The fight against such deposits without establishing the exact cause of their occurrence will be ineffective, since It is impossible to eliminate the layers without curing the underlying disease.
For this reason, parents need to become familiar with all possible pathological factors that contribute to the formation of white deposits.
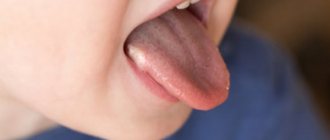
What color should a child's tongue be aged 3-7 years?
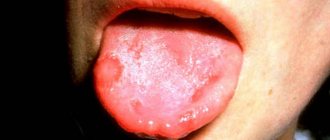
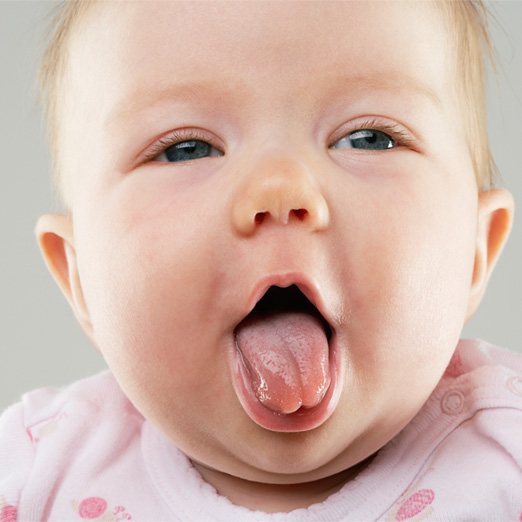
Keep in mind! In normal condition, the child's tongue is moist, moderately shiny and has a pale pink tint.
Sometimes you can notice a thin layer of white coating on the surface of the tongue - it is not accompanied by an unpleasant odor and disappears a few hours after eating or taking a sip of water.
Such deposits can be easily removed with a piece of sterile bandage or a toothbrush.
This phenomenon cannot be called a sign of the presence of a serious disease, which means that the tongue of a healthy child can be either light pink or have a white tint.
Color change as a normal option
White coating on the tongue of a newborn can be found quite often. Many parents panic, believing that these are manifestations of candidiasis. But in fact, the reason lies in the nature of the diet. Due to the immaturity of the digestive system, children are breastfed or bottle-fed for up to 6 months. Since the baby has not yet adapted to regular food, natural cleansing does not occur. In this case, the layers on the tongue are precisely formed from the remains of milk. In addition, the inferiority of the pyloric part of the stomach affects the appearance of frequent regurgitation, which again contributes to the appearance of white plaque.
Eating sweets containing active dyes, fruits, berries, and vegetables can also stain the tongue, but not white, but yellow, burgundy or purple. There is no need to sound the alarm. It is necessary to remember what foods the child ate. If the color of the mucous membrane returns to normal after hygienic procedures, it means that the specific color resulted from exposure to artificial or natural dyes.
Reasons for appearance
Possible provoking factors influencing the formation of strong white deposits on a child’s tongue are:
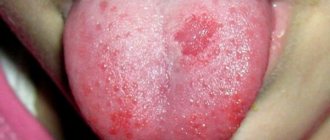
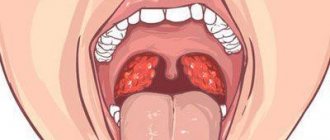
Stomatitis
Why does it appear? An inflammatory disease of the oral mucosa is accompanied not only by the formation of plaque, but also by the appearance of bleeding wounds in the mouth.
There are several types of stomatitis:
- allergic. May be caused by long-term use of medications, consumption of certain foods or drinks;
- bacterial. Occurs when bacteria enter the oral cavity through unwashed hands or fruits, as well as due to poor hygiene;
- herpetic. It appears due to the penetration of the herpes simplex virus into the child’s body;
- fungal. Thrush or candidal stomatitis, which often appears in children aged three years. The causative agent of the pathology is a fungus of the Candida family;
- aphthous. The most common form of stomatitis, which is a complication after suffering from influenza, measles or similar diseases.
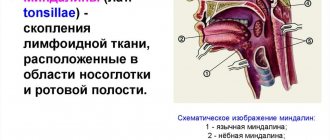
Infectious diseases
Stay up to date! These include adenovirus infection, influenza, scarlet fever, chicken pox and mononucleosis.
They occur with such characteristic symptoms as fever, headache, general weakness and the formation of white deposits on the tongue.
The layers are considered normal and disappear immediately after the child recovers .
Dysbacteriosis
A state of microbial imbalance is most often caused by past infectious diseases and intestinal motility disorders..
Dysbacteriosis appear as a result of poor nutrition or an allergic reaction , accompanied by many unpleasant symptoms, including the formation of plaque on the tongue.
Digestive tract disorders
You should know! Gastrointestinal diseases in children can go unnoticed, since at the initial stage of development they do not have pronounced symptoms and do not bother the child at all.
In this case, white plaque located in certain areas helps to find out about the development of the pathological process. For example:
- deposits on the root of the tongue warn of diseases of the small or large intestine;
- plaque localized in the central part of the tongue indicates problems with the stomach.
Iron-deficiency anemia
The disease develops due to a decrease in iron reserves in the child's body .
Note! This leads to disruption of hemoglobin synthesis and a decrease in the number of red blood cells in the blood.
As a result, the transport of oxygen and carbon dioxide is disrupted .
The body begins to experience oxygen starvation and, as a result,
the baby is bothered by dry mucous membranes, a coating on the tongue and weakness.
Diabetes
The primary signs of chronic metabolic disorders in preschool children are quite difficult to notice .
However, endocrine disease recognized of its development by a decrease in motor activity, the appearance of plaque on the surface of the tongue and an increase in the volume of the abdomen.
Dehydration
For your information! Losing a large amount of fluid during poisoning or not drinking enough water leads to drying out of the oral mucosa.
Without saliva breaking down bacteria, pathogenic microorganisms accumulate on a dry tongue, forming layers of white coating.
Children
often have a “geographical” tongue, characterized by a whitish coating and the appearance of various stripes or spots on the surface .
Such a change in the mucosa does not cause discomfort, but can warn of the presence of pathology.
Prevention of tongue thrush in infants
Do not forget about preventive measures to prevent the formation of candidiasis in the baby’s mouth. It is important to regularly ventilate and humidify the air in the room. Do not forget about the importance of walks in the fresh air, after them the baby’s sleep normalizes and the immune system is strengthened.
If a child is fed artificially, then you need to thoroughly wash all the items necessary for feeding (bottle, pacifier), and even the pacifier. When breastfeeding, it is important for the mother to monitor her health and not eat a lot of sweets, which can provoke active reproduction of the Candida fungus. There is no need to wash or wipe your breasts with antiseptic agents. The Candida fungus is present in the body of every person, and the further development of the infection depends only on the state of immunity.

Frequent washing of the mother's breasts can dry out the skin, resulting in the formation of microcracks, which are the main factor contributing to the appearance of thrush in the baby. If you are not sure about the cause of thrush in your child, consult your doctor for help. A competent pediatrician will prescribe the optimal treatment specifically for your case. If you determine the cause of the white coating on your baby’s tongue in time and complete the prescribed course of treatment, the likelihood of complications will be minimized.
Features of consistency and thickness of plaque
Important! Having noticed a white coating on a child’s tongue, parents should pay attention to the structure and density of the deposits, which may vary depending on the cause of the appearance of the deposits.
- A thin layer of uniform plaque occurs during viral infections;
- A small layer of dry plaque forms during dehydration;
- Thick plaque with a heterogeneous structure is characteristic of stomatitis;
- A wet, dense layer of deposits indicates problems with the digestive tract;
- A thick layer of whitish plaque , under which the main color of the tongue is not visible, indicates the presence of severe chronic diseases.
White coating on the tongue of a baby during breastfeeding
Mother's milk is not as rich as formula, so in the first months the baby may nurse almost every 30 minutes. Due to the constant presence of milk in the mouth, a baby may have a coating on his tongue throughout the day, and this is absolutely normal. Until approximately 3-4 months of life, the baby's salivary glands are underdeveloped and do not produce enough saliva. This is why a white coating forms on the baby’s tongue.

There is no need to clean off such a coating on a baby’s tongue; it does not bother the baby at all and does not cause discomfort, because it is ordinary mother’s milk, which does not have time to be washed off the tongue. When the baby’s condition is normal, he is cheerful, cheerful and actively suckles at the breast - there is no reason to worry.
Associated symptoms
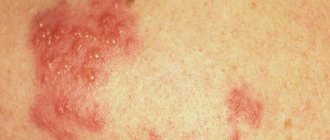
In addition to a white coating on the surface of the tongue, when pathology develops, a child may develop other symptoms that can cause him a lot of inconvenience.
Reference! The following symptoms indicate the need to visit a pediatrician as soon as possible:
- bitter taste in the mouth;
- bad breath;
- fatigue, drowsiness;
- general weakness;
- heartburn or belching;
- nausea;
- swollen lymph nodes;
- excessive sweating;
- pale skin;
- muscle pain;
- redness of the tongue;
- increased body temperature;
- skin rashes;
- a sore throat;
- dry skin and mucous membranes;
- formation of ulcers or wounds in the mouth;
- constant thirst;
- irregular urination;
- change in urine color;
- diarrhea or constipation;
- headache;
- lack of appetite;
- redness of the oral mucosa;
- dark circles in the eye area;
- short sleep;
- passive state.
Causes of yellow coating on a child’s tongue
The appearance of a yellow coating on a baby's tongue can seriously frighten parents. If such plaque lasts for a long time and looks like a thick dense mass, and at the same time a sharp, unpleasant odor is felt from the baby’s mouth, then this is a sign of a serious illness. Do not forget that the tongue is one of the organs of the digestive system, and changes in its color may indicate diseases of the gastrointestinal tract (pancreatitis, hepatitis, colitis, cholecystitis, gastritis).

Pathological changes in the digestive system are accompanied by a decrease in the child’s appetite, stool disturbances, and the baby’s crying (due to abdominal pain). There are other reasons for the appearance of a yellow coating on the tongue in an older child:
- overeating (the child may have eaten too much fatty food, resulting in nausea, dry mouth and a yellow coating on the tongue);
- infectious disease (infection is accompanied by high temperature, which provokes the formation of a yellow-brown coating, you can also notice bleeding wounds on the tongue);
- poisoning (in this case, liver function is disrupted, the body becomes intoxicated and dehydrated, which leads to the appearance of plaque);
- jaundice (the tongue itself and the mucous membranes of the mouth become stained);
- local inflammatory processes in the child’s mouth (caries, sore throat, gingivitis, stomatitis, glossitis);
- somatic diseases (autoimmune processes, diabetes mellitus and kidney disease).
When should you consult a doctor?
Remember! Experts strongly recommend visiting your doctor and undergoing a medical examination in cases where:
- plaque persists throughout the day , and not just in the morning;
- deposits cannot be removed with a toothbrush or a damp bandage;
- In addition to the tongue, plaque forms on the inside of the cheeks ;
- the layers have a thick cheesy consistency.
The appearance of one or more additional symptoms in a child also becomes a signal informing about the need for examination.
Carrying out diagnostics
Keep in mind! The first specialist you need to contact after identifying a tongue coated with a white coating is a pediatrician.
After carefully examining the child’s oral cavity, the doctor will assess the condition of the teeth and gums and check the lymph nodes.
After this,
he will make a diagnosis and prescribe effective medications to eliminate the underlying disease.
If it was not possible to determine the cause of the formation of layers during the examination, the pediatrician will give a referral to an infectious disease specialist, gastroenterologist, endocrinologist or other specialized specialists.
In some cases, doctors prescribe a bacterial culture from the surface of the tongue and a general blood and urine test.
Based on the results of laboratory tests and examination, the small patient will be prescribed suitable treatment.
Treatment
It is worth noting! Treatment is carried out taking into account the cause of the symptom and the individual characteristics of the child’s body.
To eliminate white plaque and underlying pathology, the following are used :
- antibacterial, anti-inflammatory and immunostimulating drugs - for the treatment of infectious diseases;
- antiseptic solutions, regenerating and painkillers - for the treatment of stomatitis;
- antacids, prebiotics and enzyme preparations - to normalize the functioning of the digestive tract.
Note! Many doctors advise cleaning a child’s tongue with a soda solution or herbal infusions.
However, when using such products, you should first make sure that the baby is not allergic to the components included in the medicinal rinses prepared at home.
To avoid the appearance of white plaque, parents of a preschooler should also adhere to the following rules:
- Keep your child's hands clean and teach him proper oral hygiene.
- Make sure your baby does not have a dry throat and regularly give him warm water to drink.
- When identifying various diseases, do not self-medicate , but immediately seek help from a specialist.
- Provide your child with a nutritious diet with enough fresh vegetables and fruits.
- Ventilate the room in which the child is located, and also carry out wet cleaning.
Comparative table describing the color and possible causes of plaque
Below are common shades of deposits on a child’s tongue with a description of possible causes (including indications of specific diseases):
| Plaque color | Causes | Which doctor should I contact? |
| 1. White | Candidiasis of the oral mucosa (thrush), inflammatory processes in the oral cavity (caries, stomatitis, gingivitis, etc.), pathologies of the respiratory systems (colds, flu, bronchitis, acute respiratory infections, tonsillitis and pharyngitis), infectious diseases (scarlet fever, diphtheria, etc. .), dysbacteriosis. | First of all, to a pediatrician or dentist, and then, as necessary (if the doctor refers) to a gastroenterologist or infectious disease specialist. |
| 2. Yellow | Consumption of coloring products (deposits in this case are easily removed with a toothbrush), gastrointestinal disorders (gastritis, pancreatitis, gastric and duodenal ulcers, etc.), diseases of the liver and biliary system, helminthic infestations, infectious diseases and food poisoning (accompanied by nausea , vomiting, diarrhea, high body temperature, etc.). | See a pediatrician, gastroenterologist, hepatologist or endocrinologist (the pediatrician will point you in the right direction). |
| 3. Green | Kidney failure, poor oral hygiene, diseases of the digestive tract, poisoning with low-quality products or medications, fungus in the body, weakened immunity, unbalanced diet, lack of vitamins and microelements, hormonal disorders. | To a pediatrician, pediatric nephrologist, endocrinologist, immunologist. |
| 4. Orange | Gastrointestinal pathologies (gastritis with high acidity, reflux disease, initial stage of ulcer development). | It is necessary to contact a gastroenterologist. |
| 5. Black | Bacterial tonsillitis (accompanied by inflammation of the tonsils, fever, pain when swallowing, weakness), diabetes mellitus, reaction to taking certain antibacterial drugs. | To a pediatrician, ENT specialist, endocrinologist. |
| 6. Brown | Severe diseases of the digestive system, stagnation of bile in the bile ducts, dehydration, lack of B vitamins, taking certain types of antibiotics. | To a gastroenterologist, hepatologist, immunologist. |
| 7. Blue | Stagnation of blood in the body, diseases of the cardiovascular system (arrhythmia, congenital heart disease, etc.), epilepsy. | See a pediatrician, pediatric cardiologist, psychotherapist (if epilepsy is suspected). |
| 8. Gray | Infectious diseases (diphtheria, scarlet fever, etc.), dehydration. | To a pediatrician, infectious disease specialist. If the condition is severe and the body temperature rises, the child may be immediately hospitalized. |
Note! In some cases, different shades of plaque on the tongue may indicate the same disease.
Therefore, it is important to focus on the accompanying symptoms and signs, and also contact a specialist in a timely manner.