Purpose of the visit
The female body experiences enormous stress during childbirth and becomes the most vulnerable. Therefore, every expectant mother is warned about the need to visit a gynecologist after childbirth. A mother's careless attitude towards her health can lead to complications and big problems. Restoring the body after the birth of a child is a very complex process, which without a doubt should be carried out under the supervision of a doctor. This is the only way to detect diseases that can negatively affect the female body’s ability to reproduce and health.
It would seem, why go to the gynecologist after childbirth? After all, everything is behind us, but complications can develop in the postpartum period. The sooner they are detected, the easier the treatment will be.
Features of the first gynecological examination
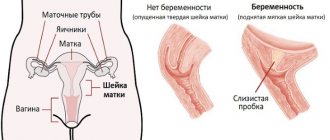
During the first examination after childbirth, the doctor takes a detailed medical history: how the birth went, how postpartum rehabilitation is proceeding, and will conduct a visual gynecological examination.
The time after which a young mother should see a doctor after the birth of her baby depends on the method of birth, postpartum complications and the woman’s well-being.

The first gynecological examination is carried out by the doctor who was in charge of the pregnancy or at your place of residence and usually lasts no more than half an hour
If the child was born naturally , and there was no internal bleeding or tissue ruptures, then the mother needs to see a gynecologist when the lochia (postpartum discharge in the form of blood clots and placental remnants) becomes normal.
Women with a cesarean section should see a doctor within a few days after the baby is born.
To more accurately determine the condition after childbirth, the gynecologist prescribes a cervical smear and other tests. This will make it possible to identify inflammation and prescribe treatment in time and prevent the development of infection.
During the first gynecological examination, the doctor pays special attention to the healing of sutures, the speed of recovery and suppuration
Recovery after childbirth - a gynecologist answers your questions
Number of views: 17,006
The birth of a baby is a serious test for the female body. The baby that is born requires the mother’s attention and strength, and therefore recovery after childbirth must be successful so that the woman can enjoy life and her motherhood. As part of the Hotline “Question and Answer”, gynecologist Alexandra Vitalievna Plotnikova visited MomExpert. She answered questions about modern methods of recovery after childbirth.
Multidisciplinary medical provides services such as:
consultations with specialists for children and adults, home visits by therapists and pediatricians, collection of tests at home, research conducted in our own laboratory.

Question: After childbirth, when sneezing, coughing, etc., spontaneous urination occurs a little, Kegel exercises do not help, what else can be done to cure this ailment? And after childbirth, sexual desire is almost absent due to severe physical fatigue, orgasm does not occur during sexual intercourse, what can be done to make both desire and orgasms appear?
Answer: Your symptoms are most likely directly related to childbirth. Immediately after the birth of the baby, the vagina becomes more voluminous. Over time, when recovery takes place after childbirth, it narrows significantly, but does not reach its original size.
The faster the recovery after childbirth occurs, the more the woman will enjoy intimacy, and regular sex life is important both for well-being and for preserving the family. In this case, the condition of the pelvic floor muscles is very important. Kegel exercises will help keep them in good shape.
These are exercises to improve the tone of the pelvic floor muscles. In everyday life, these muscles are practically not used, and over time they can lose their elasticity and become weak. Deterioration of elasticity and weakening of the pelvic floor muscles leads to a deterioration in sexual life even to various diseases.
How can a woman find the muscles she needs?
If you place a finger in the vagina, the target muscles should contract around the finger, but should not involve the muscles of the abdomen, buttocks or back. Those. if you feel the muscles around your finger tightening, then you are training the right thing. All other muscles at this moment should be relaxed, breathing should remain deep and even.
Kegel exercises are:
- Slow squeezes: Tighten your muscles as you did to stop urination, then slowly count to three and relax.
- Contractions: Tighten and relax the same muscles as quickly as possible.
- Pushing: Push as you would when passing urine or stool.
Where can you do Kegel exercises?
You can practice anywhere: while driving, on a walk, sitting in front of the TV, at the table, in bed.
Training scheme
Start your workout with 10 slow squeezes, contractions, and thrusts. Repeat the exercises 5 times a day. If your muscles get tired quickly, rest for a few seconds and continue the exercises.
After a week, repeat each exercise 15 times. In another week, 20 each. Bring the number of repetitions to 30. Thus, every day you will perform 150 Kegel exercises.
At the beginning of classes, it may be difficult for you to tense your muscles with slow contractions and perform contractions quickly and rhythmically, because the necessary muscles are not yet toned. Over time, the skill will improve. You need to perform exercises at least 3-4 times a week. You can achieve noticeable results after 6-12 weeks of training. When performing these exercises, only the necessary muscles should be involved; you should not squeeze the muscles of the buttocks, abdomen and anal muscles.
Strengthening the pelvic floor muscles helps normalize sex life, cure stress urinary incontinence (spontaneous urination) and sexual dysfunction.
An alternative to Kegel exercises can be vaginal cones. This is a kind of exercise machine, the set of which includes 4 cones of different weights. The woman inserts the cone into the vagina (for easy removal it is equipped with a cord, like a tampon), stands up and tries to keep the object inside. At the same time, just the right muscle group is tensed.
In terms of effectiveness, both methods are approximately the same, but cones give the effect much faster (in about a week), and Kegel exercises - in 6-12 weeks. A set of cones online costs an average of 70 rubles.
You can start exercising with cones after childbirth only when the genital tract has completely healed and there are no infections in the vagina, uterus, or tubes. If you give birth without complications, you can start after about 2 months. At this time, the doctor already allows sexual activity and removes all other restrictions, it is believed that recovery after childbirth has occurred.
At the same time, it is recommended to do Kegel exercises during pregnancy and, in the absence of injuries, you can do them immediately after childbirth.
Another extremely effective method is the Femilift laser correction procedure. This is an effective modern way to get rid of discomfort without surgery. The procedure helps with:
- Urinary incontinence due to stress (sneezing, sudden laughter)
- Atrophy of the mucous membrane and dryness in the vagina
- Initial forms of prolapse of the vaginal walls
- Age-related changes in the vaginal mucosa and labia
- Repeated infections
It has been used by leading clinics in the world since 2009, its effectiveness has been clinically proven. “Kravir” has been practicing it for 3.5 years and has managed to collect its own statistics. It is noted that laser correction is not inferior in effectiveness to surgical plastic surgery of the genital tract.
Three virtually painless twenty-minute treatments spaced one month apart eliminate urinary incontinence and sexual dysfunction. Read more about the procedure at the link and watch the video at the end of the article (time 9.47).
Great news for our mothers - a 30% discount on the Femilift procedure!

Question: What are the modern and safe (for the child) methods of contraception for breastfeeding?
Answer: The methods are the same as for all others with the exception of oral contraceptives. So-called mini-pills were previously recommended, but due to side effects they are no longer prescribed. You can use: a condom, vaginal rings, vaginal caps, spermicides (for dry vaginal mucosa), intrauterine contraceptive device (spiral). To insert the IUD, the gynecologist must assess the condition of the cervix and the absence of contraindications, preferably after the end of the postpartum period (6-8 weeks after birth).
If it is the 2nd or 3rd caesarean section, the issue of surgical sterilization is discussed with the woman before the operation.
Question: What are the pros and cons of the IUD contraceptive method?
Answer: The advantage is that this is a very reliable method of contraception, however, if the IUD is inserted incorrectly and is located in the cervical canal, then pregnancy is possible.
The disadvantages are that the IUD can be a conductor of infection between the vagina and fallopian tubes and, against the background of a banal infection in the vagina, cause a serious inflammatory process in the appendages. There is also a certain risk of ectopic pregnancy.
Question: If there were cervical ruptures in 2 births. What should be done next with her and how soon after birth?
Answer: It all depends on the severity of the tears (sometimes no action is required). What to do will be determined by the gynecologist during a gynecological examination and colposcopy if necessary. Options for surgical correction or radio wave excision (excision) of the cervix are possible. If there is no need for emergency interventions (dysplasia, precancerous conditions), then this is performed no earlier than 2 months after birth, when the postpartum period ends, and if possible, it is not necessary to postpone all measures until the period when the child becomes relatively independent (about a year). will carry it in his arms, since after the operation it is necessary to limit lifting heavy objects.
Question: What is the likelihood of getting pregnant during breastfeeding if you don’t use protection?
Answer: It is impossible to indicate the exact percentage, but there is a possibility. Unfortunately, breastfeeding is not a contraceptive. Even if you think that pregnancy is possible in 1 case in 100, there is no guarantee that you will not be that one case. You don't have to use protection if you're ready for your next baby. However, it should be noted that when breastfeeding there is a possibility of a non-developing pregnancy.
Question: I am 40 years old. They did IVF due to low AMH (anti-Mullerian hormone). At the end of March, my daughter was born, at 40 weeks, natural birth, everything was ok. The dosage of hormones during stimulation is significant. Although at the ultrasound at 12 weeks the gynecologist said that no changes were visible in the ovaries, and that the dosage was chosen very correctly. During pregnancy, many papillomas appeared on my body, not 10 or 20, they appeared every day, on my neck, stomach and chest. After childbirth, they partially fall off, but not all. Tell me, given that this virus causes cervical cancer, am I at risk? Maybe I should consult a specialist, or have more frequent cytology tests, or other tests (markers). What do you recommend?
Answer: Almost all people are carriers of HPV (human papillomavirus). Like all viruses, it can become more active during periods of decreased immunity. This is precisely the reason for the appearance of papillomas during pregnancy. The body of a pregnant woman is in a state of immunosuppression because she is carrying a “foreign body.” To prevent fetal rejection, a natural mechanism of immune suppression is activated. Hence the appearance of papillomas; many pregnant women suffer from thrush for the same reason. After giving birth, the body will return to normal and will be able to suppress the virus itself, but it will not be a bad idea to go to an appointment with an oncologist-dermatologist. To find out whether you have cervical cancer, you need to take a smear for high-carcinogenic risk HPV and oncocytology. If both tests are good, then the next time they can be taken only after 5 years.
Question: Is it necessary to treat cervical erosion after childbirth? If yes, what modern methods can it be cured? It was the first birth. The erosion was there before pregnancy.
Answer: It is impossible to resolve this issue without additional examination. Erosion in the simplest sense is redness on the cervix, but underneath it can hide either a banal congenital ectopia, which goes away on its own, or cervical cancer. Extended pulposcopy will help determine the nature of the redness. Depending on the results of the examination, the procedure for further actions will be clear.
Question: A month ago I had a planned CS, but I am still bleeding. Sometimes it doesn’t, but then it bleeds for two days. Then again there is nothing for a while. Tell me, is this normal? I don't feel any pain.
Answer: After a cesarean section, discharge is normal for up to 6-8 weeks (during the entire postpartum period). This is the norm.

Question: After giving birth, painful sensations appeared during intimacy. (There was a rapid birth, cesarean section. I also have a one-horned small uterus.) What could cause this?
Answer: Painful sensations during sexual intercourse are called dyspareunia. After childbirth it occurs in 45% of cases. It can be psychogenic or organic. Psychogenic is caused by the fear of repetition of the pain experienced during childbirth, fear of repeated ruptures during coitus, fear of unwanted pregnancy. And also organic, which can be caused by inflammation of the mucous membrane of the genital tract, thrush, dry mucous membranes due to altered hormonal levels during lactation. Deep dyspareunia is the location of the uterus in the back, varicose veins of the small pelvis, endometriosis, uterine fibroids, inflammatory diseases of the pelvic organs, adhesions, cystitis, uterine prolapse, incorrectly sized condom, allergy to the condom, intrauterine contraceptive, spermicides, vaginal caps , diaphragms and rings, as well as sexual technique, partner behavior, lack of love and trust. Sometimes the joint work of a psychologist, sexologist, and gynecologist is required.
Question: 2 weeks after giving birth, the discharge became scanty, even every other day. Is this the norm? A month later, rare, insignificant, but bright red discharge appeared. The birth was natural, there were stitches, on the fifth day, according to ultrasound, the clots were removed in a chair. Injected with oxytocin.
Answer: An ultrasound of the pelvic organs and a gynecological examination will help determine whether this is normal or not.
Question about contraception after childbirth: What advice do you have for breastfeeding women?
Answer: The methods are the same as for all others with the exception of oral contraceptives. So-called mini-pills were previously recommended, but due to side effects they are no longer prescribed. You can use: a condom, vaginal rings, vaginal caps, spermicides (for dry vaginal mucosa), intrauterine contraceptive device (spiral). To insert the IUD, the gynecologist must assess the condition of the cervix and the absence of contraindications, preferably after the end of the postpartum period (6-8 weeks after birth). If it is the 2nd or 3rd caesarean section, the issue of surgical sterilization is discussed with the woman before the operation.
Question: I gave birth a year ago, now I am pregnant again. How does this affect the body? I understand that until he has fully recovered, what can you advise during this period for recovery and strengthening? GW ended in the 2nd month after the first birth .
Answer: Stay pregnant and enjoy motherhood. When monitoring your pregnancy, your gynecologist will give you recommendations on correcting iron and calcium deficiency, and taking vitamins according to your test data. Consultation with an endocrinologist and therapist is required for proper management of pregnancy.
Question: The child is already one year and 3 months old, there is still no menstruation, we are breastfed. Tell me how normal/abnormal this is? Any tests may be needed? And tell me how to restore vaginal elasticity (what procedures/surgery are needed)?
Answer: As long as you are breastfeeding, the absence of menstruation is normal. High levels of prolactin during lactation suppress the production of estrogens, which determine the hydration and elasticity of the vaginal mucosa, so when lactation stops, the condition of the vaginal mucosa will significantly improve. If symptoms of insufficient elasticity persist, laser correction (Femilift procedure), PRP therapy (injection of platelet-rich plasma) or injection of fillers with hyaluronic acid into the area under the scar is possible.
Question: What to do with chronic cystitis? How can I help myself if my bladder sometimes becomes inflamed? I am also breastfeeding (child is 1 year 3 months old).
Answer: When breastfeeding, only herbal uroantiseptics are used: phytolysin paste, bear ears, bearberry, canephron. If you have chronic cystitis, you should consult a specialist in the field - a urologist.
Was this information interesting and useful for you? Please share your opinion!
comments powered by HyperComments
Threats of the postpartum period
After the birth of a child, women quite often experience health difficulties, and unpleasant symptoms and complications may appear.

There is no need to put off visiting a gynecologist out of fear. This procedure can indeed be a little painful, but if you refuse treatment, complications will develop into chronic diseases
Gynecological complications
The most common complications after childbirth are those associated with the uterus, as it begins to shrink, taking on its previous shape. As a result, young mothers may experience:
- Endometritis – inflammation of the uterine mucosa
- Subinvolution is a slow contraction of the uterus, the cause of which is labor rupture, undelivered placenta or remnants of the fertilized egg.
To identify and prevent these diseases, a woman needs to undergo a cervical examination after childbirth.
Breast pathologies
After childbirth, women in labor may experience breast pathologies such as:
- Mastitis is an inflammation of the mammary gland that is caused by infection. It manifests itself as swelling, redness and hardening of the breast. Possible swelling, fever and deterioration of general condition
- Lactostasis - appears when milk stagnates in the mammary gland. It can develop into a more dangerous disease - mastitis. To avoid this, constant full pumping and frequent breastfeeding of the baby is required.
- Hypogalactia is insufficient milk production. To increase the amount of milk, you need to feed the baby more often, alternating breasts. You can use special teas to improve lactation. Proper nutrition and daily routine will help with this problem.
- Cracked nipples . They most often appear due to improper attachment to the breast. In addition, cracks can be caused by improper nipple hygiene. Proper feeding should not create any painful sensations.
Urological diseases and gastrointestinal pathologies
The most commonly observed complications are:
- Pyelonephritis is a disease that occurs due to bacterial infection of the kidneys and kidney complications. This is a fairly common problem for women in the postpartum period, since childbirth contributes to the activation of flora in the genitourinary tract
- Hemorrhoids are inflammation and enlargement of the veins around the rectum. During childbirth, a lot of pressure is placed on these vessels, which is why this disease appears.
- Incontinence is a complication that is caused by weakening of the pelvic floor muscles after a difficult birth.
- Constipation is a common occurrence in women in labor with multiple ruptures, as well as after a cesarean section.
Endocrine complications
After the birth of the baby, the mother may face complications of the endocrine system:
- Diseases of the thyroid gland , which quite often appear during the restoration of hormonal levels after childbirth
- An increase in blood sugar levels is a rather dangerous pathology, so in this case special medical supervision is necessary
- Postpartum obesity is a common pathology caused by disruption of the thyroid gland and adrenal glands. Develops within a year after childbirth, characterized by impaired reproductive function with an increase in body weight
Cardiovascular postpartum disorders
After the birth of a child, a cardiologist can detect arterial hypertension and tachycardia in a woman.
Arterial hypertension is a change in blood pressure that manifests itself as a result of postpartum complications.
High blood pressure is difficult to treat and weakens the female body.
Another unpleasant postpartum symptom is tachycardia - a sharp increase in heart rate. Most often appears in women in labor with severe toxicosis.
Mood swings
Childbirth and the postpartum period are a difficult time for a young mother, so they are often accompanied by various changes in the woman’s psyche. During this period, chronic fatigue, depression and emotional breakdowns occur.
Postpartum psychosis and depression are the consequences of complications arising during childbirth, difficult pregnancy and the stress of caring for a baby.
A woman should listen to her body after giving birth to a baby. If your temperature rises, pain appears in the lower abdomen, or other symptoms appear, be sure to consult a doctor.
What affects the number of days until release?
Maternal health
How many days after birth they stay in a medical facility is determined using various factors. First of all, this is the general condition of the woman, the quality and speed of healing of the sutures, the nature of the discharge, the degree of uterine contractions. The doctor examines the female breast to identify cracks or inflammatory processes.
Before discharge, the woman is sent for an ultrasound to determine whether the surface of the uterus is clean and whether there are any postpartum residues.
A general blood and urine test is prescribed. A urine test will show the presence of diseases of the genitourinary system, gestosis, a blood test to detect inflammatory processes and anemia.
These manipulations will make it clear to the gynecologist whether it is time to discharge the woman or whether she should be left for a more complete period of recovery.
Read also: What kind of food can you take and give to mothers in labor at the maternity hospital after giving birth?
For what reasons can a woman be left in a hospital for a longer period:
- Pathology, possible complications after delivery.
- Sutures on the genitals, both external and internal.
- Presence of bleeding. In the case of difficult childbirth, with manual removal of the placenta, for example, large blood losses often occur, and as a result, anemia. Vitamins and iron-containing medications are prescribed to treat this disease, and severe anemia may warrant a blood transfusion.

If inflammatory processes occur, the period for which the woman remains in the hospital becomes uncertain. If antibiotics are prescribed, as in case of inflammation of the uterine cavity, for example, or when the scar is not healing well, discharge is postponed. With gestosis, high blood pressure is observed, and the patient has to be under medical supervision to reduce it.
Health status of the newborn
The health of the baby also influences how many days later they are discharged from the hospital. Caring for the health of a new person should also be careful and attentive, just like taking care of the mother. The neonatologist checks the skin, muscle tone, weight changes, stool and urine. Examinations are prescribed that will help to timely identify dangerous diseases (adrenogenital syndrome, for example, hypothyroidism, galactosemia, etc.) Before being discharged, vaccinations are given, and only after a complete and satisfactory examination is a conclusion made about the possibility of being discharged and sent home.
For what reasons can a newborn stay in the maternity hospital?
- Jaundice. This disease is a common occurrence when there is a conflict between the Rh factors of the baby and his mother. Treatment involves the appointment of a drip and phototherapy. Until complete recovery occurs, the woman remains here.
- Weight loss. The maximum weight a newborn can lose after birth is 8% of what it was initially. If weight is lost in large quantities, an examination is necessary to identify the reasons for this, which will also take some time.
- The baby is premature. If a baby is born before the due date, weight loss is also quite likely; the baby is placed in a special incubator, where he is fully nursed.
- Oxygen starvation of the fetus (hypoxia). Usually observed during childbirth. If there was such a factor, the baby may have nervous system disorders, and very serious ones at that. And he remains in the institution for treatment.
- Infections. Any infection during this period requires treatment with antibiotics and antiviral drugs. It also requires the child to be in the clinic.
Read also: What should I give to a woman in labor at the maternity hospital during her visit and upon discharge?
It's better to stay a little longer than to leave the clinic early.