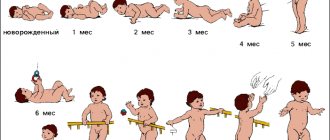
Why is fever dangerous in children, and how to deal with it?
advises a medical pediatrician. Fever is the most common sign of the development of infectious and some other diseases in children.
Many things can cause a child to have a fever, from common childhood illnesses such as chicken pox and tonsillitis to reactions to vaccinations. An increase in body temperature is an innate protective mechanism by which the body stimulates the functioning of the protective factors of the immune system. Also, the increased temperature of the internal environment of the body itself can lead to inactivation or death of pathogens of many diseases. Remember that everyone's body temperature normally fluctuates 1-2 degrees throughout the day and may vary depending on age, activity level and other factors.
So rising temperatures are not a “problem.” This is an indicator that some kind of attack by microbes, viruses or other factors has occurred on the body, and the body reacts to it, gives a “response”. It is much worse when bacteria or viruses attack, but the temperature does not rise (i.e. there is no immune response, or it is insufficient).
Myth No. 3. Fever is harmful to the body.
The temperature reaction is protective in nature. Many bacteria and viruses die at elevated temperatures; the production of interferon gamma increases at temperatures above 38.0°C, and this is the most important mediator of a full immune response, stimulating the formation of antibodies.
A rise in body temperature in a child during an infectious disease indicates a higher level of health in comparison with a child who, with the same frequency of infectious diseases, does not develop a high temperature.
What is a fever?
The normal temperature for babies and children is around 36.4°C, but this may vary slightly from child to child.
- Low-grade fever is an increase in temperature from 36.7 to 38 degrees.
- Fever is a high temperature of 38 C or more.
The following symptoms appear when you have a fever:
- Your baby's forehead, back, or stomach feels hotter than usual.
- The surface of the skin becomes sweaty (moist) and sticky.
- The baby's cheeks and sometimes forehead turn red.
To measure temperature, it is best to use a safe digital thermometer without mercury filling.
Some features of fever in children
High fever in children is perhaps the only emergency condition that most mothers cope with on their own. Especially when there are several children in the family and the temperature reduction school has been completed more than once. In every home where there is a baby, as a rule, there is a set of antipyretic drugs. But sometimes the temperature lasts a very long time or even rises, despite all efforts. Why is this happening?
Good to know for parents
You should not determine the presence of fever by touching your baby’s forehead with your lips or palm; the temperature should only be measured with a medical thermometer.
The temperature is not lowered below 38.5 °C; it protects the body from germs and viruses. This does not apply to babies who have previously had seizures; their temperature begins to drop after 37.5 °C or even with any increase.
When the baby is vomiting, it is better to insert a rectal suppository; for diarrhea, syrups or tablets are used. It happens that a slight increase in temperature is provoked by third-party objects, for example, specks in the eye. Read here how to deal with this.
If the temperature does not decrease after taking antipyretic medications
It is useless to measure the temperature immediately after taking the medicine; it usually drops an hour after the drug is taken orally. Therefore, during this time there is no need to repeat the dose or give another antipyretic drug. If you lower the temperature very quickly, children often feel worse and become weak.
Before giving an antipyretic, it is important to pay attention to the baby's skin. Hot and red skin indicates that the blood vessels are dilated; it will be easy to get rid of this temperature. This is red hyperthermia. In this situation, sometimes it is enough to wipe the skin with alcohol or a weak solution of vinegar, put a wet napkin on the forehead, and the temperature will drop without medication.
But if the thermometer goes off scale, and the hands and feet are pale and icy to the touch, it means that the skin vessels are compressed and do not give off heat; antipyretics alone will not have an effect. This is already white hyperthermia and most often it is precisely this that parents cannot cope with without the help of doctors. To increase heat transfer, it is necessary to dilate the vessels. For this purpose, drugs that relieve vascular spasms are used, for example, no-spa, drotaverine or papaverine; they are taken together with antipyretics.
Sometimes the temperature rises very quickly after decreasing, parents panic and do not know what to do, since not enough time has passed to re-use the medicine. The solution is to alternate drugs from different groups. For example, after Nurofen you can give paracetamol, Nurofen will be next again, and so on.
The most common cause of fever in children is the common cold, in which the temperature does not last more than three days.
If all measures have been taken, and the temperature stubbornly remains at high levels, it is better not to risk the baby’s health and contact a specialist so as not to miss dangerous diseases.
How to measure a child's temperature:
- The child's armpit should be clean and dry! If it is wet, the thermometer will show an inflated result!
- Move your child's arm to the side and place the thermometer in the upper armpit.
- Gently place your hand against your body and keep it pressed while taking the temperature.
- Leave the thermometer in place for as long as indicated in the instructions. Some digital thermometers beep when the temperature measurement is complete.
- Take out the thermometer. The display will show the baby's body temperature.
- If your child has just had a bath or has been wrapped tightly in a blanket, wait 10 minutes before taking their temperature.
- Professional infrared thermometers allow you to instantly measure body temperature. If there is a need to measure the temperature as accurately as possible, but there is no professional thermometer at hand, the most accurate results are obtained by measuring the temperature rectally.
Temperature in a newborn baby
It often happens that a mother, who has just returned from the maternity hospital, measures the baby’s temperature, sees the number 37.5˚C on the thermometer, gives the child paracetamol, measures the temperature again and realizes that there is no effect.
If the baby willingly takes the breast, does not worry, the umbilical wound is not red, everything is fine with the baby.
Newborn children adapt to life in this imperfect world; their organ systems also adapt, including thermoregulation processes.
Before giving your child medicine, undress him completely, remove the diaper, put a diaper on him, if you are worried about the furniture, check the temperature in the room where the baby is. It should be 18 - 22˚С. Ventilate the room and measure the temperature again. If the actions have an effect, most likely you are overheating the child. If not, watch your child. Perhaps he was crying or was quite active at the time of taking the temperature or before it, or the baby recently ate. These facts also lead to an increase in body temperature.
If you are also concerned about nasal congestion, change in stool color, severe anxiety in the child, redness of the umbilical wound or discharge from it, it is better to consult a doctor.
And of course, you need to call a doctor if the newborn’s temperature is 38˚C or higher.
There is another group of children whose parents should be more wary than usual. These are children with somatic pathologies. Such as congenital heart defects, cardiac arrhythmias, epilepsy, central nervous system diseases, thyroid diseases, children who have previously had febrile seizures. These children have to bring down the temperature, which has not reached 38.5˚C. The tactics for reducing the temperature of these children are the same as for everyone else, only with lower numbers. And it is advisable to reduce the temperature of these children sharply.
What to do if your child has a high temperature
The child must be kept at home and supervised. The temperature should drop within 3 or 4 days.
After vaccination, the temperature can remain normal for up to 48 hours.
What do we have to do:
- if the child is less than 6 months old, call a doctor immediately
- Give your baby plenty of fluids to drink (or continue breastfeeding)
- monitor signs of dehydration
- feed if the baby wants to eat
- Regularly monitor your child's condition at night
- give the child antipyretics prescribed by the doctor
Why does my child’s temperature not go down, and what should I do?
This question comes up quite often, and very often parents make the same mistakes.

1) The first mistake is a diaper, or rather its presence. Nowadays, this thing has become an integral part of raising children, and many people can’t even imagine how to remove it from a child, and even for the whole day. The disadvantage of this thing is that when you put it on the baby’s bottom, you also put it on the groin area, which is rich in large blood vessels. Instead of giving off excess heat, the baby, thanks to this “compress,” adds an extra degree to himself.
Try to replace the diaper with panties with gauze or old towels during the child's illness. Sometimes you can find fishnet panties on sale. It is important that the groin area is as open and dry as possible. Unfortunately, such a replacement will have to be changed every time the child relieves himself.
2) Mothers often complain that they cannot bring down their child’s temperature, and the room where the sick child is is stuffy and hot.
In the room where the baby is, the air temperature should be low 18 - 22˚C, and the humidity should be at least 70%.
The room must be ventilated regularly. Firstly, it will reduce the number of pathogenic microorganisms in the room. Secondly, it will be easier for the child to breathe. Thirdly, it will help you reduce your child's temperature.
3) Clothes. Attempts to wrap him up more, give him hot tea with raspberry jam and do everything to make the child sweat and thus recover can worsen the condition. Clothes should be made from natural fabrics. If the child is chilly, cover and warm him.
But if you see that the child is hot and open, give him a sheet or a very light blanket.
4) Food. Not feeding a child or feeding for two are two extremes. If the child already knows how to speak, ask his opinion. Perhaps he wants some fruit or a particularly tasty dish prepared by his mother. If the baby refuses, do not force him to eat, just put washed fruits and vegetables in a visible place.
In your diet, try to stick to more carbohydrate foods (vegetables, fruits, cereals); if your child doesn’t mind eating yogurt or kefir, don’t deny him this either.
5) Incorrect calculation of the dosage of antipyretics.
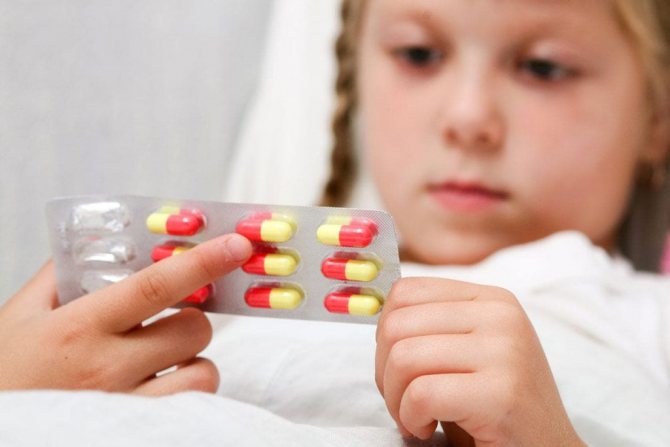

Dr. Komarovsky says: “Sit down with dad while your baby is healthy and calculate how much medicine is needed for your baby’s weight.”
The fact is that the calculation of the medicine on the packaging is made for the average child. Thus, if your baby weighs more than average, then you need more medicine than indicated on the back of the package.
6) Rubdowns and cold compresses for white fever. This error is rare.
7) Rubbing with vodka, vinegar or water below the child’s body temperature.
Vodka and vinegar increase intoxication of the body and can lead to allergies or poisoning. Ice water can provoke spasm of peripheral vessels and lead to a decrease in the area of heat transfer.



Loss of fluid and salts through sweat and exhaled air can lead to a serious condition of the child and subsequently to the threshold of the intensive care unit.
What not to do when the temperature rises
- Do not undress your child or cool him or her with blows or rubs; fever is a natural and healthy response to infection. Hypothermia can lead to complications from the infection.
- Do not cover your baby with a warm blanket or wrap him up, as this may cause heat stroke. Just cover your baby with a sheet or light blanket.
- Do not give aspirin to children under 16 years of age. Absolutely never! This may be due to a rare but dangerous disease called Reye's syndrome.
- In children under one year of age, medications available in the form of rectal suppositories are recommended to reduce fever.
- Do not self-medicate. For young children, the dose of drugs and the frequency of their use should be calculated individually; the prescription can only be made by a doctor after diagnosis.
First aid instructions for a child with a high fever.
- If the temperature does not exceed 38 °C, and the child tolerates it normally, then there is no need to give antipyretics. The fact is that at elevated temperatures the body fights infection more effectively, therefore, unless absolutely necessary, it should not be brought down. The exception is those cases when the child suffers from a neurological disease (registered with a neurologist) or simply has a hard time tolerating the temperature - then antipyretics should be given starting at 37.5 ° C.
- If the temperature rises above 38 °C, the child should be given an antipyretic drug recommended by a doctor (Children's Panadol, Efferalgan, Nurofen). For very young children, it is better to use the medicine in suppositories; for older children, you can give the medicine in syrup form. Do not use aspirin under any circumstances! Aspirin during a viral infection (in children under 12 years of age) can cause a dangerous complication - Reye's syndrome.
- Be sure to call a doctor to determine the cause of the fever. Note the symptoms that accompany an increase in temperature - runny nose, cough, vomiting, diarrhea, pain in the head, stomach, rash, etc.
When should you seek emergency medical help?
It is necessary to call a doctor or ambulance in the following cases:
- The child is less than 3 months old and has a temperature of 38°C or higher
- The baby is between 3 and 6 months old and has a temperature of 39°C or higher
- Against the background of fever, rash, vomiting, and diarrhea appeared
- Fever lasts for 5 days or more
- The child refuses the breast, does not eat, behaves unnaturally
- The child has signs of dehydration: dry diapers, sunken eyes, crying without tears.
Still have questions?
Get an online consultation from leading pediatricians in St. Petersburg!
A professional and experienced pediatrician will answer your questions.
Medical care for a child without leaving home at a convenient time.
sign up for a consultation
A Skype consultation lasts 45 minutes.

Antipyretics for children
In most cases, non-drug methods can reduce the temperature by 1-1.5 degrees. This is enough for the body to fight the disease without severe overload.
But sometimes you can’t do without medicine.
When to give antipyretics:
- Temperature indicators. If the temperature is 39 degrees, there is a clear tendency for the values to increase.
- Focus on your well-being . Doctors do not recommend lowering the temperature if the temperature is below 39 degrees. It is at these rates that many pathogenic microorganisms die. But if your baby is frankly unwell with a reading of 37.5-38.5, you should resort to medication.
- Dangerous symptoms . Difficulty breathing, signs of dehydration, the child refuses to drink, the baby is hysterical, delirious. Profuse sweating is accompanied by diarrhea and vomiting.
- Accompanying illnesses . Severe pathologies of the nervous system - meningitis, epilepsy, cerebral palsy, convulsive syndrome. Chronic diseases of the lungs and heart.
If your child decreases the number of urinations, the fontanel becomes sunken, or the skin is dry, call a doctor immediately.
Urgent medical attention is required for convulsions, the appearance of a purple rash on the body, impaired consciousness, repeated vomiting and diarrhea, and severe headaches that do not subside after taking medications.
How to bring down a child’s fever – approved medications
Medicines to reduce fever in children are produced in the form of rectal suppositories, tablets, syrup, and injections. Most antipyretics additionally have an analgesic, anti-inflammatory effect, regulate the process of sweating, and thin the blood.
Signs of particularly dangerous diseases accompanied by fever
Fever can be a sign of serious illnesses such as meningitis, urinary tract infection and sepsis. It is necessary to urgently call an ambulance or take the child to the hospital emergency room if he has:
- There is tension and stiffness in the neck muscles,
- A rash has appeared that does not go away when you press on it with a finger
- The child is very irritated by light,
- The attack of fever does not go away, the child “shakes” with chills
- The child has unusually cold hands and feet
- Your baby has pale, mottled, blue, or gray skin
- The baby's crying has become weak, moaning, and does not look like usual
- The baby is sleepy, lethargic, and difficult to wake up
- The child has difficulty breathing, the stomach is pulled in under the ribs when breathing
- In a newborn baby, the fontanel on the top of the head has become bulging
What should you do if your child has a seizure? Seizures are a very serious side effect of fever in some children. Febrile seizures occur in 2–4% of all children under 5 years of age. Not all seizures cause sudden muscle twitching. Some seizures look like "fainting." If your child develops a seizure, do the following:
- Place your baby on his side.
- Do not put anything in your child’s mouth, even if “experienced” grandmothers recommend doing so.
- Call an ambulance immediately if the attack lasts more than five minutes.
- If the attack lasts less than five minutes, call your doctor or make an emergency visit to your doctor.
How to lower the temperature correctly?
If a child has a high temperature, the main thing that parents should remember is not to panic. Only clear actions and calm will help you quickly overcome the problem and normalize the baby’s condition.
How to reduce a baby's temperature
You can alleviate the child’s condition and provide first aid before the pediatrician arrives by doing the following:
- Provide a supply of fresh, clean, cool air. The room where the baby is located needs to be ventilated. The temperature in the room must be maintained in the range of 18-20 ° C, with a humidity of 45-55%.
- Let's drink more. High temperatures contribute to rapid dehydration of the baby's body. You can avoid severe complications of this process by offering your child warm drinks as often as possible. For a newborn, in addition to breast milk, you can offer warm sweetened water, fruit drinks, and diluted tea.
- Perform a light rubdown. In combination with antipyretics, rubbing will help to quickly reduce body temperature. Rubbing can only be done with clean, warm water, without adding vinegar or alcohol.
- Free your baby from warm clothes. Even if the child is chilling, you should not wrap him up. Light clothing made from natural fabrics is ideal.
- Give an antipyretic. For children in the first year of life, the following antipyretic drugs are recommended for use: Efferalgan (syrup or suppositories), Paracetamol (syrup or suppositories), Nurofen suspension.
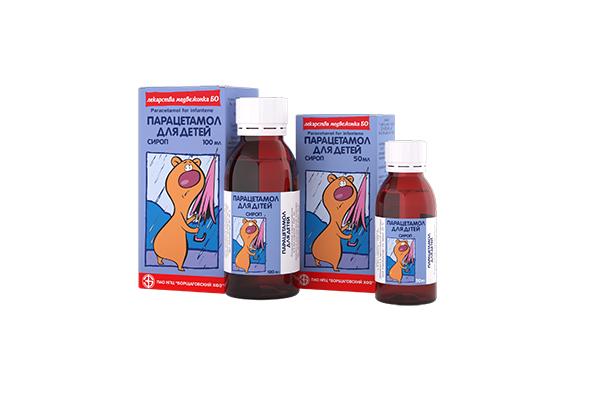

Paracetomol - 68 rub.
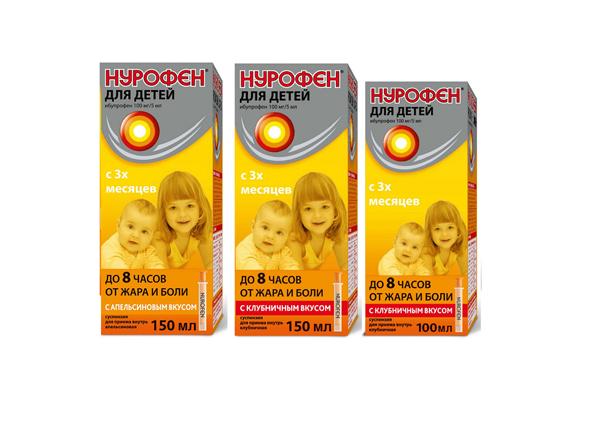

Nurofen - 210 rub.

Efferalgan — 97 rub.
Rules for the use of drugs
Most medications contain flavorings and dyes that can cause an allergic reaction. At the first sign of an allergy, you should stop taking the antipyretic drug.
When using antipyretics you must remember:
- Paracetamol, Efferalgan or Nurofen do not reduce the temperature if the dosage is calculated incorrectly (the dose of the drug corresponds to the child’s weight, not his age);
- When using the medicine in syrup form, before using it, the bottle is heated in the hand to room temperature;
- never exceed the calculated dose of the drug;
- the same antipyretic drug in different forms (syrup, suppositories) can be alternated, the interval between doses should not be less than four hours.
How to properly reduce high fever in preschool children
The algorithm for parents' actions when a preschool child has a high temperature is not much different from the manipulations carried out with a newborn. The only difference is that older children can be given antipyretics in tablet form. The dose is calculated based on the child's weight.
Drinking plenty of fluids (juices, fruit drinks, herbal teas) and the necessary microclimate in the room - the ratio of cool, clean air with moderate humidity - will help normalize the situation.
High temperature, as a symptom of the disease, will disappear only when the reasons for its appearance are identified and the necessary therapeutic therapy is carried out.
How to properly provide emergency care to your child with a high temperature, says Dr. Komarovsky.
Medicines for fever
If, despite all the steps taken, the temperature does not go down, you should resort to medications.
Paracetamol or Ibuprofen are used as antipyretic drugs. Only these drugs are allowed for independent use without consulting a doctor. Such products are produced in the form of sweet syrups, in packaging with a dispenser and detailed instructions for use, depending on the age and weight of the baby. If the temperature does not subside after the first use, another medicine can be given after 4 hours (not earlier).
Analgin and Diphenhydramine injections help a lot, but not every mother is able to give an injection to her child. The solution is suppositories in the butt containing these 2 drugs. If the second dose of antipyretics does not help, and the temperature remains at 38.5-39.5 °C, you need to urgently call a doctor or call an ambulance.
Why doesn't the temperature drop?
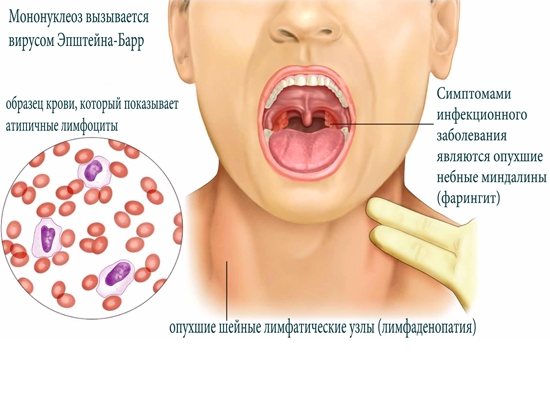
There are situations when a decision is made to bring down the temperature, but antipyretics do not work. Time passes, but the baby remains hot and restless, capricious and crying. The reasons that lead to this condition may be different. First of all, if an acute viral disease is at the peak of its development or the disease is caused by a bacterial infection (meningitis, otitis media, pneumonia). A child’s temperature does not drop above 40 °C if it is caused by purulent inflammatory processes - an abscess or phlegm, especially in the complication stage.
Even the temperature of 39 °C does not go astray when special, specific viruses enter the body, such as Elstein-Barr, which leads to the development of mononucleosis, or rotavirus. If a child’s high temperature, which cannot be brought down, is accompanied by symptoms such as headaches, convulsions, consciousness disorders, stomach and intestinal disorders, then most often the diagnosis may sound like encephalitis or meningitis.
Sometimes parents, without knowing it, prevent the temperature from going down. They wrap the baby warmly, put warm socks on him, tie a scarf around his throat, close the windows, thereby preventing proper heat transfer. You shouldn't do this.
It is advisable to dress the child in cotton, but not woolen, clothes and cover with a blanket.