While the baby is in the womb, its intestinal tract is sterile.
But as soon as the baby is born, various microorganisms enter the body.
Bifidobacteria and lactobacilli, as well as individual representatives of colibacteria, which can be classified as opportunistic, are considered beneficial.
With rapid reproduction, E. coli in an infant can cause a coli infection.
Reasons for the growth of E. coli in infants
Several types of pathogenic bacillus may be present in a child’s body – hemolysing and lactose-negative.
The latter belongs to the group of opportunistic pathogens, and in certain quantities it can be present in the body of an infant.
As for the hemolyzing bacillus, it can lead to serious disturbances in the functioning of the digestive tract.
The infection can enter the baby's body through the fecal-oral route. Hemolyzing bacillus can be passed through mother's milk during breastfeeding. Sometimes a child picks up an infection while in the maternity ward.
The main reason contributing to the development of E. coli in young children is reduced immunity. But even completely healthy babies can get an infection if they put dirty things in their mouths.
Therefore, parents should carefully monitor their children. Bottles should always be disinfected. If the pacifier falls on the floor, you must first wash it well and only then give it to the child. E. coli can also be transmitted through unwashed hands.
The meaning of E. coli
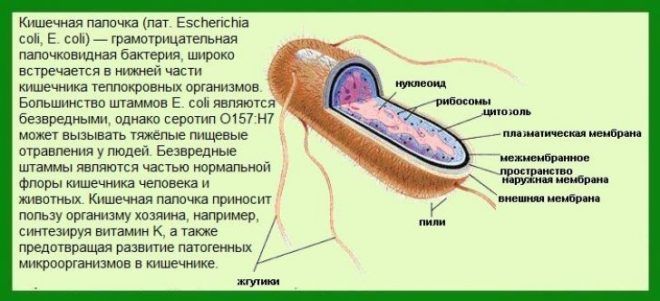
Escherichia coli is a small bacterium that has an oblong shape with rounded corners. The normal levels of these opportunistic microbes in the human body are 10*8 CFU. The child’s digestive tract is populated by these microorganisms almost immediately after birth, so if their number does not exceed the norm, then they do not cause pathological conditions. A particularly active increase in the number of bacteria in the body is observed when there is a lack of oxygen, which leads to the development of inflammatory processes. Today, experts identify more than a hundred harmful bacterial agents, which are divided into the following classes:
- enteroinvasive;
- enteropathogenic;
- enterotoxigenic;
- enterohemorrhagic.
E. coli enters the body through dirty food or poor-quality water. Among food, the main threat is:
- raw meat;
- fruits;
- vegetables.
This type of bacteria also actively multiplies if the rules of personal hygiene are not observed (for example, by not washing hands thoroughly).
Symptoms

Most often, a child becomes infected with E. coli due to carelessness of parents.
If such a problem occurs, then you will need to be able to recognize the symptoms characteristic of the infection.
It will not be difficult to understand whether a baby has E. coli, since he will react acutely to the infection.
The main signs of the presence of E. coli:
- Hyperthermia. Infection is accompanied by an inflammatory process, and the body always fights it in the same way. Therefore, if parents notice a high temperature in their baby, then they should start to worry. As a rule, fever is accompanied by hyperemia of the extremities and general weakness.
- Loose stools are a symptom that accurately indicates the presence of an infection of intestinal etiology.
- Vomiting or excessive regurgitation.
- Restless behavior. The child becomes whiny, sleeps poorly, and refuses to eat.
Diagnostics
If a baby develops the symptoms described above, parents should urgently show the baby to a doctor. To identify E. coli, it will be necessary to conduct a number of studies.

There are several methods to identify pathology:
- Bacterioscopy . The patient needs to donate blood, urine and feces. All analyzes obtained will be examined in laboratories using a microscope.
- Bacteriological research. Biological material taken from the patient is placed in a nutrient medium. If it contains pathogenic microorganisms, their number will rapidly increase.
Treatment of E. coli in children must be supervised by specialists. The duration of antibiotic therapy should not exceed 5 days. In addition to taking medications, it is very important to maintain a proper diet.
General recommendations for the treatment of E. coli in children:
- If an infection is detected, you should call a doctor as soon as possible.
- Most often, treatment can be carried out at home, but only with the consent of a specialist.
- In severe cases of the disease, hospitalization in a hospital is necessary.
Only after the type of E. coli has been identified and a diagnosis made, should the doctor prescribe appropriate treatment.
Therapy for lactose-negative Escherichia coli

Lactose-negative Escherichia coli belongs to the group of opportunistic bacteria. If the percentage of its content in the intestines does not exceed 5% of the total microflora, then it does not pose a danger, but, on the contrary, affects various processes:
- stimulates the production of vitamins belonging to group K and B;
- actively participates in metabolic processes;
- Helps the body absorb calcium and iron.
If the percentage of lactose-negative bacillus in the intestines exceeds the permissible norm, the following symptoms will be observed:
- the appearance of frequent regurgitation;
- increased gas formation;
- if the child is already receiving complementary foods, then particles of undigested food may be noticeable in the stool;
- abdominal pain;
- alternating constipation and diarrhea.
Experts believe that an increase in the percentage of lactose-negative bacillus in an infant is not a serious violation. To correct this, children are prescribed special medications that contain probiotics (for example, Bifidumbacterin) as well as prebiotics (for example, Hilak Forte).
What to do if your newborn has elevated lactose-negative Escherichia coli
Immediately after birth, the baby has a sterile intestinal tract. It is gradually filled with microflora. Lacto- and bifidobacteria, as well as other microorganisms, appear in it.
Escherichia coli (Escherichia coli) is one of the types of opportunistic microorganisms. A small amount of them is simply necessary for the normal breakdown and digestion of food.
When E. coli grows, various unpleasant symptoms and disorders of the digestive system are observed.
E. coli is part of the microflora of a child's stomach
Varieties
Only if a certain balance of microorganisms in the digestive system is maintained, the child feels good. If the ratio of beneficial and pathogenic bacteria changes, then the baby’s well-being may worsen. Most often, the cause of infection is one of the E. coli bacteria: hemolyzing or lactose-negative.
Hemolyzing (hemolytic)
The presence of hemolyzing Escherichia coli is unusual for a child’s intestines. Ideally, this bacterium should not be in the gastrointestinal tract at all. If hemolyzing E. coli appears in a baby, the following symptoms are observed:
- constipation, which is accompanied by gas formation;
- the appearance of green streaks in the stool;
- diarrhea;
- nausea and vomiting;
- weakness;
- painful sensations in the abdomen;
- lack of appetite;
- fatigue;
- halitosis.
On a note! This infection is not characterized by fever, so it is more difficult to detect the disease in the early stages.
Lactose negative
Lactose-negative Escherichia coli is an opportunistic bacteria; it must be present in the intestines at a certain rate. Its presence in a child’s body is mandatory, since the microorganism is necessary for the production of vitamins B and K. Bacteria help the body absorb calcium and participate in metabolism.
When the amount of lactose-negative Escherichia coli increases, an infant experiences the same symptoms as when a hemolytic microorganism appears. Additionally, there may be an elevated temperature.
Treatment is systematic, with the use of prebiotics and probiotics.
Causes of the disease
The main route of entry of E. coli into a baby’s body is fecal-oral. The bacteria can penetrate into the infant's fragile stomach through breast milk or through contact with the mother. A baby can also get bacteria within the walls of the maternity ward.
Intestinal obstruction in a child - symptoms
The development and growth of E. coli in the small ventricle is accelerated by the weakened immunity of the child. The baby's hands or a poorly disinfected bottle or pacifier can become carriers of infection for a child.
On a note ! To minimize the likelihood of Escherichia coli, strictly observe the rules of personal hygiene.
Development of the disease
The essence of E. coli disease is damage to the digestive system. The waste products of pathogenic microorganisms lead to metabolic disorders, which causes poisoning. Symptoms of intoxication determine the stage of development of intestinal infection. The incubation period ranges from 3 to 10 days.
Roseola in a baby - symptoms of rashes
The onset of the disease is very acute. The baby cries, is capricious, has pain, colic and other unpleasant symptoms. If you do not start timely treatment, dehydration begins.
On a note! Infection with E. coli is very dangerous, as the infection gradually poisons all vital internal organs. If left untreated, death can occur.
Hemolyzing E. coli usually develops in people with weakened immune systems. Newborn babies, especially premature ones, are always at risk.
The development of such infections is often observed in hot summer months, as well as in autumn. During this period, people do not monitor the purity of fruits and vegetables that grow in their own gardens and vegetable gardens.
Symptoms
Hungry stool in a baby - what it looks like, symptoms
After pathogenic E. coli enters the baby’s body, its active reproduction and increase in the number of bacteria begin. As a result of an imbalance of microflora, dysbacteriosis develops. The complexity of the development of the pathology will be indicated by symptoms that gradually intensify, worsening the child’s condition.
With intestinal infections, the child behaves restlessly, the symptoms resemble colic
Bloating and rumbling tummy
Active reproduction of E. coli in the stomach leads to an imbalance of microflora. The baby does not sleep well and is constantly restless. Against the background of general malaise, the following symptoms are clearly noticeable:
- colic (paroxysmal pain);
- frequent rumbling in the tummy;
- increased formation of gases;
- bloating.
All syndromes manifest themselves most clearly after feeding.
Impaired passage in the intestine
Due to the large number of pathogenic microorganisms, problems arise with the digestion and breakdown of food. Because of this, it accumulates in the stomach, and disruptions in the passage of food in the intestines are observed. This causes frequent regurgitation, which sometimes turns into bouts of vomiting.
Malabsorption syndrome
In rare cases, malabsorption syndrome may occur - certain disturbances in the functioning of the small intestine and the condition of its mucous membranes.
Failures occur in the process of assimilation of nutritional components, which provokes the improper functioning of other body systems.
As a result, the baby experiences a lack of specific substances (vitaminosis), since many of them remain in the intestines or are transformed into the blood or lymph.
Diarrhea, dehydration
One of the main symptoms of Escherichia coli is diarrhea. Severe diarrhea quickly causes dehydration, which is manifested by the following symptoms:
- weakness;
- drowsiness;
- increase in temperature;
- dry skin and tongue;
- rare urination.
With prolonged diarrhea and lack of treatment, the child's general condition will become worse and worse.
Weight loss
The baby refuses to eat due to discomfort and pain. He does not receive the required amount of nutrients, which leads to a stop in weight gain. Constant diarrhea and regurgitation also provoke weight loss. Weight loss is a very alarming signal.
Diagnostics
To diagnose an intestinal infection, in addition to collecting a detailed history and measuring temperature, the doctor will prescribe additional tests, in particular, stool testing and scatology.
In addition to examination and examination, the pediatrician prescribes additional tests
Testing stool for dysbacteriosis
This test is used to examine the child's digestive system. The composition of the intestinal microflora is determined. This is how dysbacteriosis is detected and whether the baby has Escherichia coli in the feces.
As a result, doctors determine the composition of bacteria that are in the body. The results of the analysis help determine the overall picture of the baby’s condition and the causes of his illness.
Scatology
For a more accurate diagnosis of intestinal infection, scatology is prescribed. The laboratory assistant initially studies the appearance of the feces, and also examines their composition in detail under a microscope. All results are displayed in a coprogram. In addition to the composition of the microflora, the presence of ammonia, fatty acids and other components in the feces will be detected.
Treatment and prevention
When drawing up a treatment plan for an intestinal infection, many factors are taken into account:
- child's age;
- complexity of the disease;
- symptoms;
- the reaction of a small organism to medications.
It is important to provide the baby with fluids in the body.
You need to treat in several directions:
- Fighting the pathogen. To prevent further development and reproduction of pathogenic bacteria, antibacterial drugs are prescribed. The fluoroquinolone, penicillin or nitrofuran series are most often prescribed.
- Fight dehydration. During the period of fighting infection, the child should consume a lot of fluid (at least 3 liters per day). This will help restore the water-salt balance. To speed up the process, special powdered rehydration preparations are used.
- Fighting intoxication. Drinking a large amount of fluid is also necessary to remove toxins from the body. Infusion detoxification therapy consists of administering saline solutions and glucose intravenously.
- Symptomatic treatment. To speed up the recovery process, they fight all associated symptoms. Complex therapy will consist of the additional administration of sorbents, antidiarrheal and non-steroidal drugs, antispasmodics, and complex vitamins. It is mandatory to take eubiotics (prebiotics and probiotics), which accelerate the restoration of intestinal microflora.
To restore a small body from dehydration, glucose drips are often prescribed.
On a note! Throughout the treatment, the child must adhere to a special diet (diet No. 2), which will provide the small body with all useful and nutrients.
Since the main reason for the development of E. coli is the weakened immunity of the infant, the main preventive protection against infection is breastfeeding. Pediatricians recommend not giving up breastfeeding for up to a year if possible. If breastfeeding is not possible, then formulas containing prebiotics are selected.
It is very important to observe the rules of personal hygiene so that objects of constant use do not become carriers of bacteria. Mothers need to monitor the purity and quality of the foods she eats. If the parent eats infected food, the pathogen will enter the small body along with breast milk.
Breastfeeding helps your baby develop a strong immune system
In the early stages of development, hemolyzing intestinal infection resembles colic symptoms. Parents need to closely monitor the baby’s condition so as not to develop the disease. The earlier the disease is detected, the easier it is to fight it.
Source: https://kpoxa.info/zdorovie-pitanie/gemoliziruyuschaya-kishechnaya-palochka-grudnichka.html
Therapy for hemolytic Escherichia coli
Normally, a healthy child should not have a hemolytic bacillus in the intestines, and its detection in culture is considered by doctors as a pathological condition.
To cope with this problem, treatment is prescribed using sorbents and rehydration solutions.
The action of the drugs included in these groups is aimed at restoring the water-salt balance, because the appearance of hemolytic bacillus leads to serious disruption of the intestines.
In addition, the use of bifidobacteria, bacteriophages and probiotics is indicated.
Antibiotics are prescribed to children who have hemolytic E. coli very rarely, only in extreme cases. The doctor must take into account not only the general well-being of the baby, but also the results of the studies.
Antibacterial drugs not only fight the problem, but also destroy the bacteria necessary for normal intestinal function.
Symptoms of E. coli development in children
Intestinal infection occurs in children mainly in the warm season, because it is the child’s fragile body that is most vulnerable to pathogenic bacteria in the summer. When infected, symptoms of food poisoning in children begin to manifest themselves acutely within a day.
Among the main symptoms of E. coli infection are the following pathological conditions:
- nausea and vomiting (lead to dehydration);
- spasmodic pain in the intestines;
- lack of appetite;
- diarrhea;
- intoxication of the body;
- increase in body temperature.
Intestinal damage in children manifests itself quite quickly, so at the first signs of infection you should contact a specialist. If the disease is not diagnosed in time and appropriate measures are not taken to treat it, the blood supply to the intestinal walls is disrupted with their subsequent destruction.