Types of conjunctivitis in children
Conjunctivitis of various etiologies is among the most common ailments in children.
In this article
- Types of conjunctivitis in children
- Allergic conjunctivitis
- Bacterial conjunctivitis
- Dacryocystitis
- Treatment of bacterial conjunctivitis in infants under one year of age
- Treatment of viral conjunctivitis in children
- Prevention of childhood conjunctivitis
The causative agents of the disease spread through household contact and airborne droplets, and infants in the first year of life still have very weak immunity and are not able to sufficiently resist infections. Viral infection can occur when visiting a public place, from parents, while bacteria from dirty hands easily enter the mucous membrane of the eyes. Depending on the cause that caused the development of conjunctivitis in a child under one year old, several types are distinguished.
- Allergic. Eye inflammation develops when the conjunctiva is irritated by various substances. At this age, this most often occurs, for example, when introducing a new type of food. Allergies can also occur to medications, hygiene products, and insect bites.
- Bacterial. The most common type of conjunctivitis in children, which they often become infected with from a sick mother during childbirth (blennorrhea of newborns, chlamydial conjunctivitis), as well as when various microorganisms get into the eyes.
- Viral. It is provoked by various microorganisms, in particular adenoviruses, enteroviruses, etc.
- Dacryocystitis. Occurs due to obstruction of the lacrimal canaliculus. This eye pathology can be treated quite successfully with timely measures taken.
A common symptom for all types of eye inflammation is redness and swelling of the inner lining of the eyelid, but each of them also has its own characteristics. Let's look at the causes and symptoms of various types of conjunctivitis, as well as dacryocystitis in babies under one year old.
Types and forms of conjunctivitis in children
Viral conjunctivitis
The disease develops under the influence of viruses and is often acute. The symptoms are not very pronounced, but even a young mother will not have difficulty recognizing them.
The baby experiences profuse lacrimation and itching - the child constantly scratches his eyes, sometimes to such an extent that there is a feeling of severe burning and fogging. Copious clear mucus discharges from the eyes.

Bacterial conjunctivitis
The disease is most often a complication of the progression of infections caused by pathogens. This type of infection often occurs in conjunction with otitis media and requires the use of topical antibiotics.
Depending on the type of pathogen, the main forms of bacterial conjunctivitis are distinguished:
- staphylococcal;
- Haemophilus influenzae (caused by Haemophilus influenzae);
- streptococcal;
- pneumococcal;
- gonococcal;
- Pseudomonas aeruginosa, etc.
All forms of bacterial conjunctivitis are accompanied by the appearance of characteristic signs that differ from the clinical picture of viral eye damage, for example:
- sticking of eyelids and eyelashes in the morning, when the child just wakes up (sometimes you have to moisten your eyes generously to “unstick” the eyelids);
- the appearance of a yellow dry crust;
- discharge of pus.
Allergic conjunctivitis
It occurs as a reaction to external irritants (allergens), as a result of which histamine begins to be produced. It is this substance that provokes redness and swelling of the eyelids, as well as attacks of severe itching - the main signs of allergic conjunctivitis.
Treatment of allergic conjunctivitis begins with identifying the factors that provoked the disease and eliminating them.
Adenoviral conjunctivitis
The organs of vision and the epithelium of the nasal cavity are closely related to each other, therefore, with ARVI, the damage also affects the mucous membrane of the eyes.
In this case, conjunctivitis is a complication of the underlying disease and is accompanied by all the main symptoms of respiratory infections: fever, nasal congestion, runny nose, sore throat, etc.
This form of the disease is called adenoviral conjunctivitis and is treated using complex therapy aimed at destroying viruses and eliminating symptoms.
Allergic conjunctivitis
For very young children this phenomenon is quite rare. Typically, allergic inflammation can occur as a reaction to a new product in the diet or to an inappropriate medicine. With an allergy, profuse lacrimation appears, the eyes become red and swollen, the baby begins to worry and rub them. In case of an acute reaction of the body, Quincke's edema, urticaria and other complications may occur. For the treatment of allergic conjunctivitis, children under one year of age are prescribed drops that relieve swelling and irritation, for example, Vizin, as well as antihistamines Allergodil, Alezastin, Olopatadine. They help reduce the symptoms of the disease.
Allergic conjunctivitis photo
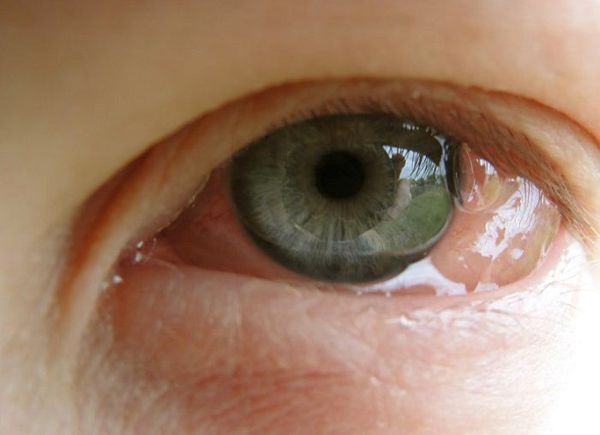
Allergic conjunctivitis is the most common subtype of non-infectious conjunctivitis and is caused by an allergen such as pollen, dust, or animal dander.
If you have conjunctivitis, do not touch your eyes with your hands; it is important to follow the rules of personal hygiene and wash your hands thoroughly. Contact other people as little as possible to avoid infecting them.
Viral conjunctivitis
This disease develops when various viruses enter the body:
- adenoviruses;
- herpes simplex viruses;
- Coxsackie viruses;
- enteroviruses, etc.
Quite often, conjunctivitis occurs against the background of colds - ARVI and influenza. Viral diseases spread very quickly through airborne droplets. Parents should be especially careful during periods of mass epidemics of these diseases and should not visit public places with their children unless absolutely necessary. Here are the symptoms of conjunctivitis in children under one year old that may indicate this disease:
- redness and swelling of the conjunctiva;
- irritation and itching in the eyes, the baby constantly rubs them and shows anxiety;
- profuse lacrimation;
- negative reaction to light;
- enlarged lymph nodes near the ears.

External signs of viral inflammation are quite similar to the manifestations of allergic conjunctivitis. If such symptoms appear, you should promptly visit a doctor or call him at home. Only after diagnosis will the ophthalmologist be able to find out the true cause of the disease and prescribe the necessary treatment. For the treatment of conjunctivitis in children under one year of age, anti-inflammatory drops and ointments approved for use at this age are prescribed. Independent choice of medications can negatively affect the child’s health.
Viral conjunctivitis in a child: symptoms
After the virus enters the child’s body, the following signs of the disease occur:
- lacrimation, swelling and hyperemia of the eyelids;
- feeling of “sand” in the eyes, pain, dryness, negative reaction to bright light;
- weakness and lethargy in the muscles;
- deterioration of sleep and appetite.
If a child has such signs, you should promptly visit a pediatrician or call him to your home for an examination. Advanced conjunctivitis can be treated within 2-3 months, but this greatly interferes with a full life.
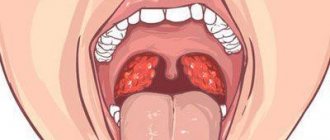
Bacterial conjunctivitis
It develops when pathogenic bacteria enter the body: gonococci, staphylococci, chlamydia, etc. The main symptom of bacterial conjunctivitis is purulent discharge from the eyes, while with allergic and viral inflammation it is clear or mucous. The pus often causes the baby's eyelashes to stick together, especially after sleep. With some forms of bacterial infection, such as chlamydia, the lymph nodes may become enlarged. If you do not promptly treat bacterial conjunctivitis in a child, it can become chronic, and then it will take a lot of time for a complete recovery. In addition, untimely treatment can lead to severe ulceration of the cornea and even loss of vision. To eliminate the symptoms of purulent inflammation, drops and ointments with antibiotics are used - they are prescribed by a doctor in accordance with the age of the child. In addition, it is necessary to wash the eyes several times a day with some antiseptic solution to mechanically remove the pus.
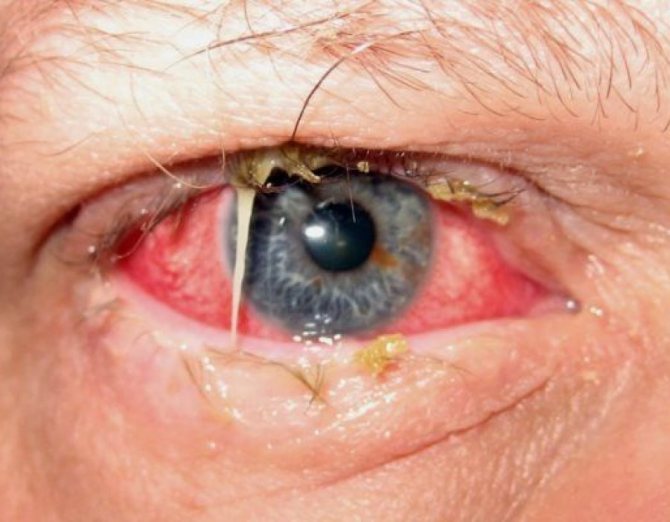
Bacterial conjunctivitis photo
Bacterial conjunctivitis is redness of the eye caused by infection with bacteria such as Staphylococcus aureus and streptococcal pneumonia, or, less commonly, the bacteria chlamydia (which causes chlamydial conjunctivitis) and gonorrhea (which causes gonococcal conjunctivitis), which are sexually transmitted infections (STIs).
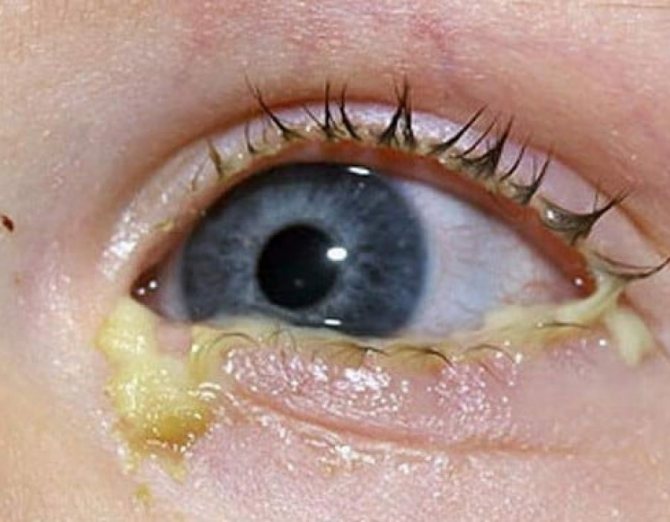
Bacterial conjunctivitis in a child in the photo. Symptoms: redness of the sclera and eyelids, discharge of pus or mucous pus, slight sticking of the eyelids after sleep due to this purulent discharge, burning sensation in the eyes.
The main symptoms of bacterial conjunctivitis include:
- Redness of the eyes
- Burning, itching, roughness, mild pain or discomfort in the eye
- Thick, sticky discharge from the eyes
- Swollen or red eyelids
Many cases of mild bacterial conjunctivitis resolve without treatment within a week. Cleaning your eyes throughout the day with water and a clean cloth or sterile pad, and using lubricating eye drops, also known as artificial tears, can help relieve symptoms. However, antibiotic eye drops or ointments may be recommended, especially in more severe cases of bacterial conjunctivitis.
It is important to remember that conjunctivitis is, as a rule, a disease of dirty hands . Do not touch your eyes without washing your hands with soap.
Typically, people make a full recovery and the condition does not cause any complications. However, if bacterial conjunctivitis occurs in newborns or people with weakened immune systems, such as those who have HIV or are being treated for cancer, it can be very serious and you should seek immediate medical attention.
Additionally, anyone experiencing severe symptoms should seek medical attention immediately. These include:
- Severe eye pain
- Severe redness of the eyes
- Inability to open an eye
- Severe sensitivity to light
- Blurred vision that persists after the discharge is removed
- Additionally, if symptoms are mild but persist for a long time, you should also seek medical help.
Conjunctivitis can affect people of any age, but is more common in children than adults.
Bacterial conjunctivitis is caused by bacteria, which means it can be transmitted from person to person. Be sure to wash your hands after contact with a sick person.
Dacryocystitis
A common disease among children in the first year of life. Its signs appear 6-10 days after birth. If treatment is not treated in time, dacryocystitis can progress to the chronic stage. The cause of this eye pathology is the obstruction of tears through the lacrimal canal, which is clogged with pieces of embryonic tissue. Microorganisms accumulate there, and as a result, purulent inflammation of the eyes develops. Based on its external symptoms, dacryocystitis can be confused with bacterial conjunctivitis, but additional means must also be used to eliminate it. Thus, an important point in the treatment of dacryocystitis is massage of the lacrimal sac, located at the inner edge of the palpebral fissure. It is necessary to remove accumulated pus. This massage is best done after feeding the baby during the day. Place your index finger near the inner corner of the eye and move it towards the baby's nose with a slight but gentle force. It is necessary to make approximately 6-10 such movements. In this case, pus should come out of the lacrimal sac - confirmation that the massage is being carried out correctly. After its completion, you need to rinse the eyes with antiseptic solutions, and then introduce antibiotic drops. These procedures need to be repeated for two weeks - usually during this time it is possible to clean the canal; it is important to do this regularly. If massage does not help, mechanical cleaning of the tubule is prescribed.

Features of disease prevention in childhood
Babies have an increased risk of contracting conjunctivitis because they are just learning to observe basic rules of personal hygiene. However, parents are recommended to study the following nuances and monitor their observance in everyday life:
- If the baby shows the first signs of the disease, then he should not be sent to school or kindergarten. It is recommended to immediately consult a pediatrician. At the first stage, it is much easier to eliminate the causes of the disease, because it takes so much time.
- If one of your relatives has conjunctivitis, he must be isolated in a separate room. The rule must be followed until the symptoms disappear completely.
- A child from an early age must be taught to use personal hygiene products. The rule must be followed in relation to towels. A person should have three types of them: for hands, face and body. Of these, only the first type can be general; all others must be strictly for personal use.
- Parents should constantly tell their child that rubbing their eyes with dirty hands is strictly prohibited. This should especially not be done after walking on the street or communicating with other children.
- In infants, the spread of conjunctivitis of various forms is diagnosed. In the period from 2 to 4 days after birth, the disease manifests itself in case of infection with gonococcus. When infected with chlamydia, the symptoms are bright and characteristic for the period from 5 to 14 days. Herpes does not appear until a few weeks after birth.

At the time of birth, the risk of infection of the child as it moves through the birth canal increases. As a preventive measure, a woman is recommended to undergo a full examination, which allows even hidden genital infections to be squeezed out. It is best to get tested at the stage of pregnancy planning, in which case you will be able to insure your baby against a large number of dangerous diseases.
Treatment of bacterial conjunctivitis in infants under one year of age
For each type of pathology, their own medications are used. To diagnose the causative agent of the disease, the doctor takes a smear from the conjunctival cavity and then determines its sensitivity to various antibiotics. Only after this does he prescribe antibacterial drugs for the eyes.
"Albucid"
The most common eye drops for children of any age, starting from birth, which effectively eliminate the symptoms of the disease. They contain sulfonamide, an active antimicrobial substance. "Albucid" is also used to treat blenorrhea and purulent ulcers.
"Tobrex"
The active ingredient is tobramycin. This is a strong antibiotic that suppresses protein synthesis in the cells of microorganisms, disrupting their active functioning. Copes with most pathogens of bacterial conjunctivitis. Adverse reactions such as allergies and urinary disorders are possible. In case of such phenomena, you should consult a doctor to change the medicine.
"Vigamox"
The active ingredient is moxifloxacin 0.5%, which belongs to the fluoroquinolones and has an extended bactericidal effect. If there is severe discharge of pus, you can use an additional antibacterial ointment, for example, Erythromycin 1%. It has proven its effectiveness in forms of the disease that are difficult to treat (fungal, gonococcal, diphtheria and others). The ointment should be used after administering all the drops three times a day for 7-10 days, after which see a doctor.
Bacterial conjunctivitis in a child
When various bacteria enter the body - streptococci, staphylococci, gonococci, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, chlamydia and others - dangerous bacterial infections develop, including those affecting the eyes. Preschool children often touch their mucous membranes with dirty hands, introducing germs. Infection with bacterial conjunctivitis can also occur when swimming in ponds, pools, or visiting public baths.
Even a newborn baby can suffer from bacterial conjunctivitis if it is infected from the mother during childbirth. A particularly severe course of the disease in an infant is caused by gonococci and chlamydia. Thus, when gonococcus gets into the eyes, blenorrhea develops, which, if not treated in a timely manner, can lead to blindness.
Treatment of viral conjunctivitis in children
Viral pathology usually develops against the background of ARVI or influenza. and in both eyes at once. Outbreaks of viral conjunctivitis often develop into epidemics. Antiviral drugs are used to eliminate the symptoms of this disease in children.
"Ophthalmoferon"
Their active ingredients are recombinant interferon 2-alpha and diphenhydramine - thus, antiviral and antihistamine effects are achieved simultaneously. For the treatment of children under one year of age, it is advisable to use Oftalmoferon when the first signs of the disease appear.
"Poludan"
A drug that enhances the synthesis of interferon, which significantly reduces the manifestations of viral eye inflammation in children. The main substances in these drops are polyadenylic and polyuridylic acids. The recommended dose for instillation is 1-2 drops three to four times a day. Already on the third day after starting to use Poludan, improvements in the condition are noticeable, irritation, redness of the eyes, and lacrimation disappear.
"Aktipol"
Antiviral drops that produce interferon in the body, which helps to significantly strengthen its own immune defense. The use of this medicine helps eliminate swelling and redness of the conjunctiva, reduce itching and irritation. "Aktipol" also has a keratoprotective effect, promoting the healing of corneal tissue. Since the product is applied topically, the main active ingredient - aminobenzoic acid - is well absorbed, contributing to a rapid therapeutic effect.
Symptoms of bacterial conjunctivitis in children
In addition to the signs inherent in all types of conjunctivitis - hyperemia and swelling of the eyelids and conjunctiva, a distinctive manifestation of this disease is purulent discharge from the eyes. They can be so strong that a child’s eyelashes stick together after sleep. An increase in temperature and deterioration in vision clarity may also occur.
If such signs appear, prompt action must be taken. Bacterial conjunctivitis can lead to very negative consequences for the visual organs. To eliminate its symptoms, the doctor prescribes antibacterial drops and ointments with antibiotics. Before administering medications, the eyes must be rinsed and cleared of traces of purulent discharge. To do this, use weak solutions of furatsilin or boric acid, as well as specially developed liquids. For example, “Blefarolion” from the Russian one is well suited for washing. Apply a little product to a cotton pad and clean your eyes. Before starting the procedures, you should wash your hands well to avoid introducing dirt. It is advisable to rinse 6-8 times a day.
For the treatment of bacterial conjunctivitis in children, mainly topical agents are prescribed that do not penetrate the blood, but act only on eye tissue, and therefore are safe for children's health. This method allows you to quickly cope with the symptoms of the disease. In this situation, the following drugs can be used: Albucid, Tobrex, Floxal, Vitabact, Levomycetin, etc. Visible improvements should occur in 2-3 days. If this does not happen, then you need to contact an ophthalmologist - he will prescribe another medicine.
Rules for administering drops and ointments
Before starting procedures, you should wash your hands. Before starting the instillation procedure, you need to wash the baby's eyes with antiseptic solutions to remove any remaining pus. These can be weak solutions of boric acid, furatsilin, etc. Take a separate cotton pad for each eye. When administering drops, make sure that the tip of the bottle dispenser does not touch the mucous membrane and skin around the eyes, so as not to spread the infection. Administer exactly the dose of medication prescribed by your doctor. After completing the procedure, you need to blot the area around the eyes with a clean napkin and wash your hands again. Medicinal drops and ointments are effective means for eliminating the symptoms of conjunctivitis in children. They have a local effect without penetration into the bloodstream. The drugs fight pathogens, performing antibacterial and anti-inflammatory functions. With the correct selection of medicine and following the doctor’s recommendations, the disease can be cured in 7-14 days.
Types of conjunctivitis in children aged 1 year

In this article
- Types of conjunctivitis in children aged 1 year
- Viral conjunctivitis
- Treatment of adenoviral conjunctivitis in children aged 1 year
- Herpetic conjunctivitis
- How to treat conjunctivitis with chickenpox, measles and rubella
- Bacterial conjunctivitis
- How to treat allergic conjunctivitis in a one-year-old child?
- How to treat hay conjunctivitis in a 1 year old child
The nature of conjunctivitis in children is varied. The most common types of diseases are:
- viral;
- bacterial;
- allergic.
If disturbing symptoms appear, it is important not to delay calling a pediatrician, who can identify the most likely cause of the disease and either prescribe symptomatic treatment or give a referral to an ophthalmologist. You should not neglect to see a doctor even in cases of minor manifestations of the disease. After all, advanced conjunctivitis in a child aged 1 year can have serious complications and can cause irreparable harm to his vision.
Prevention of childhood conjunctivitis
To prevent bacterial conjunctivitis in children under one year of age, a woman should take care of her health even before the baby is born. She needs to undergo a full examination by a gynecologist and cure sexually transmitted infections, if any. This will help protect the newborn from chlamydial conjunctivitis and blenorrhea. After the birth of a baby, special attention must be paid to the sterility of objects and hygiene products used to care for him. Bacterial infections quickly spread through household contact, as germs easily reach mucous membranes from insufficiently clean hands. It will be useful to ventilate the room, walk with the child more often, and perform water procedures, strengthening his immunity. Always keep the room clean and wet-clean surfaces more often to minimize the risk of infections. During periods of epidemic outbreaks of viral diseases, it is better to maintain a home regime, not visiting public places with your child unnecessarily.

How is conjunctivitis transmitted in children?
Infectious and viral diseases are transmitted from a sick organism to a susceptible one - this is how the main mechanism for preserving the pathogen as a species works.
During this process, there are three stages of movement:
- entry of the pathogen from the source of infection into the external environment;
- his stay in the external environment;
- introduction of a pathogen into a susceptible organism.
The transmission mechanism always corresponds to this scheme, but there are some nuances. For example, if the pathogen is in the human blood, then its carriers are blood-sucking insects (transmissible route). Bacterial and viral types of conjunctivitis are transmitted in two main ways.
Aerogenic (airborne and dusty)

Viruses and microbes located in the upper respiratory tract are dispersed into the surrounding atmosphere in the form of an aerosol when a child sneezes or coughs. The radius of such an infectious “cloud” can reach 2-3 meters. Pathogenic microorganisms are able to remain in the air for quite a long period, moving over significant distances due to electric charge and Brownian motion. As soon as a person inhales such a suspension of microbes, infection occurs. It is not for nothing that in case of diseases of the upper respiratory tract it is recommended to wear protective masks, especially in the autumn-spring period.
Many pathogenic organisms are very tenacious and can survive on contaminated surfaces in an active state for up to 7-10 days (for example, adenoviruses). When such dust particles are inhaled, the infection enters the mucous membrane of the nose and eyes, causing disease.
Contact and household
In this case, infection occurs through direct contact between children or indirectly through common objects - toys, dishes, hygiene products. Bacterial conjunctivitis spreads this way especially often. It is called "dirty hands disease." As soon as a child touches a contaminated surface or object, and then scratches his eyes or touches other mucous membranes (nose, mouth), infection occurs.

From the description of the ways of spreading bacterial and viral conjunctivitis, it becomes clear why these diseases so often take an epidemic course in children's groups. When such a situation occurs, a quarantine is introduced, which usually lasts up to 2 weeks. At the same time, sick children are exempted from attending kindergarten, and all premises are subject to thorough sanitary and hygienic treatment in order to maximally protect children and staff from infection.
What is the danger of conjunctivitis?
Conjunctivitis in babies under one year of age can be successfully cured with timely consultation with a specialist and initiation of therapy. Self-therapy at home is strictly unacceptable. If conjunctivitis is suspected, a small child should be examined by at least two doctors - a pediatrician and then an ophthalmologist.
If symptoms of conjunctivitis appear in children, you should not use advice gleaned from forums on the Internet. The external manifestations of various ophthalmological diseases can be very similar, and only a specialist will be able to determine the true cause after taking the appropriate tests. Successful treatment of conjunctivitis in a child under one year of age depends on following all the specialist’s recommendations. It will be much more difficult to cope with an advanced disease. In addition, inflammation of bacterial or viral etiology can seriously harm the baby’s vision. In general, this visual ailment is not dangerous. With timely medical care, there is no threat to the visual organs.
Allergic conjunctivitis in a child
Unlike bacterial and viral types, allergies are individual and are not transmitted through the usual routes for infections. Inflammation of the conjunctiva and eye irritation can be caused by various allergens:
- pollen of flowering plants;
- secretions of pets: saliva, sweat, etc.;
- some products, medicines;
- household chemicals, etc.
As soon as a certain substance to which the child is sensitive gets on the mucous membrane of the eyes, the body’s reaction begins: the eyes turn red, the eyelids swell, increased secretion of tear fluid occurs, and a runny nose and cough may begin.

Here are the common types of allergic reactions that children are susceptible to:
- Hay fever, or seasonal rhinoconjunctivitis. It occurs in spring and summer during the flowering period of certain plants: cereals, weeds, etc. Antihistamines are prescribed for treatment, supplemented with corticosteroids in severe cases.
- Drug-induced conjunctivitis. A child may develop an individual negative reaction to the components of the medications taken, both within a few hours after starting treatment, and after some time has passed (cumulative effect). In addition to the standard manifestations of allergies - swelling and inflammation of the conjunctiva - skin rashes and swelling of the nasal mucosa may also be observed. If a child develops an allergy, you should immediately stop taking the medications and contact an ophthalmologist to clarify the circumstances. Allergies can also be caused by uncontrolled intake of vitamins.
- Chronic allergies can manifest themselves throughout life when the mucous membrane of the eye is exposed to a specific irritant: cosmetics, house dust, certain products, etc. Inflammation can occur at any time upon contact with an allergen. Once the cause of the irritation is eliminated, the symptoms disappear.
For the treatment of allergic conjunctivitis, small children are prescribed drops that eliminate eyelid swelling and redness, for example, Visine, as well as antihistamines Allergodil, Alezastin, Olopatadine. All prescribed medications must be used strictly in accordance with the doctor’s instructions in the prescription.
Treatment of viral conjunctivitis in a 6-month-old child
The cause of conjunctivitis is often an adenovirus infection. It appears as follows:
- increased body temperature;
- cough and runny nose;
- inflammation of the lymph nodes.
There are other symptoms that a 6-month-old sick child cannot report: drowsiness, weakness, headache. Conjunctivitis can occur a few days to a week after infection. The presence of the disease is indicated by such signs as redness of the edges of the eyelids and conjunctiva, lacrimation, and mucous discharge. With adenoviral inflammation, photophobia is a concern. When the light in the room is turned on, the child begins to squint and cry.
This type of conjunctivitis is treated with antiviral drugs. To prevent bacterial infection, antibacterial agents are also prescribed. All these medications are used topically, that is, by instillation of drops. Both eyes are always treated, even if inflammation is observed in only one.
Treatment of conjunctivitis in children at home
Ophthalmic diseases rarely require hospitalization. A child can be admitted to a hospital only if the disease is very advanced or when it comes to the health of a very young patient who requires constant supervision by a specialist. In other cases, the ophthalmologist prescribes home treatment. Your doctor will tell you in detail how to treat conjunctivitis in children at home at your appointment.
The main causes of conjunctivitis in children
One of the main causes of conjunctivitis is poor personal hygiene. This happens quite often in children. Pathogenic microorganisms (viruses, bacteria, fungi) enter the conjunctiva (the membrane covering the outside of the eyes) and cause inflammation.
The disease can develop against the background of an acute respiratory viral infection, a general weakening of the body due to decreased immunity, injury to the organs of vision, or the entry of a foreign body into them. The most common causes of conjunctivitis include:
- Bacteria. The disease is caused by chlamydia, streptococci, pneumococci, Haemophilus influenzae, and staphylococci. Conjunctivitis caused by bacteria is contagious. Therefore, children attending kindergarten and school are more susceptible to it than others. The bacterial infection is severe and requires long-term treatment. In some cases, antibiotics are prescribed. The illness can last for two weeks.
- Viruses. The most common causes of conjunctivitis are adeno- and enteroviruses. Sometimes viral conjunctivitis becomes a consequence of other diseases: chickenpox, rubella, ARVI, pharyngitis, tonsillitis, influenza. The disease is also contagious and is transmitted through airborne droplets and household routes. The duration of the disease is 5-7 days.
- Allergy. The cause of the disease can be any allergen. This can be dust, chemicals in detergents and cleaning products, pollen, food, medicines and others. It may appear during certain seasons or all the time.
- Injuries. Toddlers and young children, like schoolchildren, are very active. During active games they can injure your eyes. Damage to the mucous membrane sometimes results in conjunctivitis. Even a small grain of sand caught in the eye can injure the thin membrane of the conjunctiva. The child, feeling a foreign body, begins to rub his eyes, thereby causing even greater irritation.
Typically, the disease appears first in one eye and then affects the second. The exception is conjunctivitis caused by allergies. In this case, the pathology manifests itself in both eyes at once.
Symptoms of bacterial conjunctivitis
A characteristic sign of this pathology, in addition to swelling and hyperemia of the eyelids, is profuse purulent discharge from the eyes, which sticks the child’s eyelashes together after sleep. Corneal ulceration, increased body temperature, and deterioration in vision clarity may also occur. Before administering drops or ointments when treating bacterial conjunctivitis, it is necessary to pre-wash the child's eyes. To do this, you can use a weak solution of boric acid, furatsilin tablets dissolved in clean water, or a special preparation “Blefarolion” from the Russian one.
Before starting the procedures, you need to wash your hands well so as not to get dirt into your eyes. It is advisable to rinse several times a day to eliminate traces of purulent discharge. To treat bacterial conjunctivitis, medications with antibiotics are prescribed, which are not absorbed into the blood, but act only on the eye structures, and therefore are safe for children. This therapy helps to quickly eliminate the symptoms of the disease. In this situation, the following drugs can be used: Sulfacyl sodium, Vitabact, Levomycetin, Tobrex, Floxal and others. If after 2-3 days there is no improvement, then you need to contact an ophthalmologist - he will prescribe another medicine.
Treatment of conjunctivitis in young children
At the first signs of conjunctivitis, you should contact your pediatrician. If the disease was caused by an adenovirus infection, then in addition to redness and swelling of the eyes, the child may develop a cough, a high temperature, and inflammation of the mucous membrane of the throat and nose. If a bacterial infection develops, the disease will affect both eyes and purulent discharge will appear, which will need to be removed with a warm antiseptic solution. The attending physician will be able to determine which pathogen caused conjunctivitis in a child based on the existing symptoms. Scraping of the mucous membrane is prescribed in cases where the origin of the disease is unknown and it is difficult to treat. Viral conjunctivitis can be treated with antiviral drops and ointments. For example, a doctor may prescribe drugs such as Acyclovir, Zovirax. Only broad-spectrum antibiotics will be effective against microbial infections. Children are prescribed medications whose active ingredients are least toxic.
What should parents do, how to provide proper care? How to treat conjunctivitis in children:
- regular cleansing of the eyes from mucus and purulent discharge - for this, make decoctions of herbs that have an antiseptic effect (chamomile, calendula) or prepare a solution from furatsilin tablets; you need to clean the eyes as pus and mucus accumulate;
- eye drops - children resist eye drops, and in order for a sufficient amount of the drug to reach the mucous membrane, the child must be calm; if the child is afraid, you can invite him to close his eyelids and drop liquid into the outer corner, and when the baby opens his eyes, it will be evenly distributed over the entire surface;
- ointments - ointments are highly effective in treating bacterial infections, but they need to be placed behind the lower eyelid, which can cause certain difficulties if the baby is restless; before squeezing 0.5 cm of ointment into the corner of the eye, moving the eyelid back a little, you need to explain your actions to the child;
- vitamins - help strengthen the protective functions of the child’s body, prescribed by a doctor;
- antipyretics - if a child’s illness occurs with fever, paracetamol can be used to alleviate the condition.
Scarves used by a child during illness should be washed regularly and ironed before use. Timely treatment of viral conjunctivitis will allow you to return to kindergarten after 5-7 days, and bacterial conjunctivitis - after 7-10 days. To prevent the disease from recurring, it is necessary to harden the baby, strengthen the immune system by increasing the number of walks in the fresh air, allow the child to move more and constantly remind him of the need to wash his hands, not touch his eyes with them, and not use other people’s towels.