Treatment of ARVI during lactation is a process that should be carried out under the supervision of a doctor. It involves both the use of medications approved for nursing and folk remedies. There is no need to interrupt breastfeeding.
Absolutely all people are susceptible to acute respiratory viral infections at any time of the year. The main rule for a nursing mother is not to panic, but to take timely measures so that she can recover faster and not infect the baby.
It is promptly necessary to begin treatment for ARVI during breastfeeding if the first symptoms of the disease appear:
- temperature rise to more than 37 °C;
- nasal congestion, runny nose;
- cough and sneezing;
- sore or sore throat;
- muscle aches;
- feeling of weakness and fatigue, lethargy.
Proper treatment using medications approved for nursing mothers will help overcome the disease within a week.
Is it possible to continue breastfeeding if a woman has a cold? In the past, most doctors advised isolating the sick mother from the baby during the acute course of the disease and avoiding breastfeeding during this time. Today, doctors have come to a consensus: breastfeeding during ARVI in the mother is not only allowed, but also necessary for the baby.
The opinion of pediatricians is based on two arguments:
- Weaning from the mother's breast during illness helps to reduce the child's immunity, so breast milk will bring much more benefits than the potential harm of a cold.
- Before the first signs of the disease appeared, the virus had already been in the mother’s body for some time. By the time they appear, the pathogens, along with antibodies, have already entered the child’s body through breast milk. In this case, if the baby gets sick, mother’s milk will contribute to a speedy recovery and a milder course of the disease. And if you don’t get sick, it will only strengthen your immune system.
It is necessary to treat a cold immediately after the first symptoms appear. To achieve this, pharmaceutical companies offer many effective medications that are compatible with breastfeeding and have a minimum of side effects and components harmful to the baby's health. You shouldn’t discount traditional methods either.
The main rule of treatment during lactation is to consult a doctor. Only a doctor can prescribe the treatment that is most effective for a nursing woman and safe for the baby.
What medications are most often prescribed by doctors, and what can a nursing mother take for ARVI without fear of harming the baby:
- antiviral drugs that are approved for pregnant and lactating women are Grippferon, Aflubin and Oscillococcinum. If necessary, they are used in the treatment of ARVI in children under three years of age;
- remedies for the treatment of runny nose. It is permissible to use salt water solutions of Aquamaris or Salin. Some pediatricians prescribe drops with antimicrobial effects Pinosol. When breastfeeding, Xymelin or Otrivin are often prescribed;
- cough medicines - Lazolvan and Ambroxol. It is allowed to drink syrups based on medicinal herbs;
- The safest antipyretic medications for acute respiratory viral infections while breastfeeding are those that contain paracetamol. Children's antipyretic syrups Panadol or Nurofen are also used;
- for sore throat, topical drugs with an antimicrobial effect are prescribed: Miramistin, Ingalipt and Iodinol;
- Antibiotics are prescribed in extreme cases. There are no absolutely safe antibiotics, so they should be used only under the supervision of doctors and according to their recommendations.
Along with medications, traditional medicine is often used, but only as an aid to traditional treatment. Some tips on how to treat a nursing mother with ARVI using folk remedies:
- tea with lemon and honey, sea buckthorn or raspberries;
- aromatherapy using essential oils: eucalyptus, rosemary, fir;
- inhalations using boiled potatoes, chamomile or calendula infusions;
- gargling with water, baking soda and salt;
- warming the chest with boiled potatoes;
- drinking radish juice diluted with honey.
There are many alternative medicines, but you should always consult a doctor first, since many of them cause allergic reactions in the child.
According to Dr. Komarovsky, treatment of ARVI in a nursing mother should begin at the first signs of infection. The pediatrician advises dressing warmly, drinking plenty of warm liquids, ensuring cool, moist air enters the room, and drip saline solutions into the nose more often. It is clear: you should not stop breastfeeding, but it is necessary to take precautions when interacting with your baby.
How to protect your baby from illness and continue lactation:
- Use a four-layer gauze dressing, which must be changed every 2-3 hours.
- Wash your hands regularly and treat them with antiseptics.
- Ventilate the room frequently for 15 minutes and do wet cleaning.
- If possible, communicate less with the baby (besides feeding time), because ARVI is transmitted not through breast milk, but by airborne droplets.
Remember: you should not self-medicate - any type of acute respiratory disease can lead to complications, and the baby needs a healthy mother.
One of the pressing questions from the moment the child is born is the following: if the mother gets sick while breastfeeding, will the baby get sick? Difficulties arise when the food supply is based on guards. You need to take into account all the nuances in advance in order to think through a feeding plan for a newborn or treatment.

The painful condition does not depend on the time of year
If mom is sick
You can suddenly get sick at any time of the year. Nursing mothers who have established lactation are susceptible to colds. The reason is that the respiratory system works with increased loads, which go towards milk production. As a result, the immune system weakens and infections enter the body faster.
The main question in the event of a negative development of events is whether a newborn child can become infected with ARVI from his mother while breastfeeding. Modern research and WHO recommendations indicate the need to preserve this method of feeding infants.
Important! In 90% of cases, you will not have to limit contact with your child. There is no need to boil milk or other disinfection methods.
There are a number of situations in which it will be necessary to temporarily or permanently abandon the guard and switch to formula nutrition. The need for weaning is determined by the type or severity of the disease.
Important! You should stop breastfeeding completely (switch to formula) only after consulting a pediatrician.
If the mother of a newborn baby is sick, she also needs to undergo examination. Diseases incompatible with gw:
- infectious in an acute form (toxic substances from microorganisms can get into the milk);
- purulent mastitis;
- recovery period after surgery (effects of anesthesia, taking medications, antibiotics).
It is possible to partially retain breast milk nutrition. If your doctor allows, you should pump frequently. It is recommended to repeat the procedure every 3-4 hours to prevent stagnation of fluid in the chest. In some cases, this is not done to ensure that the newborn is fed, but to eliminate side effects or reduce future milk production. After the mother has fully recovered, the baby in 90% of cases can return to the usual way of eating.
If the cause of the development of the disease was not an infection or a dangerous viral type of pathogen, then you can continue breastfeeding during the period when the mother is feeling unwell. When a cold strikes during breastfeeding, how not to infect the baby is the first question that arises. A common acute respiratory infection will not cause harm, so to prevent the child from becoming infected, it is enough to use a medical mask.
90% of viruses and bacteria are transmitted by airborne droplets or after contact. In order to minimize the likelihood that a newborn baby will get sick (infected), it is recommended, in addition to using a gauze mask, to ventilate the room.
Wet cleaning and the use of disposable items for hygiene procedures also help keep the baby healthy and continue to feed him milk. It is also necessary to wash your hands thoroughly before interacting with the toddler. Lactation can be continued if the treatment program does not use antibiotics or other drugs that are unsafe for the baby.
Important! It is recommended to agree with your pediatrician on the optimal feeding schedule, as the schedule may shift slightly.
In what cases should lactation be stopped?
Is it possible to feed a child with the flu if the mother’s health is very bad? There are cases in which you should stop breastfeeding:
- at a temperature of more than 40 degrees;
- if a complication occurs;
- when the body is dehydrated;
- if the disease does not subside within a week.
We also advise: How many days does it take for the flu to appear after infection?
Be sure to consult your doctor . Some forms of influenza require hospital treatment. In such a situation, feeding a child is quite dangerous, since lactation creates additional stress on the female body.
List of treatment rules
In order to reduce infection to zero, it is recommended to follow a few simple rules:
- organize the treatment process in such a way that a certain amount of time passes between taking the medication and direct contact with the baby (in most cases, the maximum concentration of the drug in the blood is recorded 1.5-2 hours after administration);
- Feeding intervals should be increased to 4-5 hours (formula or age-appropriate complementary foods are used for supplementary feeding);
- during the period when the main phase of treatment takes place, the mother should carefully monitor the child’s condition;
- Natural feeding should be stopped if the baby reacts negatively: rash, itching or swelling appears.
If treatment involves taking antibiotics, then for this period it will be necessary to switch the child to formula. You need to continue expressing milk. To improve the microflora, the pediatrician may prescribe a course of probiotics for the child.
If a woman manages to catch a cold 3-6 months after the start of feeding (mature stage of lactation), there is no need to abruptly stop the feeding process. After consulting with your doctor, you will be able to choose the optimal schedule. The reason is that the mother may experience stress, as a result of which the milk will disappear partially or completely.
Important! A woman should not independently refuse medications prescribed for treatment, as this action can lead to various complications.

Ventilation reduces the number of bacteria in the air
After the consultation, it will be clear whether the mother gets sick while breastfeeding or whether the baby will get sick. In most cases, a common cold or runny nose does not harm the health of the newborn. There are drugs that are approved for use without restrictions during breastfeeding, but their inclusion in the recovery program must be carried out by a doctor. If a cold occurs while breastfeeding, a specialist decides how to recover and treat it.
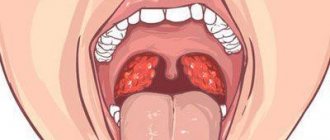
A nursing mother has a sore throat
This situation, when a nursing mother has a sore throat, occurs quite often, but not every woman knows what to do.
Let's take a closer look at this situation and talk about the principles of treating sore throat during breastfeeding. What should you do if a nursing mother has a sore throat?
First of all, it must be said that taking any kind of medication during this period must be agreed with a doctor. The thing is that most drugs, or rather their components, can partially pass into breast milk, which has a negative effect on the baby’s health.
In view of the fact described above, mothers often ask doctors whether it is even possible to breastfeed if they have a sore throat. It is worth remembering that such a violation in no case can be a contraindication for breastfeeding.
As for the treatment itself, perhaps the only possible option may be rinsing the mouth.
What can be used to treat pain in breastfeeding women?
Having answered the question as to whether a mother can breastfeed her child if she has a sore throat, we will list the main remedies that can be used for treatment.
The safest, and also effective, remedy in such a situation is a saline solution. In order to prepare it, it is better to take sea salt (if you don’t have it, table salt will do), which is taken at the rate of 1 teaspoon per 100 ml of boiled water. For a greater antiseptic effect, you can add 1-2 drops of iodine. Rinse with this solution every 2 hours. In this case, it is necessary to use up the entire prepared solution in one session.
You can also use baking soda as a rinse, which only takes 1/2 teaspoon per 100 ml of water.
When talking about how you can treat a nursing mother’s throat when it hurts badly, we cannot fail to mention antiseptic solutions. The most common is furatsilin. You can buy ready-made, or you can make it yourself. It is enough to crush 2 tablets of the drug and then pour the powder into a glass of warm water, then stir until completely dissolved. Rinsing is also carried out every 2 hours.
ARVI during breastfeeding
You need to know in advance what to do if a nursing mother falls ill not with a common cold, but with an acute respiratory viral infection. In this situation, the body contains pathogens that can penetrate into the milk. Contact will be contagious for the child when the mother does not follow the rules:
- be sure to use a medical mask;
- mother of the hand;
- carry out wet cleaning and ventilation daily.
If the temperature rises, it is recommended to pump; most of the time, relatives (father, grandmother) should take care of the baby.
Attention! If antibiotics are not taken, breastfeeding can continue.

It is necessary to wash your hands when you have a cold
In the treatment of ARVI in nursing women, the following drugs are used: Viferon, Grippferon. The course of treatment, dosage and duration are determined based on the results of a medical examination.
The answer to the question whether it is possible to infect a child with a cold directly through breast milk is negative in 90% of cases. The child will not become infected from the mother through contact if she carries out the treatment process correctly and follows the doctor’s instructions. A sick woman is advised to remain in bed to avoid additional or repeated colds or complications. To prevent breast pain when breastfeeding is stopped completely or partially, regular pumping is carried out.
How to avoid infecting your baby with a sore throat
If a nursing mother has a sore throat, there is a high risk that the baby may contract an infection. To avoid infecting the baby, a woman needs to follow simple rules:
· Be sure to feed your baby breast milk, as it contains immunoglobulins that help protect against diseases.
·Be sure to wash your hands with soap before feeding.
· During feeding, use a four-layer gauze bandage. After each use it must be replaced with a clean one.
· Ventilate the room frequently, regardless of the weather and time of year. While the child is being ventilated, take him to another room.
· Do regular wet cleaning of the premises.
· To reduce the possible risk of infection for your baby, make garlic beads. Peel the garlic, divide into cloves and thread on a thread. Place the beads near the baby's crib. Or you can place an onion cut into pieces in the room. Onions and garlic are natural phytoncides that help prevent the spread of viruses.
· To stimulate the immune system, the pediatrician may recommend dripping Gipferon or Interferon into the nose.
Video
Coronavirus is the most discussed topic of the beginning of 2020. In February, the pathogen was named COVID-19. Breastfeeding mothers all over the world are in panic. What if I catch the virus and infect my child? Is it possible to breastfeed during coronavirus? What if infection is not proven, but there was contact with a carrier? What is worse - exposing the child to the risk of contact with infection or quitting breastfeeding and leaving him without immune protection? Doctors don't have a clear opinion yet. So far there are no recommendations from the Russian Ministry of Health. But the World Health Organization (WHO) gave its recommendations on breastfeeding for COVID-19.
What it is
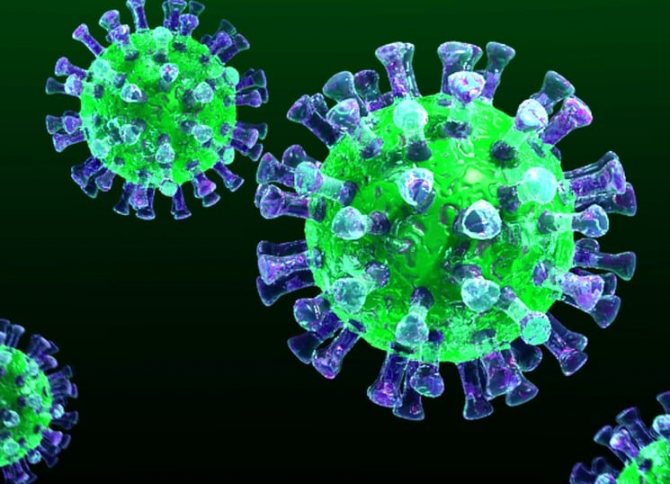
Coronavirus is a viral infection. It spreads across the planet with lightning speed and affects almost all corners of the globe. In some regions there are more infected people, in others there are fewer. However, COVID-19's speed of spread and serious complications quickly caused panic among people.
On January 30, 2020, the World Health Organization at a meeting of the Emergency Committee recognized the current situation as extremely dangerous and assigned it international significance.
On March 11, 2020, it was announced that the outbreak was becoming a pandemic (the spread of the disease on a global scale). And Europe became the center of the pandemic.
Coronavirus is not the bubonic plague. In many ways, the severity of the current situation is exaggerated due to the scale and speed of spread, as well as insufficient awareness of the pathogen.
COVID-19 is a virus of the Coronaviridae family. Until December 2019, 39 strains of the virus were known. COVID-19 has become the fortieth. The virus contains RNA, one of three macromolecules that are present in almost all living organisms. The infectious agent received its name because of its special structure. If you look at the virus under magnification under a microscope, you will see spiny processes on it.
Visually they look like a crown. The peculiarity of the virus is that it successfully imitates molecules to which cellular receptors respond. Upon penetration into the body of a person or animal, it causes catarrhal manifestations, like most viral infections. Complications include viral pneumonia, respiratory distress syndrome, respiratory failure, and may culminate in death.