his head, and exposed skin is protected by light clothing. Precautions must be taken before leaving home.
When does a child get moles? According to statistics, the first nevi can appear in children as early as one or two years old. At this age, children go with their parents to the dacha. They are starting to be taken to the beach. Moreover, even a short stay in the sun, just a couple of hours, becomes a sufficient condition for the appearance of a mole on the body. Daily walks in the park or on the street are enough for nevus to appear. Ultraviolet rays will do their job.
If parents are frightened by moles that appear on their child, they should contact a pediatrician or dermatologist. The doctor will examine the tumors and determine whether they pose a danger to the baby’s health. It is worth saying that malignant spots in infancy are extremely rare. However, it is important to monitor how a child’s mole grows, develops, and how it manifests itself.
You should also pay attention to the baby’s reaction to this neoplasm, because nevi appear in those areas of the skin where the immune defense is significantly reduced, which causes changes in their color and size. In this case, there is a high probability of inflammatory processes and even degeneration of birthmarks.
Considering this fact, we can talk about the potential danger of even the most inconspicuous nevi. However, parents should not panic in advance. The likelihood that a baby’s moles will begin to degenerate is extremely low. This does not depend either on the number of newly formed spots, or on whether they were present on the newborn’s body when he was born or not.
Types of moles
When a baby appears in a family, few parents imagine what his appearance will be like in the future. But skin defects such as congenital nevi or birthmarks will not disappear over time. Some parents do not attach importance to birthmarks in children, and some are literally afraid of them. Today we will try to shed light on the phenomenon of birthmarks in newborns.
Definition
Reasons for the absence of moles in children
There are practically no people with clear skin, without a single pigment spot. They are rare in infants. In the first months of life, newborns may develop small pigment spots (freckles), which will later increase in size or disappear. This can be seen in teenagers. During puberty, due to hormonal changes, their number may increase sharply, but over time some will disappear.
This is an individual trait that depends on heredity. If one or both parents had birthmarks, then with a high degree of probability the baby will also have them. But if they are not there, you should not worry.
Features of children's moles
The peculiarity of moles in newborns is that with age they completely disappear or their number increases significantly. Moles in children form when pigment cells containing melanin accumulate in one place.
Predisposition to pigment elements occurs during embryonic development. Nevi can be localized in various places, and also have a variety of shapes, colors and sizes. These benign formations are sometimes prone to the process of malignancy. Over the course of a lifetime, the number of nevi changes many times.
Reasons for appearance
The most common and natural one is genetic . The number and location of nevi in a child directly depends on the number and location of them in his immediate family. Hence the name of education.- Internal reasons. Hormonal. The peaks in the formation and disappearance of birthmarks directly depend on the peaks of hormonal changes in the human body, so the first occurs during the period of 2-3 years, the second during adolescence; often during pregnancy, a woman can also notice the appearance or disappearance of nevi. And this process is also natural.
- External reasons. First of all, the activity of melanocytes is influenced by solar activity and the effect of ultraviolet radiation in particular. Under the influence of this particular radiation, a mole can change its size, color, and even degenerate into a deadly disease - melanoma.
- A less common cause (and not yet fully proven) is traumatic . According to this hypothesis, the formation of foci of hyperpigmentation in children can form in the post-traumatic period, after suffering insect bites, skin injuries, as well as viral infections.
Attention: a post-traumatic lighter mole may change its color and acquire a rich color.
Varieties
There are conventional classifications of nevi based on their color, shape, size, origin, and the degree of threat of cancer development.
Based on color, including shades of color, moles are divided into brown, red, black, purple or blue. The appearance of a nevus of a certain color on a person’s body is associated with his skin color type.
Neoplasms can have the following typical forms:
- flat appearance (such formations are considered absolutely safe);
- convex appearance, sometimes in combination with growing short hairs;
- oblong appearance;
- round view;
- with a smooth structure;
- with a rough structure.
Pigment spots are divided into three types based on size:
- small (up to 1.5 cm in diameter);
- medium (up to 10 cm in diameter);
- large (several times larger than average in diameter).
Large pigmented neoplasms have a congenital appearance on the human body.
Classification by origin:
- vascular (appear as a result of pathology in the development of blood vessels);
- pigmented (appear due to significant production of melanocyte cells containing pigment).
According to the degree of threat of cancer, nevi are divided into two types:
- melanoma-free;
- melanoma-hazardous.
Causes of moles
Moles in infants appear immediately after birth or after 2 to 3 months. They are not signs of any disease, but they often cause some concern for parents.
Many people are interested in why moles appear in newborns, and some are born with them. Hormones and ultraviolet radiation as causes of the appearance of moles in newborns are excluded, and one of the most probable remains. Genetic predisposition.
The most common reason for the appearance of a nevus is genetics. If, for example, a father or mother has many moles, then most likely the baby will be born with moles.
Parents are especially concerned about large nevi; sometimes a newborn is born with a birthmark on the floor of the face. The following points may be triggering here. Most often people born with nevi are:
- babies with fair skin
- female newborns (approximately 4-5 times more often than boys),
- children born prematurely.
Some doctors believe that the causes of large congenital nevi and birthmarks in newborns are:
- changes in hormonal levels in the female body during pregnancy;
- infectious diseases of the genitourinary tract in the mother of a newborn;
- the course of pregnancy under negative external conditions. The presence of radiation, toxins, sudden changes in climatic conditions during pregnancy and many others.
Scientists have found that birthmarks are an accumulation of special cells called melanocytes on an area of the skin. They may have excessive pigment or not contain it at all. In the first case, the mark will be dark in color, in the second it will have a shade lighter than the color of the surrounding tissue. There are also varieties of deep burgundy, wine-colored spots formed by a concentration of blood vessels - hemangiomas. Scientists call all such formations on the body nevi.
Previously, people believed that moles and birthmarks were special marks that spoke about the fate of a little person. In order to correctly “read” the future, they attached importance to the location of moles and their number. Large brown spots on the body of newborns, according to our great-grandmothers, appeared in the place that a pregnant woman could touch during a fright. There is a belief that you should never grab the belly in which the baby is growing.
Today there is also no clear answer to the question of why birthmarks appear in newborns and where they come from during the baby’s growth. The reasons for their occurrence are not fully understood. Scientists suggest that factors such as heredity and skin color play a role. If one of the parents has a lot of moles, there is a chance that their son or daughter will also have them. In addition, moles and age spots often appear in premature babies, as well as in those children who have very fair skin.
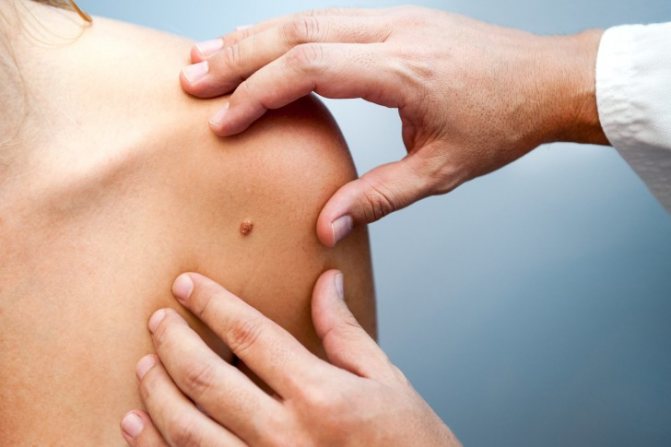
If parents have many moles, the risk of their appearance in the child is high
Also, the risk of nevus in a baby increases if his mother was exposed to toxic substances or dangerous radiation while carrying him. The balance of sex hormones in the pregnant woman’s body, as well as the presence of infections of the genitourinary system, are of great importance. Interestingly, nevi can be located on any part of the baby’s body - on the stomach, back, butt, head, leg, arm or fingers. Sometimes such formations interfere with normal life if they are located on the eyelid, in the eye, in the ear or in the mouth.
As we wrote above, there are quite a few types of birthmarks. They differ not only in color and shape, size, but also in density and relief. There are markings that are flat, not rising above the surface of the epidermis, but there are also convex ones, with enlarged pores, and covered with hair. Birthmarks in newborns and young children require special attention, and in some cases, surgical intervention. Let's look at their most common types.
The appearance of nevi (their color, shape, size) makes them quite noticeable on the human body, especially if their presence was not initially indicated in any way, that is, they were simply absent. The appearance of new moles along with existing ones, as a rule, arouses curiosity and certain concerns about their safety and aesthetics.
Assistance in conducting a diagnostic study of nevi can be provided by a dermatologist, who, in the process of collecting the necessary medical history, can clarify when the mole appeared, whether there are growing moles on the body, whether the color of the nevus has changed, whether pain or itching has occurred even occasionally in the areas where pigmented formations are located , burning, strange discharge.

The factors that provoke the appearance of nevi are different and have age-related characteristics.
Often, parents notice the presence of moles or birthmarks on the body of a newborn child and experience certain concerns about their origin and safety for the baby. In most cases, newborn girls become carriers of nevi. An infant or newborn is considered a child from the moment of birth to 1 month of life.
The reasons for the appearance of moles in infants are as follows:
- hereditary factor (genetic predisposition, since genetic information is encoded in DNA and is transmitted from parents to offspring);
- premature birth of a baby or prematurity (fetal maturity factor);
- level of skin pigmentation (very light skin of the baby and his parents);
- disturbances in the functioning of the mother's hormonal system during pregnancy (hormonal surges);
- the mother of the baby suffers a genitourinary tract infection during pregnancy;
- adverse chemical effects and exposure to various types of radiation (including ultraviolet radiation) on a pregnant woman;
- traumatization of an area of the baby’s skin with a hidden mole due to external influences (for example, insect bites and/or abrasions received, for example, during childbirth);
- targeted exposure to ultraviolet sunlight on the baby's skin.
- Nevi and birthmarks can also occur in infants. An infant is considered a child from the neonatal period to 1 year.
The appearance of moles in infants is explained by similar reasons for the appearance of moles in infants.
The appearance of moles in a child is a natural process that accompanies the growth and formation of a young body. Such neoplasms, most often, do not pose a threat to the baby’s health, but require passive monitoring.
The reasons for the appearance of moles in children can be outlined as follows:
- genetic factor or hereditary predisposition;
- period of active physiological development of the child;
- regularity of exposure to direct sunlight on the child’s body;
- chronic nature of certain diseases of internal organs and systems;
- inflammation of the skin;
- mechanical damage to skin tissue.
Moles tend to actively appear in adulthood. The appearance of moles in adults can be explained by the following reasons:
- hormonal surges. Hormonal imbalance provokes the appearance of an accumulation of melanin cells in the body of women (during pregnancy, its termination, in the postpartum period, during menopause). In men (in case of malfunction of the hypothalamic-pituitary system, during surgery or negative effects on the groin area, with an increased amount of estrogen hormones). Regardless of gender - in a situation of significant stress, during a severe course of a somatic illness;
- exposure to ultraviolet rays (in the form of direct sunlight, when visiting a solarium, in the process of getting sunburn);
- disruption of the functioning of internal organs and systems (susceptibility to viral, dermatological diseases, diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, lipid metabolism disorders);
- insect bites and abrasions (external mechanical impact leads to the appearance of microwounds, microcracks in the skin, which, in turn, provokes the grouping of melanin cells at the site of injury);
- genetic predisposition (inheritance of moles along a related line);
- natural aging of the body (moles act as a sign of biological deterioration of the body).
Features of moles in newborns
Spots form on the skin of infants either before birth or in the first weeks of the baby’s life. They belong to congenital benign formations. Pigmentation can be differentiated into vascular formations and pigmented ones. Pigmented birthmarks include birthmarks; vascular angiomas are divided into hemangiomas and lymphangiomas.
Hemangiomas are hypertrophied vascular formations that look like flat moles or convex roundness from pinkish to red, of various shapes. They do not itch, do not irritate the baby, and can be located on any part of the body. Over time, they fade and disappear, increase in size as the child grows, and normally retain their original shape.
Lymphangiomas in children are a rare disease; depending on the type of disease, the tumor can be pronounced (cystic) or in the form of nodules rising above the surface of the skin (cavernous). The tumor cells are benign, symptoms appear immediately after birth or in the first years of life, mainly up to 3 years. The disease is caused by intrauterine developmental defects, is localized in the location of the lymph nodes, treatment is surgical.
On the back of the baby's head, eyelids, bridge of the nose, forehead, and eyebrows, the mother notices pink or red spots of irregular shape. The formations are caused by vascular hypoxia during the perinatal period or during childbirth. Tumors are not dangerous, they fade over time, they are removed if they are located on visible areas of the body and represent a cosmetic defect. The spots on the face fade towards school age. They are called “angel’s kiss” and can be removed with laser if necessary; spots on the back of the head disappear more slowly, and in 40% they remain for life, their name is “stork bite”.
Red-haired babies are born without freckles on their cheeks. The spots appear at 3-5 years of age, reaching a maximum in number by the age of 25, when the formation of body systems is completed. Later, the spots do not appear, and the old ones fade.
In childhood, nevi do not carry the risk of degeneration into a malignant formation. This usually happens later, but formations require careful attention and specialist supervision. The following symptoms serve as a signal to remove pigmentation defects:
- the nevus has become asymmetrical and irregular in shape;
- the edges of the formation spread out, became jagged, the boundaries blurred;
- the nevus bleeds, there is discharge;
- the color of the spot has become uneven, inclusions of colors unnatural for the skin are visible;
- the size of the formation has increased over 6 mm;
- the dynamics of symptoms, sharp growth and deformation can be traced.
If a child has many moles, the mother should regularly examine the baby, keep records, remember or photograph the size and shape. This will allow you to notice the onset of pathological processes in skin cells. Sometimes nevi are located in places where they are regularly damaged or can be damaged: on the legs and feet, arms, head, neck, thighs, butt. The formations should be removed without waiting for injury; a violation of the integrity of moles, like the sun, are two main factors that cause the growth of malignant cells. In adults, nevi are at risk on the back; self-examination is difficult in this area.
How can they be dangerous?
Don’t be nervous about every nevus on your baby’s body. Most parents, when moles appear in their children, worry about the risk of their degeneration into melanoma. Standard pigment elements with a uniform structure and clear boundaries do not pose any threat. They may change color and size slightly throughout life, but remain just nevi, black-brown spots.
You should contact a dermatologist-oncologist when a child develops a mole.
The pathological process of transformation into melanoma can be triggered by external factors, for example, mechanical damage. For this reason, it is important to immediately visit an oncologist when a child picks off a mole. Changing the structure of the nevus can cause melanocytes to mutate. They transform into malignant cells and quickly spread to healthy tissue.
Definition
The appearance of new individual moles or new clusters of nevi on the skin cannot go undetected and can cause some concern regarding their potential danger to the health of a particular person. An accurate conclusion about the nature of nevi on human skin can be made by a qualified specialist in the field of dermatology and oncology after conducting a series of special diagnostic studies.
- there are no discharges from the neoplasm (including bleeding), it has a complete appearance;
- throughout the entire period of existence of the neoplasm, its color, size, and shape are constant;
- the nevus is not covered with scales;
- there is no pain, itching, or inflammation in the area where the nevus is located.
It is believed that it is advisable to independently examine your own body to exclude anomalies in the appearance of nevi at least once every three months. Such an examination can be carried out with the assistance of close relatives.
Thus, the very fact of the appearance of new moles is a natural process of physiological change in the human body, but due to the unpredictability of the impact of unfavorable external or internal factors, occasional passive monitoring of the condition of the nevi is necessary.
Moles are completely safe formations, but they require targeted control. Parents are recommended to examine the child’s body from time to time in order to analyze the condition of existing nevi and record the formation of new ones. Patients with a large number of large pigmented elements should consult a pediatric dermatologist regularly.
Doctors identify suspicious and potentially dangerous moles in children. They classify as suspicious neoplasms that did not appear immediately after birth, but at an older age. Those formations whose diameter is more than 10 mm or those that have sharply changed their color (turned black, become spotted) are considered potentially dangerous.
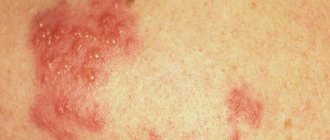
Why does a child have a red mole?
Why does a child grow a mole? A red mole, or, as doctors usually call similar manifestations on the skin, angioma, appears in those children who genetically inherited them from their parents. This tumor, which can be lymphatic (lymphangioma - a tumor filled with lymph) or vascular (hemangioma).
They come in different shapes: convex or flat, from the smallest to the largest, from light pink flowers to bright red. Usually angiomas are not removed, no matter how unpleasant they may be in appearance. Small angiomas can resolve on their own with age. Only those that bleed, itch, peel, have changed in color or size, or are damaged should be removed.
The cause of angioma may be liver or pancreas disease
Moles and age spots in a child appear due to the presence of melanocyte pigment cells. All people have such cells; this is considered normal, even with pronounced pigmentation. Red nevi can appear in a child both at the time of birth and during adolescence, during the period of active growth of hormones. It is during this period that nevi begin to actively appear on the body. The cause of angioma may be liver or pancreas disease.
In what cases should you consult a doctor?
It is recommended to regularly monitor the condition of nevi and keep records of new formations. If any changes, even minor ones, appear, it is still better to make an appointment with an oncological dermatologist. A visit to the doctor should not be postponed if the following symptoms appear:
- the skin pattern disappears on the surface of the mole;
- the formation acquires a glossy shine;
- the edges of the pathological element become uneven and the shape becomes asymmetrical;
- the mole dynamically increases or decreases in size;
- the nevus itches and a burning sensation appears in it;
- peeling appears around the pigment element;
- hair falls out on the skin adjacent to the nevus;
- the mole changes color or ulcers appear on it;
- the formation begins to bleed;
- daughter pathological elements appear;
- A red rim or white spot appears around the nevus.
If a child has more than 10 moles on his body, this is a reason to consult a dermatologist. A skin passport will be created for the baby, containing the number and size of the largest tumors. During the examination, the doctor examines changes in the skin using a dermatoscope. Every 6 months, preventive examinations allow us to identify new dangerous elements and see the dynamics of the development of old ones.
Doctors recommend removing moles in children if they have spread across the skin under the eye or are uneven in color. A convex pathological element is removed when it completely or partially changes color and also has other pathological symptoms. The degree of danger of malignancy of any pigmented neoplasm is assessed by an oncologist.
Children have mostly normal nevi that do not cause any particular discomfort (no itching, bleeding, peeling, change in color or size). However, vigilant parents even prefer to consult with a doctor about such formations, who will examine the child and explain that it is necessary to choose a sunscreen and use it for preventive protection.
If the formation turns out to be benign, then the parents will be able to sleep peacefully. And if melanocytic nevi are identified, it will be possible to begin adequate therapy in a timely manner.
Anastasia K.:
Girls, I spent 6 years of my life to return my skin to its healthy appearance and get rid of these dangerous papillomas and moles, don’t repeat my mistakes... Read here... {amp}gt;{amp}gt;
When do children get moles?
Sometimes moles are visible on the baby’s body from birth. In most cases they form later. In some babies they become noticeable as early as 6 months, in others - closer to 2 years. Perhaps they are present at an earlier age, but due to their light shade they are difficult to distinguish on the skin. A child may develop many moles between the ages of 5 and 7 years. The next outbreak is the puberty period, characterized by changes in the body due to a hormonal surge.
Advice. Doctors recommend observing moles, assessing their size and appearance. If they seem to be growing, or there are too many of them on the body, it is better to consult a dermatologist.
Difference from melanoma
Ordinary moles are quite harmless to the human body, but when exposed to unfavorable factors, they can degenerate into an aggressive malignant neoplasm called “melanoma” or skin cancer.
Characteristic signs of the degeneration of an ordinary mole into melanoma are:
- surrounding the nevus on the skin with a rim of a cluster of red or shades of red cells;
- microdamages on the surface of the nevus, visible to the ordinary eye;
- the originality of the color of the nevus on its entire surface, inclusions of blue, red, black colors;
- the appearance of ordinary or numerous scales on the surface of nevi;
- change in the shape of the nevus due to its growth to the sides;
- fuzzy or sharp-angled edges of the nevus;
- sensations of thickening of the skin area in the area of the nevus or an increase in the diameter of the tumor (especially more than 1 cm);
- inflammation, painful tingling, itching at the site of the nevus;
- bloody and other discharge from the neoplasm;
10) accumulations of cells in the form of nodules along the edge of the nevus.
Thus, knowledge of the critical features of malignant formations can contribute to the timely identification of dangerous nevi during their independent examination.
Should I delete or not?
After a thorough examination of the nevus, specialists in the field of dermatology and oncology decide on the advisability of its removal and the specific method of removal. As a rule, moles in the neck, décolleté, armpit, groin are subject to removal; they are actively growing and changing shape, causing pain and aesthetically unattractive as a result of constant mechanical irritation. Pathological moles are subject to mandatory removal.
If parents discover a mark on their child, they should definitely consult a specialist. The doctor will determine the type to which the neoplasm belongs and recommend what to do with the nevus. Sometimes it is enough to simply observe the birthmark and monitor its size. Parents can regularly take a photo of the nevus or take an imprint at regular intervals. Then it will be possible to see the dynamics of its growth.
Some birthmarks are dangerous growths and need to be removed urgently. There are several situations that do not allow you to relax and require immediate medical attention:
- in a child who is more than six months old, the birthmark began to increase in size;
- the tumor is easily touched and damaged by clothing, a comb or when putting on shoes;
- the birthmark is 20 centimeters or more in length or width;
- the mole is located in the nose, on the eyelid, in the ear canal;
- the mole is damaged, it bleeds, itches, itches;
- the birthmark began to change - to grow, darken or lighten, and hairs began to fall out of it.
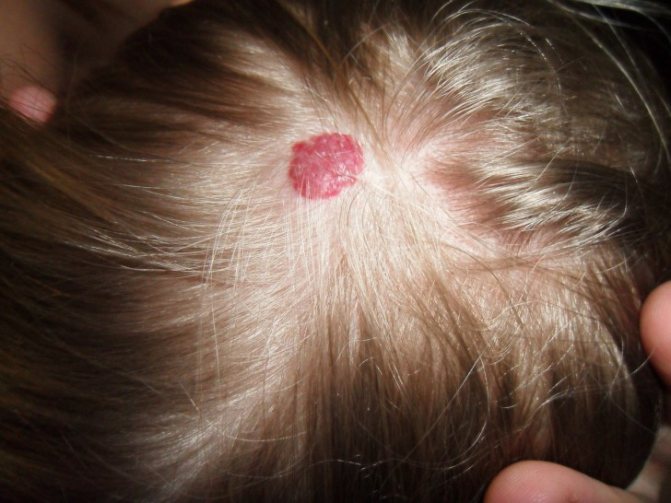
If the stain is easy to touch or is already damaged, you should consult a doctor.
Removing moles in children
Removal of skin tumors is carried out by a qualified specialist in the field of dermatology and oncology. If it is necessary to remove a mole for aesthetic purposes, no preliminary preparation is required. When removing a pathological mole, it is necessary to first undergo certain tests and conduct a specialized study.
- using a laser;
- using nitrogen (cryodestruction);
- surgical intervention;
- using radio waves (radio wave removal);
- using high frequency current (electrocoagulation).
When a pathological mole is removed, its element must be sent for histological examination. Medical observation continues to monitor the patient's condition in the postoperative period.
There is no conservative treatment that ensures complete elimination of the nevus from the epidermal tissue. Ordinary moles, stable in size, with smooth edges and uniform color, do not need to be touched. The need for surgery arises when a suspicious nevus appears in a child; the dermatologist will decide after a thorough examination whether to remove the tumor or not.
The choice of technique should also be made by a dermatologist. The laser procedure is the fastest and most effective, but after it there is no biological material left for histological analysis. For this reason, most doctors recommend removing moles with a radio knife. After manipulation, the resulting area of skin is checked for the presence of cancer cells.