Causes
Experts have not come to a consensus on the origin of pityriasis rosea. Several independent factors are believed to contribute to the problem.
The suspected causes of pityriasis rosea are:
- reduced functionality of the autoimmune system - weakened immunity is more often observed in the autumn-spring periods, when there is a lack of vitamins and minerals;
- colds and recent vaccinations affect immunity;
- using other people's things - objects taken from a sick baby are carriers of infection;
- allergic dermatitis, food and drug allergens – contribute to the appearance of pityriasis rosea;
- previous intestinal disorders;
- psycho-emotional overload and stressful situations.
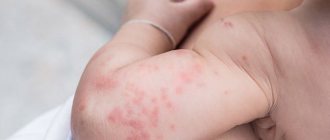
Domestic and stray animals do not suffer from pathology - babies cannot become infected from them. Pityriasis rosea and its signs in a child are clearly visible in the photo:
What do symptoms and stages of development look like in the photo?
In childhood, the first symptoms appear after infectious lesions.
Pityriasis rosea goes away with the main symptoms - the symptoms of pityriasis rosea are expressed in drying and cracking of the skin, with manifestations of skin itching, with the formation of small nodules under the dermis.
A rash does not appear on the skin of the face, under the hair, or on the mucous membranes. Favorable locations for rashes are areas with sweat glands - the thigh and groin area, the forearm area.
The stages of development of pityriasis rosea are presented:
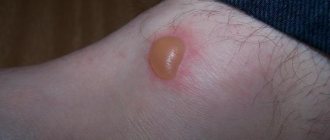
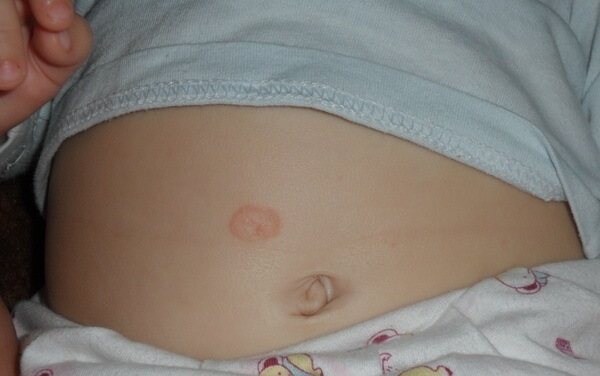
- Initial – with a large spot of maternal plaque:
- Progressive - after 10 days, reddish dots begin to spread from the main focus.
- Stationary - pink spots increase in volume and cover the entire affected area.
- Cyclic - old spots become yellowish, the skin peels and wrinkles. Not far from these places, new pink plaques begin to appear.
What does pityriasis rosea look like in children in the photo:
What is pityriasis rosea?
The disease presented in medicine is called pithiasis. It belongs to infectious-allergic erythema, so lichen Zhiber in a child always indicates a poorly functioning immune system. The pathology is diagnosed mainly in autumn and spring, when the body’s defense system is weakened. Zhiber's lichen in children occurs only once. After surviving the disease, stable immunity is formed.
Is pityriasis rosea contagious?
The described disease is characterized by spotty and extensive skin lesions, as in infectious dermatological diseases. For this reason, many parents are interested in whether pityriasis rosea is contagious in children, especially if the child attends kindergarten or school. Pythiasis is not transmitted from a sick person to a healthy person, even in the acute phase and in close contact.
Why is pityriasis rosea dangerous?
Zhiber's disease does not cause serious complications and does not in any way affect the overall health of the baby. The only thing that is dangerous about pityriasis rosea for humans is the risk of areas with disturbed pigmentation appearing on the skin. They will not remain for life, they will simply disappear very slowly. Pityriasis rosea in a child is a signal of problems with the immune system. It is necessary to take care of normalizing its work and replenishing the deficiency of minerals and vitamins in the body.
Ringworm in infants
In newborns, pityriasis rosea appears in infants in cases of exclusion. The main prerequisites for the formation of pathology are presented:
- constant overheating or hypothermia;
- insect bites;
- clothing and diapers made of synthetic materials;
- colds;
- using other people's toys - from a patient with pityriasis rosea;
- incorrect selection of food that causes allergic reactions;
- uncontrolled intake of antibacterial agents and multivitamin complexes;
- hereditary predisposition;
- the baby’s reaction to the first feeding or supplementary feeding – when the body reacts negatively to unusual food.
The appearance of pinkish spots in babies indicates the onset of the development of the disease.
Is pityriasis rosea contagious or not?
The specific microorganism that causes the disease has not yet been named. The official version suggests that transmission of pityriasis rosea from a sick person to a healthy one is impossible, however, in medical practice there have been cases of the disease affecting the entire family. It is believed that the virus can be carried by bedbugs and lice, and that the disease can be transmitted through personal items: combs, washcloths, towels.
Important! To avoid infection, you need to know how lichen is transmitted!
A foreign microorganism entering the human body provokes an allergic response, which has characteristic skin rashes.

Causes of the disease:
- overheating or hypothermia;
- stress;
- recent illness;
- vaccination;
- insect bites;
- digestive disorders;
- metabolic disorders, skin injuries.
A high incidence rate is observed in spring and autumn, when there is a natural decrease in the body's protective functions.
Important! This type of lichen affects a person only once in a lifetime. During the recovery process, the body develops lifelong immunity to the disease.
Let's go to the doctor
At the initial visit to a medical institution, the patient is referred for consultation to a specialist. A dermatologist conducts a visual examination of the condition of the dermis and writes out a referral for a series of laboratory examinations.
Parents of the baby are recommended to follow certain rules throughout therapy:
- Avoid exposure to direct sunlight on the skin;
- ban on baths;
- taking a shower occurs without hard washcloths;
- ointments are applied with extreme caution - preventing accidental spread of infection to nearby healthy areas;
- mandatory change of the daily diet - to a specialized dietary table;
- frequent walks in the fresh air;
- use of prescribed multivitamin complexes;
- exclusion of all types of woolen or synthetic clothing - these fabrics increase the sensation of itching.
Treatment with medication
Treatment of pityriasis rosea in children is carried out only with the appointment of a specialist. Self-selection of medications is strictly prohibited. The doctor prescribes the necessary dosages and course duration.
How to treat a child? Dermatologists recommend therapy:
- “Fenistil” is an antihistamine drug that suppresses obsessive itching. The required amount is calculated in relation to the baby’s age.
- “Ascorutin” is a vitamin complex in the form of tablets. The product is necessary to increase the functionality of the autoimmune system.
Ointment therapy involves:
- alcohol-free water-zinc mash - the affected areas of the skin are lubricated to alleviate the general condition of the body;
- anti-inflammatory drugs are represented by “Acyclovir”, “Hydrocortisone”, “Prednisolone” ointment;
- “Zinc” ointment – a medication that helps against the symptoms of peeling and obsessive itching.
In some cases, pityriasis rosea requires the use of systemic corticosteroids.
Demyanovich’s technique is an effective means of ridding children of the manifestations of Zhiber’s disease. The basis of the manipulation is the application of a 60% aqueous solution of sodium hyposulfite to the affected areas of the skin.
Next, a 60% solution of hydrochloric acid is used. In order to dry problem areas, it is recommended to use Furacilin or Iodine.
The famous pediatrician Komarovsky recommends a slightly different approach to the problem of pityriasis rosea. The specialist believes that therapy should be combined with the elimination of high levels of humidity and careful care of the dermis.
To avoid adverse reactions of the body to the medications used, it is necessary to consult a dermatologist. Komarovsky recommends using the following medications:
- “Oxolinic ointment” - against symptomatic manifestations of active peeling;
- "Sinaflan" - for local use - the drug is approved for children from 2 years of age;
- solutions of brilliant green, methylene blue or iodine.
Prevention is better than cure.
To reduce the risk of ringworm in a child, you should try to avoid contact with stray animals. As for pets, they need to get regular vaccinations and be examined regularly by a veterinarian. If your child does touch a stray animal, be sure to wash his hands with soap.
Anyone who suffers from ringworm must strictly follow the rules of hygiene. People who have been in contact with it should also regularly examine themselves for skin lesions.
For rosacea, it is important to avoid all allergens in food. These include: citrus fruits, cocoa-containing products, nuts, tea, red fruits, fresh milk. The consumption of currants, bananas, legumes, watermelons, peaches, cheese, potatoes, and buckwheat is subject to restrictions.
You should not season your child’s food with spices or aromatics. It is recommended to increase the consumption of products based on pasteurized milk and foods of plant origin. It is important not to limit the child’s drinking, give water and compotes more often, but exclude sweet carbonated drinks.
If the child has a well-developed immune system, even without the use of medications, the course of the disease does not exceed 2 months. Therefore, it is important to strengthen the immune system through a balanced diet, hardening, physical exercise, and maintaining the baby’s sleep and wakefulness schedule.
When diagnosing ringworm in a child, first of all, parents should inform the school, kindergarten or clubs that the child attends. Restaurant staff will take measures to prevent further spread of infection.
A disease is easier to prevent than to treat - an axiom. The best prevention to avoid infection and save yourself from other childhood diseases is optimal immune support, based on proper, balanced nutrition with all useful vitamins and microelements. Maintaining an age-appropriate daily routine.
Instill basic personal hygiene skills from an early age. Mandatory hand washing after going outside, playing with other children or animals, and before eating.
Tags: Komarovsky, treatment, deprive, child
- Related Posts
- How to cure toenail fungus at home using folk remedies
- Multi-colored skin fungus – About nail fungus
- Is it possible to really cure nail fungus?
« Previous entry
Traditional methods
Folk remedies for the treatment of the disease are allowed for use after consultation with a dermatologist. Before using them, it is necessary to test for spontaneous allergic reactions - a small amount of the medication is applied to the inner surface of the elbow and left for about 20 minutes. In the absence of negative signs (rashes, itching), the medicine is allowed for use.
Treatment with compresses is allowed for therapy for children, provided there are no allergies. Manufacturing takes place at home; ready-made compresses are applied to problem areas of the skin. Healers recommend using:
- fermented milk products, which are wrapped in cabbage leaves;
- oils of their rose hips, peach fruits, sea buckthorn or St. John's wort;
- the ash and residue that remains after burning a blank sheet of paper;
- decoctions of medicinal plants - licorice root, plantain leaves, string, hops, violet.
Some parents highly rate the effectiveness of oatmeal baths:
- With the addition of chamomile and lavender - add one glass of oatmeal, five tablespoons each of chamomile and lavender to the bath. Leave for about 20 minutes and immerse the baby in water. The total procedure time is 15-20 minutes.
- In a clean glass bowl, mix two glasses of oatmeal, 3 tablespoons of olive oil, 5 drops of vitamin E, 4 drops of lavender oil, a teaspoon of grape seeds. The finished mixture is infused for half an hour, transferred to a fabric bag, and immersed in a bath. After soaking for five minutes, they begin medicinal water procedures.
Symptoms and diagnosis
Solar lichen is a dermatological disease of a fungal nature. The skin lesion received its name due to the increase in the number of patients in the spring-autumn period.
When exposed to sunlight, the skin becomes covered with multiple spots of different shades. With “beach disease” there are no signs of the inflammatory process. Most patients are young people under 30 years of age. Sometimes “sun fungus” is registered in children.
Reasons for appearance
Most dermatologists are of the same opinion - damage to the stratum corneum of the epidermis and hair cuticles is caused by fungi of the genus Pityrosporum and Malassezia. Pathogens are transmitted only through close, prolonged contact from a sick person to a healthy person. The disease is low-contagious, that is, less contagious.
The risk of infection depends more on the condition of the body than on communication with infected people. After infection, several weeks sometimes pass before the first spots appear on the body. Under favorable conditions, active reproduction of fungi begins.
Provoking factors:
- decrease in the body's defenses;
- vegetative-vascular dystonia;
- diabetes mellitus, obesity;
- frequent colds;
- uncontrolled use of antibiotics;
- wearing synthetic items for a long time;
- the use of antibacterial gels that disrupt the composition of microflora and reduce the protective functions of the epidermis;
- increased sweating, changes in the composition of sweat;
- incorrect selection of cosmetic preparations for skin care;
- excessive exposure to UV rays with frequent visits to the solarium, long stays on the beach. Hence the popular name “sun fungus” or “beach disease”;
- abuse of tanning creams, which cause an allergic reaction and provoke the growth of fungi.
Some dermatologists believe that symptoms of lichen versicolor appear in patients suffering from lymphogranulomatosis and pulmonary tuberculosis.
Symptoms and signs
“Solar fungus” has a number of characteristic features:
- Numerous round spots with uneven, clearly defined edges appear on the body;
- no pain, redness, swelling;
- spots of coffee, yellow, pinkish-brown, milky color do not rise above the skin;
- over time, areas of a different color grow, sometimes to the size of the palm of an adult;
- When rubbing the affected areas, particles of the epidermis peel off.
Main locations:
- breast;
- back;
- lateral parts of the body;
- stomach;
- neck.
In young children and adolescents, the manifestations of “beach sickness” are located on:
- hands;
- legs;
- armpits;
- on the scalp.
A characteristic symptom of “beach sickness” is that during exposure to the sun, UV rays do not affect the affected areas. These areas do not tan and stand out noticeably against the background of healthy areas.
The disease has pronounced symptoms, but you should not prescribe treatment yourself. Do not use antifungal ointments until you consult a doctor. You can “smear” the manifestations, causing uncontrollable changes in the skin with improper therapy.
Visit a dermatologist. In most cases, the specialist does not limit himself to a visual examination, but prescribes additional tests. Specific studies will help make an accurate diagnosis:
- dermatoscopy of solar lichen spots;
- luminescent diagnostics. Under a Wood's lamp, which is used to determine many dermatological diseases, pathogenic fungi glow with certain colors and shades;
- Balzer iodine test. After the test, the affected skin looks much darker than healthy areas;
- microscopic analysis of the contents taken from the stain area. After tests, the causative agent of a fungal disease is detected in particles of the epidermis;
- test confirming Besnier's symptom. In case of pityriasis versicolor, even a slight impact produces results - the scales of the epidermis are suitable for research. It is very difficult to collect particles of the stratum corneum from healthy skin;
- A general blood test is required.
Sometimes PCR diagnostics are required to differentiate from other skin diseases. If syphilis is suspected, an RPR test is performed to confirm or refute the presence of Treponema pallidum.
How to get rid of sun lichen? Main methods of treatment:
- local therapy;
- use of traditional medicine recipes;
- prescription of general strengthening drugs;
- preventive measures.
Dermatologists recommend treating affected areas with safe products that have proven their effectiveness. Your doctor will prescribe one of the local remedies that suits you.
Lubricate lichen spots:
- Resorcinol alcohol;
- Clotrimazole;
- Salicylic ointment;
- Terbinafine;
- Sulfur ointment;
- Cycloperox;
- Naftifin;
- Salicylic alcohol;
- Lamisil.
Among the names of antifungal agents are creams, solutions, and ointments for sun lichen. Some drugs are available in different concentrations, for example, resorcinol alcohol, sulfuric ointment, salicylic ointment. Only the doctor decides which medicine to give preference to.
Taken into account:
- test results;
- affected area;
- individual tolerance of certain antifungal compounds.
Most dermatologists recommend modern antimycotic drugs in the form of solutions, lotions, and sprays. Advantages:
- high-quality treatment of every millimeter of lichen spots;
- uniform application regardless of the location of the affected areas;
- absence of an oily film on the skin, which is created by preparations in the form of a cream. In the warm season, this factor is very important.
In addition to local treatment, general therapy is recommended in advanced cases. The following drugs are designed to suppress the activity of fungi:
- Ketoconazole;
- Orgunal;
- Itraconazole
Taking Cycloserine will help restore normal pigmentation of the affected areas. The drug has earned a lot of positive reviews.
How long does treatment last? The sooner you see a doctor, the sooner you will get rid of fungal infection of the epidermis. With the correct selection of local remedies and the simultaneous use of oral medications, the condition improves quite quickly.
A late visit to a dermatologist can result in unpleasant consequences:
- treatment is delayed;
- often a bacterial infection is associated with a fungal infection;
- requires the use of antibiotics that weaken the immune system;
- side effect of antibacterial therapy - with reduced immunity, there is a high risk of relapse of the “solar fungus”.
Supplement your therapy with proven home remedies. Do not replace, but complement. Unfortunately, not all patients follow these recommendations; they self-treat with herbs and ointments and wonder why there is no result.
Only after consultation with a dermatologist can you use traditional medicine recipes. Remember - the basis of treatment is antifungal ointments, and if necessary, systemic therapy.
How to cure sunburn at home? Proven recipes:
- sea buckthorn oil. Treat affected skin with undiluted product 2 times a day. You can add a few drops of healing oil to any nourishing cream and lubricate lichen spots. Sea buckthorn oil has a healing, soothing effect;
- rosehip infusion. An excellent remedy that strengthens the immune system. Pour 2 tbsp into a thermos. l. fruits, pour in 0.5 liters of boiling water. After two hours, strain the infusion. Take half a glass orally twice a day. Some herbalists recommend treating spots with “sun fungus” with infusion;
- wild or horse sorrel. Finely chop a bunch of leaves and combine with a tablespoon of sour cream. Apply the paste onto the stains and wash off after 15 minutes;
- Apple vinegar. Only a high-quality product is suitable for treating lichen spots. Every three hours, wipe away any blemishes on your body with apple cider vinegar. Watch the reaction. If itching or severe peeling occurs, stop the procedure;
- rosehip oil. Buy healing oil at the pharmacy. Apply to affected areas twice daily.
We suggest you familiarize yourself with: The best tablets for toenail fungus
Lichen Zhibera develops in stages with the appearance of characteristic symptoms:
- Pre-initial stage. It precedes the manifestation of pityriasis rosea in the form of skin rashes. At this stage, a deterioration in general health occurs, which is accompanied by body aches and weakness, lack of appetite, and sleep disturbances. Enlarged lymph nodes and increased temperature are also possible.
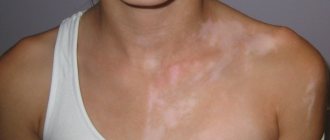
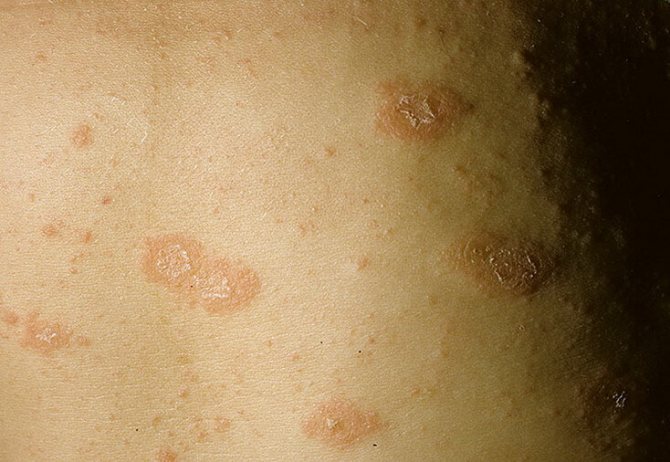
- Initial stage. The main sign that indicates the presence of this type of lichen in a person is the formation of the so-called maternal plaque. It is a large round spot of bright pink or red color. Its size can reach 2-10 cm. You can see in the photo what the maternal plaque looks like in Zhiber's lichen. It consists of transparent pityriasis-like small flaky scales; its slightly concave center has a pale tint, while the raised, smooth edges of the plaque have a pronounced color. Overall it resembles a medallion. Most often, the formation forms on the body in the area of the shoulders, chest and shoulder blades.
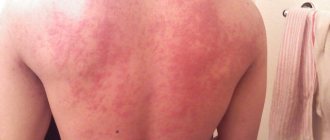
- Second stage. 7-10 days after the first spot appears, the body becomes covered with numerous secondary rashes, affecting the stomach, back, upper and lower extremities. In rare cases, the lesion reaches the head, face, hands and feet. These oval, scaly pink rashes are small in size (up to 1 cm), but can grow up to 3.5 cm. The most common place for their localization is Langer's lines. These are natural folds of the skin along which tension passes. As a result of drying and cracking of the skin in this area, itching and discomfort are possible.
- The final stage. The yellowish coating in the center of the secondary spots gradually begins to turn into scales, which fall off. Within 2-3 weeks, the lichen goes away, and in place of the plaques there remain traces in the form of dark or white spots, which disappear over time. The skin clears completely after 1.5-3 months.
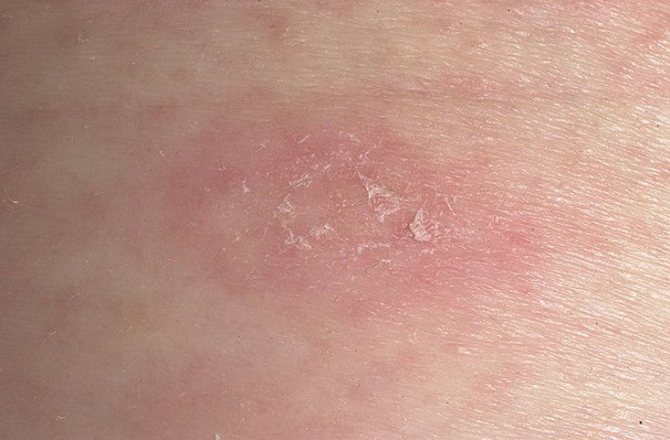
On the sides the spots peel, and closer to the center the skin in them is wrinkled, but after recovery there are no traces of the disease left on the body (more details in the article: what are the red rough spots on a child’s body called and how to treat them?)
Diet
When the diagnosis is confirmed, children are recommended to undergo a specialized diet. The total time of therapeutic nutrition is 10 days. Children are prohibited from:
- all types of sweets - confectionery, candies, jams, preserves;
- chicken eggs in any form of preparation;
- spices;
- nuts;
- coffee drinks - including cocktails.
Buckwheat, potatoes, legumes, wheat and rye products are subject to restrictions. In small quantities, fresh fruits are allowed: watermelons, bananas, black and red currants, peaches.
Nutritionists recommend using the following foods:
- semolina, oatmeal and rice porridge;
- freshly brewed berry and fruit compotes;
- fresh vegetables;
- fermented milk products;
- fish and meat with a minimum percentage of fat content;
- still mineral water.
The diet depends on the age of the patient. Your doctor will give you the necessary recommendations for your daily menu.