Causes
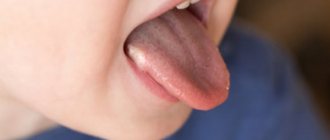
Symptoms of thrush appear in appearance as white milk foam adhering to the mucous membrane of the oral cavity, but they do not come off if rubbed. If you pull off the top film, the skin underneath begins to bleed a little and looks inflamed.
But do not confuse pale skin on the inside of the gums with thrush.
Causes of oral candidiasis in children:
- weakened immunity as a result of prematurity, maternal illnesses at different stages of pregnancy, artificial feeding;
- poor sterilization of bottles, nipples, and utensils for feeding children;
- most infections with a strain of the genus Candida occur during the passage of a child through the birth canal of an unhealthy mother;
- against the background of infectious diseases;
- microflora disturbance after taking antibiotics, dysbacteriosis;
- improper daily hygiene of a newborn.
A favorable condition for the development of fungus is the acidic environment in the baby’s mouth, which forms after each regurgitation.
Treatment
Eliminating white plaque in a child’s mouth will be successful if the cause of thrush is eliminated. If frequent regurgitation is a factor in the appearance of the fungus, changing feeding techniques or sterilizing utensils can correct the situation. If a small area of the mucous membrane is affected by the fungus, treatment consists of local treatment of the affected areas and elimination of discomfort in the baby. Therapy for severe forms of candidiasis involves taking antimycotic and iron-containing agents. Treatment should continue for the entire course prescribed by the doctor.
When not to worry
A white coating on the tongue and mucous membranes of the mouth does not always indicate the development of a disease such as thrush.
It is necessary to examine the baby's oral cavity before and after each feeding. Do not panic if a whitish, thin coating appears on the tongue after eating fermented milk and milk mixtures. Give your child a tablespoon of boiled water or soak cotton wool in water and let him suck, this will wash his mouth of the remnants of dairy products.
After regurgitation, a cheesy coating may appear, this is milk that has already begun to be digested in the baby’s stomach. It does not cause discomfort and can be easily removed with a damp sterile cloth.
In the first year of a child’s life, such physiological phenomena are considered normal and should not cause concern to parents.
Why plaque appears in the mouth of infants
If a white coating appears on the tongue of an infant, you need to assess his general health. If your baby is active, eating well and gaining weight, there is nothing to worry about. The non-standard color of a newborn's tongue may be due to breastfeeding. To wash off the remaining milk from the baby’s oral mucosa, you need to let him drink 2-3 tablespoons of chilled boiled water.
White lumps in the mouth of a healthy baby may appear due to regurgitation after feeding. In addition, the tongue may turn white before teething.
Under no circumstances should plaque be scraped off the tongue, as there is a high probability of injury to its mucous membrane.
Overheating according to Komarovsky
According to the famous pediatrician Komarovsky, plaque in the mouth of a baby up to a year old can appear due to overheating of the body. To eliminate the symptom, you need to undress the baby and wipe his body with gauze soaked in cool water.
To prevent overheating of the baby's body, the living space should be ventilated. You cannot use heaters or store carpets or other dust collectors in the apartment. You can purchase a standard humidifier, but even if you have one, you need to wet clean the nursery at least once a day.
Inflammatory process
Plaque on the tongue in children aged from a month to 1 year can be caused by many inflammatory diseases that require drug treatment. If there are auxiliary symptoms indicating inflammation, you should contact your pediatrician. Only he will be able to conduct an otolaryngological examination of the baby, appropriate laboratory diagnostics and identify the causative agent of the disease.
Signs of thrush
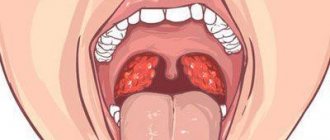
The main symptom of oral candidiasis in a newborn is white cheesy deposits on the mucous membrane of the cheeks and gums. On the palate they are initially located pointwise, in the form of small grains, then merge into large spots, which are easily removed by scraping.
During this period, the child often burps, becomes irritable and whiny, sleep patterns are disturbed, and there is a refusal to eat.
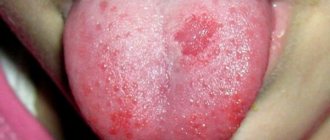
When an infection occurs in the mucous membrane of the tongue, swelling and hyperemia occurs. The baby has difficulty eating, and it becomes difficult and painful for him to suck. Older children complain of dry mouth and a burning sensation; eating food, especially hot food, is accompanied by severe pain.
If treatment is not started in time, the plaque thickens, acquires an unpleasant odor and a gray color. When you try to remove it, the mucous membrane is injured and begins to bleed. All these symptoms are accompanied by increased body temperature and general malaise, severe pain in the oral cavity.
Oral candidiasis can progress to a chronic stage, which requires long-term treatment, and in severe cases, hospitalization of the patient in a hospital.
Unpleasant consequences can be a disruption of the intestinal microflora, a decrease in the body's immune defense and the development of allergic reactions to foreign substances.
Causes of morning plaque in the mouth
A white coating on a child’s tongue that occurs in the morning does not require treatment, since its formation is caused by natural physiological processes. The salivary glands work in a gentle mode at night, which means they produce less saliva, which performs a protective function. As a result, various microorganisms are activated in the oral cavity. And plaque is just a product of their vital activity. It is easily removed during standard hygiene procedures and does not appear in the afternoon.
A morning coating on the tongue may mean that a teenager smokes. In this case, complex treatment is indicated, including giving up a bad habit, detoxification therapy and restoring the body’s water balance.
Clarifying the diagnosis
A change in the color of plaque in the mouth can signal symptoms of diseases of the internal organs and the development of inflammatory processes.
To diagnose this disease, the attending physician prescribes a number of laboratory measures:
- a visual examination of the oral cavity is performed to assess its condition;
- a clinical detailed blood test is prescribed to determine the inflammatory process based on the results of the leukogram;
- To make an accurate diagnosis, a microflora culture from the oral cavity is performed to determine the type of fungal strain;
- antibiogram – establishes the sensitivity of pathogens to therapeutic drugs and bacteriophages;
- The coprogram allows you to detect a yeast-like fungus in a child’s stool.
To clarify the diagnosis, the doctor may prescribe additional blood tests to detect the bacterium Helicobacter pylori and cytology of the contents of plaque on the mucous membranes of the mouth.
Read how suction cup dentures work. How much do suction cup dentures cost? More details here.
Treatment of thrush in children using medicines and folk remedies
Previously, thrush in an infant was not treated with drugs; all antifungal agents were designed for later life. Now, if necessary, drugs for systemic action are prescribed. Diflucan or Fluconazole helps.
Having the form of a powder, they dissolve in water or milk and are given to the baby from a spoon. The first dose should be calculated as 6 mg per unit of weight. 1 serving of medicine per day is enough. On day 2, the dosage is halved. The course of treatment is 3-5 days. A systemic effect on the cause of plaque allows you to quickly deal with it.
The prerogative of treating oral thrush belongs to local remedies. They dissolve in water, after which a sterile swab or cotton ball is moistened in the solution. With a quick movement, mom treats the mucous membrane of the cheeks, gums and tongue. To make processing more convenient, you can wrap a gauze swab or cotton wool around your finger.
For this purpose the following is used:
- Nystatin, powdered;
- Kanesten;
- Clotrimazole;
- Levorin.
The frequency of the procedure is 3-6 times daily, after meals. From birth, Miconaz gel is approved for treating the mucous membrane, an effective remedy in the fight against fungal flora.
An effective way to cope with the manifestations of oral thrush is to treat with a soda solution.
For 200 ml. boiled chilled water, use 1 tsp. powder. A new solution is prepared daily. Plaque can also be removed with a weak solution of hydrogen peroxide or potassium permanganate.
Other traditional medicine that can neutralize fungus in the mouth is a decoction:
- chamomile;
- calendula;
- St. John's wort.
They have an analgesic, sedative, and antiseptic effect. To prepare the decoction, take 1 tbsp. dried herbs of the desired type, pour cold water, bring to a boil in a water bath, filter after 5 minutes, cool. In the absence of an allergic reaction to the components of the solution, you can use it 5-6 times every day.
Features of treatment and symptom relief
After all diagnostic examinations have been carried out and the etiology of the disease has been determined, the attending physician prescribes a course of medication. Correctly prescribed therapeutic drugs improve the baby’s condition already on the first day of their use.
Despite the disappearance of the symptoms of the disease, treatment must be completed in full to avoid relapse after vaccination or previous illnesses.
Popular drugs in the fight against oral thrush in children are listed in the table.
| A drug | pharmachologic effect |
| Candide | Broad-spectrum antifungal agent, imidazole derivative. The solution is completely safe for newborns; the glycerin in its composition gives it a sweet taste. It is used according to the following scheme: 10 drops are applied to a cotton swab and distributed evenly throughout the mucous membrane of the mouth. The course of treatment is 10 days. |
| Diflucan | There are no age restrictions for use, but give this medicine to newborns under the strict supervision of a pediatrician. The convenient form of release in the form of a suspension is suitable for any age. The dose for a single dose is calculated from the ratio of 3 mg of active substance per 1 kg of child’s body weight. The frequency of administration is 1 time per day, the course of treatment is 3 days. |
| Retinol | Widely used as a means of accelerating the healing of wounds and ulcers of the mucous membranes in various diseases. Eliminates dryness and irritation. After eating, treat the oral cavity with a cotton swab soaked in a solution of vitamin A. |
| Nystatin | Available in the form of ointments, tablets, a very convenient form in the form of drops for treating children under one year of age. Nystatin is a very good remedy in the fight against thrush and stomatitis in children, but is rarely prescribed, as it has a large list of contraindications and side effects. |
| 1% sodium bicarbonate solution | The solution is prepared in the following ratio: 1 glass of boiled water at room temperature and 1 teaspoon of baking soda, mix well. Using a sterile cloth soaked in solution, the inside of the cheeks, gums, and tongue are treated. |
In combination with the use of medications, it is necessary to treat pacifiers, rattles, and all objects and surfaces with which the child comes into contact with a soda solution several times a day. Sterilize bottles, nipples and utensils.
Preventive measures
In order to protect your child from the appearance of white plaque in the mouth, as well as to prevent the development of related ailments, it is advisable:
- Wash pacifiers, bottles, and all kitchen utensils used for cooking and feeding (as well as pour boiling water over them and carry out antiseptic treatment).
- Keep all toys and other objects that the baby comes into contact with clean and systematically treat with safe antiseptics.
- Strictly follow the rules of hygiene (in particular, take care of the cleanliness of your hands and the whole body).
- When breastfeeding: before each feeding and after it ends, treat the breast with a soda solution. The frequency of feedings should also be increased, since the regular supply of mother's milk, which is characterized by a rich composition, has a positive effect on the state of the immune and other systems of the child's body. Breastfeed your baby for as long as possible, since no formula can compare with mother’s milk in composition and beneficial properties. After feeding, as well as after burping, give the baby some water to remove any remaining milk from the mouth.
Carry out periodic examinations of your child's mouth. The oral cavity of infants requires special attention, the condition of which must be regularly monitored. According to statistics, children under six months of age with fragile immunity are at high risk.
If pathological symptoms are detected in the mother, you need to consult a doctor who will organize therapeutic measures. This will prevent the child from becoming infected.
The appearance of spots of white or another shade in a child’s mouth is not a reason to panic. When contacting a medical specialist and organized therapy, the detected symptoms and causes are successfully eliminated.
Adults need to be vigilant
It is quite difficult to recognize the development of thrush at the initial stage, since it manifests itself in the form of barely noticeable whitish dots. It can be localized both in individual areas of the mucous membrane and throughout the entire oral cavity.
The development of the inflammatory process is signaled by redness and thickening of white plaques; when trying to remove plaque from them, slight bleeding begins.
If parents are not vigilant and miss the development of the disease at the very beginning, thrush can become severe.
Spread to the larynx and throat area. In infants, this stage very often manifests itself in the form of cracks in the corner of the mouth, candidiasis. They are accompanied by an increase in body temperature to 39 degrees, moodiness and refusal to eat.
The main difference between milk residues and pathological plaque is that milk disappears after a short period of time, but thrush remains.
Recurrence of candidiasis in children of the first year of life can occur repeatedly, even after a full course of drug treatment. During this period of the baby’s life, parents should be especially vigilant and attentive to avoid complications.
What is the danger of the disease
Delayed initiation of treatment for candidiasis can progress to a chronic stage and provoke allergic reactions and decreased immunity.
White plaque in the mouth is not only a sign of thrush, but also a signal about the onset of the following inflammatory processes in the body:
- stomatitis;
- gastrointestinal diseases: gastritis, enterocolitis, duodenitis;
- acute respiratory infections, acute respiratory viral infections, influenza;
- diphtheria;
- whooping cough;
- scarlet fever;
- leptotrichosis.
There are often cases when candidiasis affects other organs. It poses the greatest danger to premature babies with low weight and an immature immune system, causing severe complications that can be fatal.
Treatment of gastrointestinal diseases
White spots in a child's mouth can be caused by problems with the digestive tract. Then the first point of treatment should be diet.

For an infant receiving only milk, nutritional recommendations are related to the mother's diet. She should exclude aggressive foods, with a lot of spices, salty and spicy foods. All these components enter the milk and damage the mucous membrane of the child’s sensitive digestive tract.
If he is older than 2 years and has already switched to a common table, then his diet should consist of warm food, ground as much as possible, so as not to injure the inflamed elements.
Children's diet rules:
- The child should chew as little as possible, since with stomatitis these functions are impaired.
- Avoid spicy, fried, smoked, salty, sour foods (to prevent pain).
- Ban carbonated water, processed foods and fast food.
If the cause of the appearance of white spots in the mouth is a gastrointestinal disease, then measures must be taken to eliminate the main factor. The reasons for the appearance of processes are often associated with congenital factors and underdevelopment of structures.
The most common situation is regurgitation, when the remains of milk or formula fall back into the oral cavity, which becomes a favorable environment for the proliferation of microflora. Disorders often go away on their own as the body and internal organs grow. Gastritis, enterocolitis, and dysbacteriosis appear in school-age children. They are caused by irregular nutrition and aggressive food intake.
For the treatment of older children, the following are used:
- enveloping agents;
- painkillers;
- antispasmodics.
At the discretion of the doctor, the following drugs are prescribed:
- Almagel;
- No-shpa;
- Omeprazole;
- Smecta;
- Activated carbon.
In addition to etiological treatment, the doctor prescribes symptomatic treatment to alleviate the patient’s condition.