Glucose is prescribed to a child, especially in the first days of life, quite often. What is this connected with? Let's start with the fact that glucose is a very valuable source of nutrition, which is also easily absorbed by the body. It is necessary for some babies, as it can significantly increase the baby’s energy reserves.
Who is it shown to? Who is it contraindicated for? For what problems does a child need glucose? Are pediatricians exaggerating the role of this organic compound? We will try to answer all these questions in this article.
Glucose
Let's start with an introduction to glucose. What is it? This compound is also called grape sugar, and it is considered the most abundant source of energy in all living organisms on our planet. Where did this name come from? The thing is that glucose can be found in the juice of many berries and fruits, including grapes.
Anyone who loved chemistry and biology must know that our body is capable of breaking down some compounds into glucose and fructose. This list includes:
- cellulose;
- starch;
- glycogen;
- maltose;
- lactose;
- sucrose.
To what has been said, we can also add that the substance described is the main product of photosynthesis. Energy is necessary for the implementation of metabolic processes, and glucose is its universal source.
In animals this compound is found as glycogen, and in plants it is found as starch. Cellulose is a polymer of glucose and forms the basis of the cell wall of plants. Glucose helps animals survive the winter. As an example, consider the wintering of frogs. During cold weather, the level of grape sugar in their blood increases, and due to this, the frog can easily survive being frozen in ice.
In our pharmacies you can find both a liquid solution and tablets with this compound. Note that children are given glucose in ampoules much more often than in tablet form.
Now we propose to move on to the issue of indications and contraindications for taking these drugs.
When does acetone appear?
Acetonemia is a typical childhood problem, and children who are thin, emotional and active are at much greater risk of increased acetonemia.
The release of ketone bodies, which contain acetone, occurs when the child’s body overuses available energy. As we know, the main fuel for us is glucose, which comes from food, and excess carbohydrates are partially deposited in the liver and stored there until needed, and some are converted into fat deposits.
During violent games, a strong emotional outburst, a sharp increase in temperature and other unforeseen situations that require energy consumption, glycogen stored in the liver is used. But the child’s reserve of this is too small and runs out very quickly, and then energy begins to come from fat deposits, and when fat is broken down, in addition to glucose, those same ketone bodies enter the blood. The danger is that ketone bodies can irritate the vomiting centers in a child's brain, causing severe uncontrollable vomiting with a high risk of dehydration.

Indications and contraindications
So, can you give your child glucose, and when is it needed? Indications for use are the following cases:
- avitaminosis;
- hypovitaminosis;
- pregnancy;
- lactation period;
- acute lack of glucose;
- period of intensive growth;
- convalescence;
- increased physical activity.
They can prescribe glucose for a one-year-old child, a baby in the first days of life, or an adult. In this case, the attending physician must make sure that there are no obstacles to taking this medicine. In the list below you can see all possible contraindications:
- diabetes;
- hyperglycemia;
- glucosuria;
- hypersensitivity to a component of the drug (this applies to glucose tablets);
- thrombophlebitis;
- tendency to thrombosis.
In addition, you need to know that glucose in tablet form is not recommended for children under six years of age. If a person has diabetes mellitus or a deficiency of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase, then it should be taken only after consulting a doctor, and only if he agrees to this type of treatment.
Natural and healthy sugar substitutes in the baby menu
As a rule, the question of introducing sugar begins to worry parents when their baby flatly refuses to eat unleavened porridge or fermented milk products.
In this situation, natural and at the same time healthy sweeteners will come to the rescue - fruits, which may be present on the child’s menu in raw, boiled, baked or dried form.
You can add fruit puree, chopped fresh fruit or seasonal berries, etc. to porridge, kefir or cottage cheese.
You can make a compote from dried fruits, and after a year, offer them dried to your baby as sweets.
Attention! It is recommended to introduce sweet fruits into a child’s diet from the age of 8 months, and only after he gets acquainted with all seasonal vegetables and tries “unsweetened” cereals.
Blood sugar
Glucose solution is prescribed to children, as well as to adults, only after a blood test. In this section of the article we will talk about normal blood sugar levels in adults and children.
Surely everyone has heard that you need to regularly test your blood for sugar. Although this is a generally accepted name, it is not entirely correct.
The fact is that in the Middle Ages, doctors believed that increased thirst, frequent urination, purulent infections were all the result of excess sugar in a person’s blood. But nowadays doctors are sure that it is completely absent there, since all simple sugars are converted into glucose.
Thus, when they talk about blood sugar, they mean the concentration of glucose, which plays a big role in metabolism and supplies energy to all tissues and organs. In the table below you will see the normal blood sugar level for an adult.
| Index | Normal for a person with diabetes | Normal for a healthy person |
| Fasting (mmol/l) | From 5 to 7.2 | From 3.9 to 5 |
| One hour after eating (mmol/l) | To 10 | Up to 5.5 |
| Glycated hemoglobin (%) | No more than 7 | From 4.6 to 5.4 |
In the following table you can see the normal glucose concentration in a child from the first days of life to eleven years.
| Age | Norm (mmol/l) |
| Up to a year | 2,8-4,4 |
| 1-5 | 3,3-5 |
| 6 and older | 3,3-5,5 |
What determines the level of glucose concentration in a child’s blood? The most obvious factors:
- nutrition;
- work of the digestive tract;
- influence of hormones and so on.
The fact that this indicator may fall below normal is influenced by the following reasons:
- starvation;
- the child drinks little water;
- chronic illness;
- pathologies of the digestive tract;
- nervous system;
- arsenic poisoning.
And indicators above the norm are provoked by:
- diabetes mellitus;
- incorrect performance of the analysis (eating before blood sampling, overexertion, both physical and nervous, etc.);
- thyroid disease;
- pancreatic tumor;
- obesity;
- long-term use of anti-inflammatory drugs.
Interesting article... "SUGAR FOR CHILDREN"
Children do not need sugar, but glucose. It gives energy and stimulates appetite, helps all organs stay in good shape and work as they should. Glucose is found in sugars, that is, in fruits and vegetables. To have enough of it in the body, a child under seven years old must eat a plate of vegetables and 150 g of fruit a day. Sugar and sweets are also suppliers of glucose, but not only it, so their share in the diet up to three years is no more than 10%. Until the age of three, a child has enough glucose without sugar and sweets; the benefits of these products are purely theoretical and depend on the desire of parents or relatives to pamper the child with something. Or make your life easier by feeding your child unloved porridge. The sugar norm from three to seven years is no more than 3-4 g per day. Don't forget that sugar is found in many products, including processed meats.
What are the dangers of introducing sugar early? 1. Confused taste sensations. If you started sweetening your porridge and tea too early, don’t be surprised when your child turns into a toddler. From the age of six months (from the start of complementary feeding), a child should get used to the natural taste of food. Perverted taste presupposes further demands for sweets: you yourself teach the sweet taste, and the child gets used to it, not knowing otherwise. The other side is being overweight. 2. Sugar kills vitamins and beneficial bacteria; it creates a favorable environment in the intestines for the proliferation of pathogenic flora (“stomach swelling”). Therefore, it is unacceptable to sweeten children's curds, kefir, children's yogurt and porridge during (and not at the end) cooking. Your task is to feed a healthy product, and not “at least something.” 3. Excess sweets in the diet, including sugar, leads to functional changes in the central nervous system and endocrine glands, decreased immunity, and increased risk of developing diabetes and cardiovascular diseases. The most important thing is immunity. He suffers first. Do you need it? 4. Sugar is one of the most important factors leading to the process of tooth decay, since it promotes the proliferation of bacteria that cause caries. You can read more about introducing sweets here: https://www.u-mama.ru/read/article.php?id=2693 Unfortunately, modern sweets contain more harm than good. Do not give your child under two years of age sweets loaded with low-quality fats, preservatives and flavorings. Most parents have an illusion called “there is no allergic reaction, so we give it.” A child is limited in sweets not only because of allergies. Preservatives and flavorings accumulate in the body. You will never know if this chemistry will cause chronic diseases later. An excess of sweets leads to hormonal surges: the child becomes overexcited, sleep is disturbed, and the child “suddenly” becomes aggressive. A familiar picture: a child moves with his mother along the street “from chocolate to ice cream.” Having not received the “prize”, he throws ostentatious hysterics. Mom gets used to cajoling him for her peace of mind. The more sweets, the stronger the hysterics: the body gets used to demanding fast glucose in huge doses. THIS IS IMPORTANT : children, unlike adults, do not have the habit of eating regularly. Their appetite can vary greatly from day to day. This difference may be related to physical activity. You should not introduce your child to sweets in an attempt to “plug the hole” in the little one’s diet. If a child is not eating well, this does not mean that he needs to snack on cookies more often. Baby food often contains a mixture of dextrin and maltose (maltodextrin); this substance is healthier than sugar and can replace it. Also added to cereals and cookies: glucose (grape sugar), fructose (fruit sugar), dextrose (another name for glucose), maltose (glucose polymer). These sugars do not interfere with the supply of valuable vitamins, minerals and fiber.
Professional chefs admit: it is very difficult to prepare a dish without using flavoring additives. This is a special art: to preserve the true taste of products. Food without additives is considered bland; we get used to flavoring it with something. This habit is called “cluttered taste.” A child who has just been introduced to complementary foods does not yet have an impaired taste perception, but, unfortunately, many mothers cannot restrain themselves and quickly spoil his taste - adding salt, sweetening. Why shouldn’t you rush in this case – and why is it worth adjusting your own taste before it’s too late?
SUGAR The word “sugar” comes from the Hindu “sakkara”, which means “sweet, honey-like”. Sugar is white crystalline, we are more accustomed to it than to other types, it is also called sucrose. Glucose is grape sugar, or simply a carbohydrate. It is called a monosaccharide, that is, all other types of sugars contain it. No glucose in the body - no energy. If you overuse sweets, glucose does not have time to be absorbed and begins to be deposited, turning into fat. A person should receive exactly as much glucose as his life requires, that is, energy and physical costs. Fructose is a fruit sugar, the so-called slow sugar. Fructose does not require insulin to be absorbed; it slowly walks through the body without causing additional stress on the liver, kidneys and hormonal system (unlike regular sugar). An obvious disadvantage of the non-aggressive effect of fructose: the body does not understand that it has received some kind of sweetness, and there is no quick surge of energy. A person craves sweets more often than when using regular sugar. The calorie content of fructose is even slightly higher than that of sugar, so it makes no sense to replace sugar with it during diets. Only in terms of usefulness it wins. Brown sugar is unrefined sugar, unrefined molasses crystals, and is more flavorful. It is considered more useful and... fashionable. Thanks to rough processing, trace elements are preserved in it: iron, potassium, calcium, chromium and copper. Unfortunately, research shows that brown sugar contains very little of these elements. And its calorie content is higher than that of white sugar. But unrefined sugar does not spoil the taste of drinks: try adding it to tea or coffee. Lactose (milk sugar) is the main carbohydrate of milk and dairy products. It happens that since childhood a person lacks (or has little of) the enzyme that breaks down lactose, and milk intolerance occurs. Why you can eat fermented milk products if you have lactose deficiency: kefir (and other) grains suppress lactose. If a child still has colic and unstable stools after six months, do not introduce baby milk porridge into the diet. Lactose serves as a nutrient medium for the development of intestinal microflora, including pathogenic ones. BENEFITS Sugar is a valuable source of energy, fast carbohydrates. It immediately enters the bloodstream and does not require digestion in the intestinal tract. A hot drink with sugar can quickly restore your strength. HARM At one time, sugar began to be called “white death”. Sugar really kills, so it is used as a natural preservative: it kills bacteria that cause fermentation. To process sugar you need vitamin B, one of the most valuable vitamins for humans. Wherever you put sugar (in tea, porridge), it begins to “absorb” B vitamins. If this vitamin is not enough, sugar steals it from the body. Therefore, add sugar to food only before consumption: in compotes, porridges or other brews that require sweetening, sugar is added last after turning off. Don't indulge in quick breakfasts that contain sugar. Interesting fact: once a certain company producing instant cereals was prohibited from using the slogan “Eat right!” Classic Sugared Cereal contains 12g of sugar per 30g of cereal. So do the math. Artificial substitutes for Aspartame (nutrasvit, surel) Aspartame is a complex substance. It is not just a genetically modified substance, but also a genetically created chemistry. They write that the company that created aspartame was drowning in endless lawsuits over the loss of consumer health. For example, if soda with aspartame is heated to 30 degrees (in the sun), aspartame breaks down into methanol and phenylalline, and methanol in turn is converted into formaldehyde, a strong carcinogen. During pregnancy, aspartame directly affects the fetus, even if it is consumed in very small doses. Constant consumption of drinks or food additives with aspartame provokes the occurrence of tumors and other diseases from a huge list. You probably noticed the line on the packaging of chewing gum: “contains phenylalanine, the product is contraindicated for those suffering from phenylketonuria.” And they thought - well, I don’t have this phenyl... whatever it’s called. A product labeled as such most likely contains aspartame. And there is nothing good in the daily use of chewing gum or chewing candies containing this substance: the accumulation of harmful substances in the body occurs. In addition to soda and sweets, aspartame can be found in kvass, juices, and toothpaste. A sad fact: aspartame is widely used in baby food: yogurt, curds, etc. Carefully read the ingredients of the product before giving it to your child. The popularity of sugar substitutes grew during wartime. Remember the expression “ersatz sugar” - that’s what it was. Many people use sweeteners (wort) so that fewer calories enter the body. When you drink tea with wort, your body understands that you have eaten something sweet. And it begins to obediently produce insulin to process sugar. But there’s nothing to split. Insulin sadly breaks down the already existing blood sugar, which immediately drops. The gastrointestinal tract, in turn (the body is generally a very smart system), has prepared to receive carbohydrates. But there are no carbohydrates, the wort has zero calories. After this deception, the body decides that it urgently needs to save the owner - the person. So many problems, they say. And when any carbohydrates are received, it produces glucose in triple size, its excess is stored in fat. Being satiated with “empty” calories leads to a constant feeling of hunger: you are deceiving the body, it is crying out. He didn't have enough energy. The use of sweeteners should not be a tradition: consume them occasionally. Not every day. What else is harmful about saccharin, cyclamate, and other chemicals: when used regularly, they disrupt the hormonal balance. Hormones need “live” sugar, not chemicals. These substances are completely alien to the body and do not represent any nutritional value. Natural substitutes Sorbitol Contained in seaweed, rowan, plum, and apple fruits. It is less sweet than sugar, and belongs to alcohols; it is a reduced form of glucose. Sorbitol causes a storm in the intestines; it is better not to use it without indications. Xylitol Extracted from plant materials, such as wood. It is equal in sweetness to sugar. Both substitutes contain the same amount of calories as sugar. A product containing synthetic substitutes cannot be stamped with GOST! If you bought fructose with the TU (technical specifications) designation, put it back on the shelf. “Fructose super plus” or other fructose with an embellished name is most likely flavored with aspartame or another surrogate. Codes for artificial sweeteners: E-951 (aspartame), E-952 (cyclamates), E-954 (saccharin). Natural: E-967 (xylitol), E-420 (sorbitol).
What are the consequences?
A sharp increase in blood sugar levels, as well as a drop in this indicator, can have a detrimental effect on the baby’s health. What are the symptoms of glucose imbalance? When there is a shortage:
- increased activity;
- anxiety;
- desire to eat sweets;
- heavy sweating;
- dizziness;
- pale skin;
- fainting.
All these symptoms disappear instantly if you give the baby something sweet or administer intravenous glucose. These conditions are dangerous because they can degenerate into a hypoglycemic coma, which in turn can lead to the death of the patient.
Symptoms of high blood sugar in a child include:
- weakness;
- headache;
- cold extremities;
- dry mouth;
- extreme thirst;
- itchy skin;
- Digestive problems.
The problem of high or low blood sugar should be treated extremely carefully. Long-term disruption of its level leads to deterioration of brain function. That is why later in the article you will learn how much glucose to give your child, how to give it and in what cases.
Please also note that if the blood sugar test is poor, the doctor is required to conduct a repeat test to eliminate errors in the laboratory. If the result is the same in two analyses, then the likelihood of the test being incorrect disappears. If the blood glucose level is at the lowest or highest level of normal, then additional research is also carried out. Test results can be distorted by anxiety, intense physical exertion, or a recent illness.
Indications for the study
Eggworm test - how to test for a child under one year old
It is advisable to regularly check your child's blood sugar levels, taking tests at least once a year. The following symptoms should be an indication for an unscheduled test:
- the baby is inactive, whiny, and quickly gets tired of playing;
- the child has dry skin and mucous membranes;
- wounds on the body heal slowly;
- pimples and boils constantly appear;
- the child urinates excessively and is often thirsty.

Thirst is a symptom of high glucose
Deviation of sugar levels from the norm can also affect the baby’s vision, which is why the child often squints. Blood glucose should be monitored if you have heart problems, excess weight, injuries, or even colds. These factors can cause your blood sugar to rise.
Glucose for newborns

Now we will examine in detail the questions: can children have glucose, why is it needed and how to give it? As mentioned earlier, pediatricians prescribe glucose to children quite often and for various reasons. Grape sugar is a source of energy for the whole body, which is very easily absorbed even by infants in the first days of life. We list the situations when glucose is prescribed for newborns:
- prematurity;
- problems with breastfeeding (glucose can replace the baby’s nutrition);
- jaundice;
- asphyxia (the child receives food during resuscitation);
- birth injuries of the back and head.
In the latter case, the baby’s nervous system suffers, and glucose is simply necessary for restoration and recovery. It is worth immediately drawing the attention of parents to the fact that the level of sugar concentration in the baby’s blood drops sharply at birth. An hour and a half later, doctors take a blood test to make sure he has been restored. If this does not happen, then the doctor must prescribe glucose.
For newborn babies, a special five percent solution is produced, which is either administered intravenously or added to the diet. We will talk about it in more detail in the next section.
Why are deviations possible?
If the baby is not properly prepared for the tests, the result will be erroneous and may go beyond the limits indicated in the table. When the rules are followed, but a deviation is present, the following factors are considered:
- Glucose levels are affected by the rapid growth rate of the child’s body;
- if there are people with diabetes in the family, then the child’s blood sugar may increase;
- when a baby eats an unbalanced diet, there is a disturbance in carbohydrate metabolism;
- Glucose levels will not meet standards if the child develops obesity;
- an infectious disease suffered the day before or just beginning can distort the results of the analysis;
- if the baby was overly active or cried a lot during several hours of blood sampling, this will also be reflected in the final indicator.
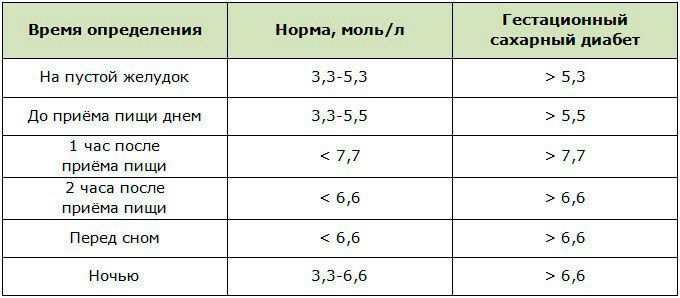
How do sugar levels change?
To understand what kind of pathology is present, the doctor pays attention to where the “arrow deviated”: to a smaller or larger direction.
Low level
Glucose is an important element for cell life. If the study shows a reading below the required level, it is referred to as hypoglycemia. In this case, the following problems can be assumed:
- the child has impaired liver function;
- there were difficulties with the pancreas;
- there is a suspicion of hypothyroidism (malfunction of the thyroid gland);
- At the time of analysis, toxins are present in the body.
Note! A low glucose level may indicate that the child is not eating well and the body is not receiving enough of all the components necessary for development.
Increase in sugar
Having detected excess glucose in the blood above normal levels, diabetes mellitus is first suspected. Here, as in the previous case, the influence of the following factors may also affect:
- development of pancreatitis;
- liver problems;
- endocrine pathologies.
Elevated levels sometimes indicate kidney disease. Even a trivial reason can lead to such an indicator - eating food a few hours before taking tests.
Important! Whatever the test result, before making a final diagnosis, the doctor must refer the child for consultation with specialized specialists: endocrinologist, gastroenterologist, urologist, neurologist, etc.
A child's diet directly affects blood glucose levels. If the diet is unbalanced, the functioning of almost all organs is disrupted. Excess sweets lead to pancreatic dysfunction and cause the development of diabetes.
Glucose deficiency impairs brain function, negatively affecting the mental, mental and physical development of the child. Therefore, it is so important to donate blood for sugar in a timely manner, thereby monitoring the health of your child (regardless of his age).
How to give glucose to a child in the first days of life?

In medical institutions, it is customary to administer glucose solution to a child intravenously, through a tube, or add it to a bottle of baby food. What to do if your baby is prescribed glucose at home? Mothers note that it is quite difficult to give the baby the solution because of its cloying taste.
Use some tips that will make it easier for you and your baby to take the medicine:
- Dilute the solution with water 1:1; the baby will definitely like the sweet water.
- It is worth giving the solution between meals, since after sweet water there is a high probability that the baby will refuse to eat.
- Divide the entire dose into small portions.
- After administration, hold the baby upright to prevent regurgitation.
Video: help with poisoning with Malysheva
Read further:
Surgical instruments. Scalpels, surgical knives and their varieties
How to quickly recover from food poisoning - real tips and tricks
Rehabilitation after a heart attack, prevention of new attacks and care
Is it harmful to consume dairy products?
How to use sodium thiosulfate to cleanse the body?
Article rating:
Share with friends:
You may also be interested in:
How to take lactofiltrum correctly for acne, for weight loss, for a hangover
Maalox for food poisoning for adults and children
Can children and adults drink nimesil if they are poisoned?
How to restore intestinal microflora after poisoning: methods
Jaundice

Jaundice in newborn babies is a fairly common occurrence. Statistics show that every third baby is born with this diagnosis. A yellow tint to the skin and mucous membranes appears as a result of an increase in the level of bilirubin in the blood. This condition appears on the second or third day after the baby is born and lasts no more than ten days.
Pediatricians often prescribe a glucose solution, but it is not able to reduce the level of bilirubin in the blood. The solution prevents intoxication. The best medicine and preventative measure is frequent breastfeeding.
Sugar and allergic reactions in children
Many parents believe that sugar can be an allergen and cause corresponding responses in the baby’s body. However, experts reject this possibility, arguing that allergic reactions in the human body can only be provoked by proteins, and sugar, as is known, is a carbohydrate.
note
Sugar can contribute to an allergy to some other product or aggravate an existing allergic reaction. The fact is that sugar entering the intestines can provoke the processes of fermentation and rotting of those food residues that have not yet had time or are poorly digested. Decomposition products enter the bloodstream, causing allergic reactions.
Factors that contribute to allergic reactions involving sugar:
- Predisposition at the genetic level.
- Excessive consumption of various types of sweets during pregnancy.
- Sweet dishes are included on the baby's menu on a regular basis.
- Immunity suppressing factors from the external environment (poor environmental conditions, living in a harmful environment, adults smoking indoors, etc.).
- Hormonal surges associated with puberty.
- Helminthic infestations and intestinal disorders.
There are two types of allergic reactions:
- Local character. In this case, the baby may develop flaky and itchy pinkish areas on the skin, or intestinal dysfunction may appear, and sometimes symptoms of a respiratory disease may occur. At an early age, children experience such ailments as:
- exudative diathesis;
- neurodermatitis;
- eczema.
- General character. These are the most dangerous allergic manifestations. The baby may suddenly experience swelling of the mucous membranes, which is manifested by difficulty breathing. It should be understood that such a clinic may be a symptom of the development of Quincke's edema. An equally terrible picture is revealed during allergic bronchospasm or an attack of bronchial asthma.
If a child has any allergic reaction after eating food, the “suspected” product should be completely excluded and immediately seek medical help , especially if we are talking about general allergic manifestations associated with difficulty breathing.
Evtushenko Oleg, doctor, medical observer
9, total, today
( 187 votes, average: 4.68 out of 5)
Kishmish: benefits and harm
The most effective foods against stress
Related Posts
Glucose tablets

Why are they prescribed glucose tablets for children? The instructions state that it is needed in the following cases:
- in case of intoxication;
- dehydration;
- collapse;
- shocked;
- hepatitis;
- liver dystrophy, etc.
This drug is produced in blisters of 10 pieces, each tablet contains 50 mg of active substance. The drug also has contraindications, which include: diabetes mellitus, hyperlactic acidemia, heart failure, hyponatremia, cerebral or pulmonary edema.
How to deal with acetone
The main method of treatment for the onset of an acetonemic crisis is proper feeding of the child.
- As soon as you smell a characteristic fruity smell from a child’s mouth, go to the pharmacy and purchase test plates for determining acetone in urine and glucose, in any available form. Possible options are a forty percent solution in ampoules, a 10 or 5 percent solution in bottles, or tablets. A ready-made solution of any concentration can be given a teaspoon every 15-20 minutes; glucose tablets can be dissolved in a small amount of water. If the child does not want to drink a concentrated glucose solution, add a little water. Thanks to the timely supply of glucose, acetonemic vomiting can be prevented.
- If vomiting begins, continue to give glucose, but it is important to prevent dehydration. This task is best accomplished by rehydron (a pharmaceutical powder that is diluted in water) or a homemade rehydration drink: per liter of water, 1 teaspoon of salt, 2 tablespoons of sugar and 0.5 teaspoon of baking soda.
- A decoction of dried fruits is suitable for drinking; it is advisable that it contains more raisins, since they are an excellent source of glucose and potassium. Compote of fresh fruits and frozen berries is also good for feeding a child.
- A weak sweet regular black or green is also suitable, the main thing is that the infusion is not too strong. All tea, like most juices, contain tannins, which can interfere with protein metabolism and complicate rehydration
- It is better not to give herbal teas to a child during an exacerbation, since any herbs have biological activity and can act unpredictably
- Sweet cranberry juice is an excellent drink for a child with acetonemia. In this case, it is better to add sweetness to the drink with sugar or glucose, rather than honey.
Features of use and dosage
If you are going to take glucose in the form of tablets, it is recommended to drink it an hour before meals. In this case, it is necessary to calculate the individual dosage: no more than 300 mg per kilogram of weight. It will be better if the dosage is calculated by the attending physician.
When administered intravenously (drip or jet method), the attending physician must independently calculate the dose based on the child’s weight. It should not exceed these indicators:
- if a child weighs up to 10 kg, then per day he should receive 100 ml for each kilogram of weight;
- if the child’s weight varies from 10 to 20 kg, then per day he needs 1000 milliliters plus 50 milliliters for each kilogram over 10;
- if the child’s weight is more than 20 kg, then 20 ml must be added to 1.5 thousand milliliters for every kilogram of weight over 20 (daily norm).
Store-bought white sugar substitutes. What is better to offer a child?
Most often, granulated sugar obtained from sugar beets and purified through a certain technology to a snow-white color is included in the children's diet. As already mentioned, white sugar is a source of sucrose.
In addition to refined granulated sugar, on store shelves and in pharmacies you can also find products such as:
- Grape sugar (glucose).
- Brown sugar (cane).
- Fructose.
- Artificial sweeteners (sweeteners).

Brown sugar is extracted from sugar cane. It has specific taste, color and unique aroma . Since brown sugar goes through a different degree of purification (practically remains in its original form), it retains a certain set of useful microelements, namely:
- B vitamins;
- minerals: phosphorus, calcium, potassium, iron and magnesium.
Important
This is the only advantage of brown sugar over white. Otherwise, it is the same high-calorie product (about 380 kcal per 100 g of sugar), and, moreover, due to the impurities it contains, it can cause allergic reactions in children.
Fructose is extracted from fruits and berries, and has a number of advantages over white sugar:
- Does not provoke a sharp rise in blood glucose.
- It does not require insulin for its absorption, which means there is no load on the pancreas.
- Fructose is broken down into:
- glucose, which goes to the body’s energy needs;
- glycogen, which accumulates in the liver, and when there is a shortage of carbohydrates, compensates for their deficiency.
- It has a richer sweet taste that is twice as sweet as white sugar.
- When consuming fruit sugar, the risk of developing dental caries is reduced by 25%.
The calorie content of fructose is 399 kcal per 100 g of product.
Important
Fructose is a fairly good alternative to white sugar, but provided that it is used in moderation and inconsistently.
Artificial sweeteners are gaining popularity because they are superior to white sugar in sweetness and have zero calories. As a rule, they are used by manufacturers of such food products as:
- ice cream;
- confectionery;
- candies;
- beverages;
- chewing gum;
- dietary food products.
note
Unnatural sweeteners include: aspartame, sucralose, saccharin, thaumatin, acesulfame, cyclamate.
These substances do not contribute to the production of insulin, and are also excreted from the body in the same form in which they enter it. Therefore, artificial sweeteners are a good option for diabetes, but they are unacceptable for baby food. The fact is that the effect of artificial sweeteners on the child’s body has not yet been well studied, and in some countries their negative effects have been noted, so they are prohibited there.
Overdose

Glucose cannot harm a child if taken correctly. In case of overdose, patients complain of the following symptoms:
- headache;
- excitability;
- insomnia;
- nausea;
- vomiting;
- diarrhea.
You also need to know that with an overdose of glucose with ascorbic acid, gastritis develops and ulcers form on the mucous membranes of the intestines and stomach. In this case, increased levels of oxalate salts, which form kidney stones, can be detected in the urine. Capillary permeability also decreases, which leads to deterioration in tissue nutrition.