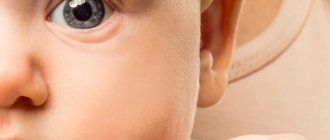
The immunity of a newly born child is in the process of development. Up to 3 months, the baby is protected by antibodies received from the mother, and only after this age does his body begin to produce its own immunoglobulins. That is why the baby is susceptible to various infectious diseases. One of them is conjunctivitis in newborns. It leads to eye discharge and other symptoms. But the fact that a baby’s eyes are festering may indicate other ophthalmological pathologies.
More articles related to your question
- Hip dysplasia in newborns: causes, symptoms, treatment
- Damage to the central nervous system of newborns: causes, severity and rehabilitation
- The baby arches his back: physiological and pathological reasons
- Using ACC during breastfeeding: doctors’ recommendations on how to take it correctly without harm to the baby
- Sab Simplex - first aid for colic in newborns
- What to do if your baby is choking
Causes
The eyes of a newborn have the same structure as those of an adult, but some of their functions are still undeveloped. For example, in the first weeks there is no lysozyme in the tear fluid, an enzyme that has antibacterial activity and is designed to protect the mucous membrane from the penetration of microbial agents. In addition, not all babies are born with a formed nasolacrimal duct, which is necessary to cleanse the conjunctiva of impurities.
These anatomical features lead to the fact that infants are predisposed to ophthalmic inflammation. Parents may notice that the baby's eyes are watery or purulent discharge appears: a white-yellow liquid of a sticky consistency appears in the corners, which dries quickly and can cause the eyelids to stick together.
A possible reason is the baby’s reaction to albucid, an antibiotic that is used to treat the eyes of children in maternity hospitals to prevent infection. In this case, the discharge will be minimal. No treatment is required, but it is important to provide proper care for the eyes.
There are also pathological reasons for a newborn’s eye to fester. The main ones:
- conjunctivitis;
- dacryocystitis;
- blenorrhea.
Only a doctor can accurately identify the cause of ophthalmological disorders. Parents should definitely consult a pediatrician or pediatric ophthalmologist to prescribe treatment.
Types of eye discharge
Red dots around the eyes of a child - possible causes of the rash
Eye discharge in an infant may be normal or indicate pathology.
What kind of discharge is normal?
The first tears begin to appear at 1.5-2 months, in some cases at 4. They are needed to protect the eyes from pathogenic organisms and moisturize the mucous membranes.

Newborn baby's eyes water
Almost every person, when waking up, can see dried tears in the corners of their eyes. Normally, the channel easily allows water to pass through it. If this does not happen, then tears accumulate and cease to protect against pathogens. On the contrary, a favorable environment is created for their development. As a result, the eyes turn red and may rot.
Therefore, the presence of tears is a normal condition, provided that they have somewhere to drain. If the baby is only a few days old, then normally a twentieth of children have a plug in the nasolacrimal canal, which dissolves on its own after a few days. If this does not happen, this is a reason to see a doctor.
Also, newborn babies normally produce mucin, a special substance that is necessary to prevent dry eyes.
What does mucus mean after sleep?
Mucin is a mucous liquid. Considering that newborns sleep almost all the time, the remnants of this substance accumulate around the eyes. This is normal, but parents must practice good hygiene to prevent infections.
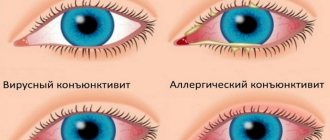
Conjunctivitis
Conjunctivitis is an inflammatory process affecting the mucous membrane of one or both eyes. Its symptoms:
- redness of the conjunctiva and eyelids;
- itching;
- lacrimation;
- discharge of pus;
- gluing eyelids and eyelashes.
In severe cases, conjunctivitis in infants may be accompanied by general weakness and fever. Inflammation can be non-infectious or infectious.
Non-infectious inflammation
The cause of non-infectious conjunctivitis is exposure to various irritants in the eyes: dust, small debris, aerosols, allergens (pollen, animal hair, particles of household chemicals). This causes swelling of the mucous membrane, redness and severe itching.
If a baby's eye is watering, but there is no pus, then most likely it is a non-infectious inflammation. In this situation, it is necessary to eliminate the irritant and take care of cleansing the eyes. As a rule, no other treatment is required. In case of severe allergies, the doctor may recommend antihistamines (Fenistil, Zyrtec).
Infectious conjunctivitis
Infectious conjunctivitis is caused by a variety of bacteria - staphylococci, streptococci, gonococci, chlamydia and others. Often, infection occurs during childbirth from the mother or in the hospital due to violation of sanitary standards by medical personnel. A feature of bacterial conjunctivitis is profuse discharge of a yellow or grayish color that makes it difficult to open the eyelids. Usually, one eye of a baby first festers, but then the infection gets into the second one.
Other possible causative agents of the disease are viruses. In this case, there are symptoms of ARVI - runny nose, fever, cough. Such conjunctivitis should be suspected if the eye is very watery, but the discharge is clear.
Non-infectious or viral inflammation can be joined by bacterial inflammation if the child has not been provided with proper care.
Treatment of purulent discharge from the eye
It is better to treat suppuration in the eyes of children after consultation with a doctor, especially for children under one year old. The specialist will determine the cause of the discharge, taking into account the individual characteristics of the child.
The occurrence of purulent processes in the spring can be facilitated by an allergic reaction; treatment in this case will be antihistamines.
Eye infections can be cured using special antiseptic ointments. Only massage will help get rid of canal blockage.
To treat conjunctivitis, the doctor may prescribe the following medications:
- Acyclovir tablets . Kill viral infections caused by herpes. Used to treat children over 2 years of age. Recommended 200 mg 5 times a day for 5 days. There are side effects in case of overdose such as nausea, vomiting, and headaches.
- Alcohol solution of chloramphenicol . Used for bacterial conjunctivitis. Designed for children from 1 year. Take 2-3 drops 1-2 times a day. May cause allergies.
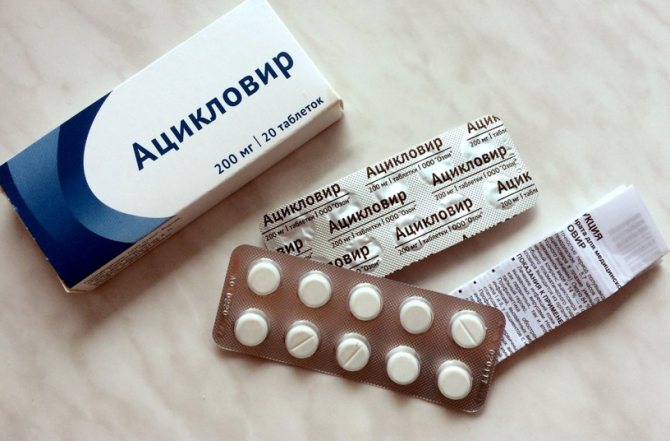
Acyclovir tablets for pus from the eyes
How to relieve inflammation from the eyes
Eye drops are prescribed to relieve inflammation They are divided into antibacterial and antiviral. They also have antihistamine and analgesic properties. Among the most famous:
- Tobrex . Antibiotic for children from 1 year. Dosage – 1 drop 5 times a day for 1 week. Overdose leads to kidney disease and muscle paralysis.
- Phloxal . Drops with antibacterial action. Prescribe 1 drop every 6 hours for 2 weeks.
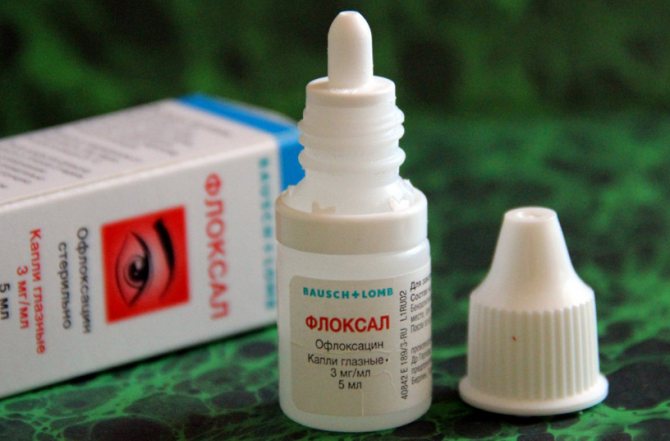
This is what Floxal drops look like
Treatment of infections
Topical ointments are also effective in combating eye infections
- Florenal . Kills viruses that cause the disease. The ointment is applied to the inside of the eyelid 2 times a day. Application can last up to 1-2 months depending on the severity of the disease. Do not use for children with sensitivity to the components of the ointment.
- Tetracycline ointment . An antibiotic used to treat children over 8 years of age. Apply under the lower eyelid 3-5 times a day. Use for up to 1 month. The ointment is contraindicated for diseases of the blood, liver and kidneys.
When the tear duct is blocked, only a special massage can help. During the massage, the film is removed from the eye and the pus is removed. The doctor must show the technique to the parents or carry out the procedure himself.

Tetracycline ointment
Dacryocystitis
Dacryocystitis is inflammation of the lacrimal sac. The disease occurs in 5-7% of children. In newborns, it occurs due to blockage of the lacrimal canaliculus with dried vernix lubrication or remnants of fetal tissue. In older children, dacryocystitis can develop against the background of an acute respiratory viral infection or an ENT disease due to swelling or obstruction of the nasolacrimal canal. In any case, the tear fluid stagnates in the bag, and pathogenic flora - bacteria, viruses or fungi - multiply in it.
Symptoms of dacryocystitis:
- lacrimation;
- redness, soreness, swelling of the mucous membrane and skin near the inner corner of the eye;
- reduction of the palpebral fissure;
- swelling, redness or blueness of the eyelids;
- discharge of pus and mucus from the lacrimal openings when pressed.
As a rule, one eye becomes inflamed. The baby may experience symptoms of general intoxication - fever, weakness, headache.
Causes and symptoms of the disease
If pus flows from the eyes and green snot from the nose, the condition indicates a bacterial infection. A change in the color of nasal discharge occurs as a result of the death of pathogenic microbes and leukocytes. The shade of the secreted secretion can be different, from yellow to brown. The brighter the color, the more pathogenic bacteria have entered the body.
Acute rhinitis in children occurs in several stages. Each stage is characterized by certain symptoms:
- At the beginning of the disease, there is no snot. There is dryness in the nasal cavity, burning, tingling. The child sneezes frequently. A rise in temperature and weakness in the body may occur.
- At the second stage of the disease, nasal congestion increases. The mucous membrane swells, copious, clear discharge is observed, breathing through the nose is impaired, and a cough may occur.
- At the third stage of inflammation development, viscous snot of a purulent nature is observed. If the infection penetrates the nasolacrimal duct, conjunctivitis develops.

Conjunctivitis can be caused by both viruses and bacteria. The disease is accompanied by yellow, brown or even greenish suppuration:
- Viral conjunctivitis is more common in newborns. In adult children, it may be the result of decreased immunity or a severe cold. Body temperature rises, tears flow from the eyes. The child is bothered by a feeling of pain in the eyes and photophobia. The eyelids become swollen, red and inflamed. Lymph nodes may become enlarged.
- Bacterial conjunctivitis affects both eyes. The child develops green snot and festering eyes. After sleep, the eyelashes stick together and yellowish, dry crusts form.
See also
Is it possible to treat teeth with a runny nose and cold?
Read
Adenoviral disease often begins with pain and discomfort in the throat. At the same time, coughing appears and nasal discharge is bothersome. The snot is initially mucous in nature, and then acquires a yellow-brown or greenish tint. When the infection spreads, the eyes fester.
A baby's eyes may become watery as a result of a disease such as dacryocystitis. Inflammation of the lacrimal sac often occurs against the background of acute rhinitis. Initially, a severe runny nose appears, and only then lacrimation, pain and swelling of the inner corner of the eye occurs, and purulent fluid is released when pressure is applied.
Another reason that a child has green snot is an allergy. Dust, animal hair, plant pollen, chemicals, and food can act as irritants. The eyelids turn red and swell, there is lacrimation, the nose is very stuffy, itching, burning, the snot is initially clear. If the eyes begin to fester, and the color of the mucus in the nose has changed, the condition indicates the addition of a bacterial infection.
Less commonly, the appearance of rhinitis and conjunctivitis is caused by herpes. Small blisters appear around the eyes and nose. When the blisters begin to burst, fluid flows into the eyes, causing purulent discharge.
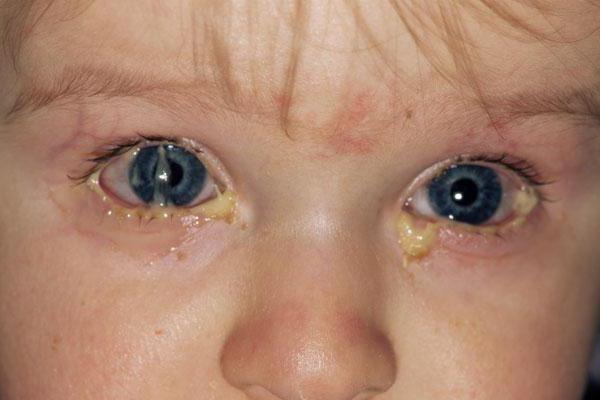
Blennorea
Blennorea is a purulent acute inflammation of the conjunctiva, which is most often provoked by gonococcus. Infection of a child occurs in utero or during natural childbirth from a mother with gonorrhea. Symptoms appear on days 2-3 and increase gradually:
- swelling of the mucous membrane;
- thickening and swelling of the eyelids;
- sanguineous, later - copious purulent secretion from the eyes;
- in severe cases - conjunctival ulcers.
One eye is affected, but the infection can also spread to the other. Without treatment, blenorrhea can lead to blindness.
Directions of treatment
First aid
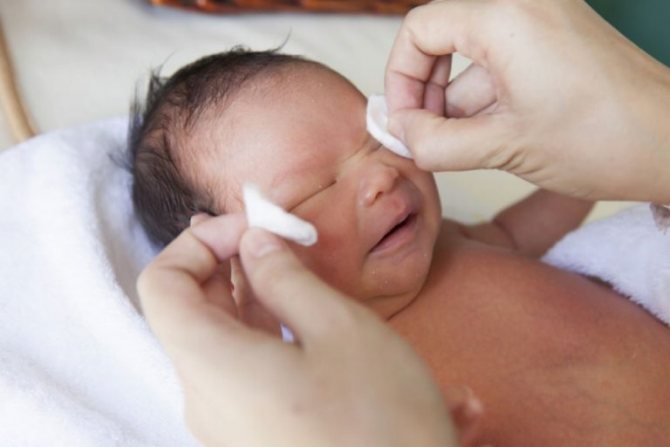
When a newborn’s eyes fester, you should definitely consult a doctor. But parents can provide first aid. It consists of removing pus and washing the mucous membrane with solutions with antiseptic and anti-inflammatory properties. It is important to treat both eyes to prevent the infection from spreading.
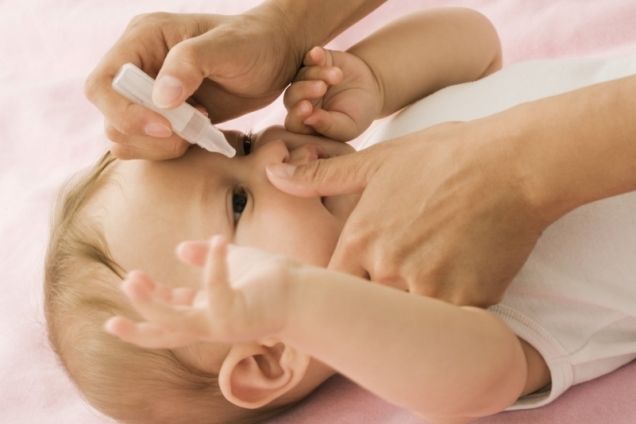

Solutions options:
- From plants - chamomile, calendula or black tea. Pour 1-1.5 tablespoons of raw material with a glass of boiling water. Leave for 1 hour. Filter.
- From furatsilin. Dissolve 1 tablet in 100 ml of boiling water. Cool.
- From Miramistin. Dilute the solution with water in a 50/50 ratio.
Processing algorithm:
- Make sure the solution temperature is close to body temperature.
- Soak a cotton pad or piece of bandage in the liquid.
- Rub the eye from the outer corner to the inner.
- Take a clean disk and repeat all manipulations with the second eye.
You should wash your eyes every 2 hours. It is advisable to prepare the cleaning solution before use.
There is an opinion that in a situation where a newborn’s eye begins to fester, breast milk should be instilled into it. This cannot be done. Despite all the benefits of milk, it is a favorable environment for the growth of bacteria and can increase inflammation and discomfort.
If allergic conjunctivitis is suspected, it is necessary to exclude the child from contact with a possible irritant: remove plants, soft toys, carpets from his room, and keep animals away. Frequent wet cleaning and regular ventilation are necessary. The same measures are appropriate for any inflammation.
Relieving inflammation
To effectively treat sour eyes, it is necessary to determine the causative agent of the disease. The most accurate method is bacterial culture of secretions from the lacrimal canals. But often doctors focus on external signs.
If the inflammation is caused by a virus, then drops with an antiviral effect are prescribed: Actipol, Poludan, Trifluridine. In addition, ophthalmic ointments can be used - oxolinic, Tebrofenovaya, Bonafton. In mild cases, it is enough to wash the eyes with antiseptic solutions and instill drugs with interferon, for example, Ophthalmoferon.
For bacterial inflammation, local antibacterial drugs are necessary. The most popular eye drops for newborns are Albucid. In addition, chloramphenicol (0.25%), gentamicin (0.3%), ciloxan (0.3%), tsifran (0.3%) and other antibiotics in the form of drops are used. Ointments can be prescribed - tetracycline, chloramphenicol. Systemic antibiotics in the form of tablets or injections in infancy are used only in severe cases, for example, with blennorrhea.
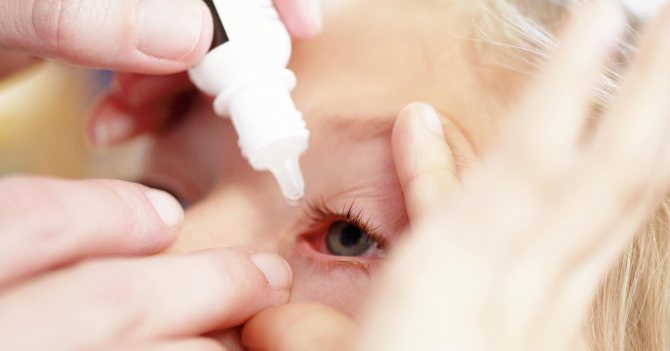
General treatment plan:
- Lay the baby horizontally without a pillow. Wash his eyes with an antiseptic solution.
- Warm the bottle with drops in your hands.
- Pull back the lower eyelid and drop the required amount of medicine using a pipette with a rounded end. It's good if someone holds the child's head.
- Remove excess drug with a clean napkin.
Usually the medicine needs to be injected into the conjunctival sac 3-4 times a day. The ointment is applied 1-2 times. To do this, move back the lower eyelid and squeeze a thin strip onto its inner surface.
Features of treatment for dacryocystitis
With dacryocystitis, it is important not only to destroy the pathogenic flora, but also to eliminate the cause of the disease - blockage of the duct. The easiest way is to massage the tear duct. Parents can conduct it themselves after training. It involves stroking movements with the thumb from the outer edge of the eyebrow, along its line, near the bridge of the nose, to the wings of the nose and in the opposite direction. Manipulations should be carried out with light pressure, but so that the child does not hurt. Frequency – 6-8 times a day.
If the massage does not lead to the removal of the “plug,” then the child is placed in a hospital and the lacrimal canal is cleaned (bougienage) under local anesthesia using a catheter. The procedure is painless. You should not refuse it, since without eliminating the blockage of the duct, attacks of dacryocystitis will be repeated, and adhesions will gradually form in the canal.
Festering eyes in a small child is a condition that requires urgent attention to a doctor. Its most common causes are conjunctivitis, dacryocystitis and blenorrhea. Parents can help their baby on their own by washing the eyes with herbal or medicinal solutions with an antiseptic effect. Only a doctor can prescribe a full range of treatment. As a rule, therapy lasts 7-10 days, after which the child fully recovers. The main measures to prevent infection are washing the eyes twice a day with boiled water or chamomile solution, as well as observing the rules of hygiene for adults.
Treatment
The first defense against red eyes is to rinse with special drops specifically designed for such conditions. It is recommended to use drops with a balanced pH, similar to tears. These include, for example, Floxal drops, recommended for use from 1 year.
Children are most often prescribed drops with extracts of medicinal herbs (for example, chamomile solution), which provide hydration, protection, and soothing of the mucous membrane. They need to be instilled several times a day, most often every 3 hours.
The next option, what to do if your eyes fester, is rinsing with sterile boron water. It is important to observe the rules of personal hygiene, washing hands not only before using the product, but also after the procedure. Parents should ensure that separate towels and other items that come into contact with the eyes of a sick child are used.
Important! When using colored lenses, contact lenses, or glasses, treatment begins with their thorough cleaning.
If redness and inflammation do not disappear after a few days, despite therapy, visit an ophthalmologist, who will determine exactly why the child has discomfort and prescribe a suitable remedy. The decision on how to treat and how to treat redness and other symptoms is made based on the diagnostic results.