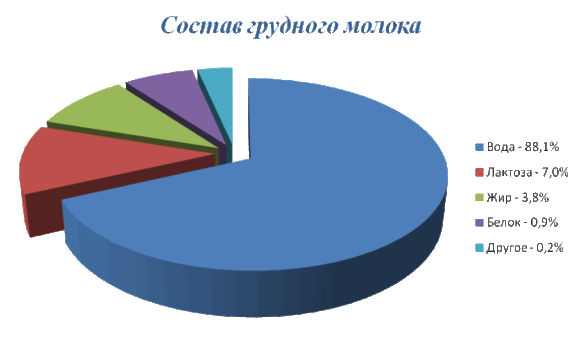
The main components of this food product
The milk of a nursing woman has a slightly sweet taste. Sometimes you can notice that it is salty. Breast milk contains the following beneficial components.
- Water (88%). Therefore, the child does not need additional fluid.
- Carbohydrates (7%). Lactose improves the absorption of minerals.
- Fats (4%). They strengthen the baby's immune system and nervous system.
- Proteins (1%). They are the basis for the growth and development of the child’s entire body.
- The remaining components (0.2%) include: iron, vitamins, several types of hormones, antibodies, white blood cells.
During feeding, the baby receives milk of different composition. First he drinks the front contents, and then the back.
The table clearly shows how healthy and rich in various nutrients breast milk is.
| Components | Amount in mature milk |
| Squirrels | 1.3 g |
| Fats | 4.2 g |
| Carbohydrates | 7 g |
| Sodium | 15 mg |
| Chlorine | 43 mg |
| Calcium | 35 mg |
| Phosphorus | 15 mg |
| Iron | 76 mcg |
| Vitamin A | 60 mcg |
| Vitamin C | 3.8 mcg |
| Vitamin D | 0.01 mcg |
| Energy | 280 kJ |
| kcal | 67 |
The composition and properties of this product do not always remain constant. They are influenced by many factors.
- During the daytime, milk is thicker than at night.
- In hot weather it thins out, and in cold weather it becomes thick.
- Weakening of the mother's immunity, taking medications, and products with a strong, pronounced odor affect the composition, color and taste of the product.
- Its consistency depends on the strength and persistence with which the baby sucks the breast. With strong, intense sucking, the milk becomes thick and fatty.
It is important for a woman to lead a healthy lifestyle while breastfeeding. You can eat only high-quality and hypoallergenic food. It is worth giving up bad habits (alcohol, nicotine). Do not eat spicy, salty or too sweet.
It is useful to feed your baby not by the hour, but on demand. This helps improve lactation and the appearance of nutrients. How much does a child need in the first days after birth?
Initially, about 40 milligrams will be enough, by a month the amount of milk will increase to 100 milligrams. The baby usually decides how much milk he needs.
Is it possible to dilute breast milk with water for a baby?
The most reliable and beneficial thing for a newborn is breastfeeding. There are women who want to put their baby to the breast, but due to certain circumstances they are forced to feed with expressed milk. In this case, you need to know how to properly collect and store this valuable product.
If there is a shortage of milk, experts recommend expressing the remaining milk from the breast after each feeding so that more comes in. It is worth doing this procedure only until it becomes enough. Also, if the mother of the baby needs to go somewhere, it will be safer to leave a portion of expressed milk.
If you are rarely separated from your baby, you can express yourself manually, but if the mother has to go to work early or the baby was born weak, premature and does not latch on to the breast, then it is better to purchase a breast pump. If you have to feed only expressed milk, it makes sense to fight for every drop of it, because the benefits of mother's milk cannot be compared with anything else. Try to express at least once every 2-3 hours to maintain lactation for as long as possible. Now let's talk about everything in order.
For faster pumping, you can use a breast pump. They are manual and electric. With a manual breast pump, expression occurs by regularly pressing a certain mechanism. The electric one does all the work itself and is considered the fastest. When using a breast pump, read the instructions and manufacturer's recommendations, make sure that the nipple is located in the center of the funnel and the fit is tight. Keep the device clean.
There are several ways to store breast milk. It all depends on what savings period you expect. Some mothers doubt the question: can breast milk be stored in the refrigerator? You can store milk at temperatures from 0 to + 4 degrees for 7 days, but do not leave it in the refrigerator door.
If a mother is forced to feed her baby only expressed milk, then, of course, it makes sense to stock up on it for future use by freezing it. This milk can be stored for 2 weeks to 3 months. It all depends on which freezer it is stored in. If in a separate box or compartment with a door that you do not use for other purposes, this increases the shelf life to three months. Label the milk container with the date when you freeze it. It is not recommended to re-freeze milk (i.e. defrost and freeze again), or to add large portions of fresh milk to already frozen milk.
Heat frozen milk in warm water by lowering the milk container into it. In order for cold areas to thaw more actively, the vessel with milk must be shaken periodically. There are special devices for heating milk. If you are forced to leave your baby with relatives, then this option will be the safest because... The heater maintains the optimal temperature. After all, mother's milk cannot be overheated or boiled, otherwise it loses its beneficial properties. It is also prohibited to heat it in the microwave due to the likelihood of uneven heating. Thawed milk should not be stored for more than two days.
Many mothers will be surprised, but breast milk does not spoil at room temperature (25 C) and is stored for 4-6 hours. Substances contained in breast milk, even at this temperature, counteract harmful bacteria. This fact is confirmed by real research. That is, if a mother needs to express milk at work, then there is every chance of storing it without refrigeration and bringing it home. If in hot weather there is a need to move somewhere, then you will need a cooler bag. Or some mothers get out of the situation with the help of a thermos, which is pre-cooled with ice cubes.
Below are general guidelines for storing breast milk in different temperature conditions. Source: La Leche League International
Colostrum (expressed within 6 days after birth):
- 12 hours at room temperature 27-32 C (80.6-89.6 F)
Mature milk:
- at 15 C (59-60F) - 24 hours
- at 19-22 C (66-72 F) - 10 hours
- at 25 C (79 F) - 4-6 hours
- in the refrigerator at 0-4 C (32-39 F) - 8 days
Frozen milk:
- Freezer shelf inside the refrigerator, without a separate door - 2 weeks
- Freezer compartment with separate door - 3-4 months (temperature varies due to frequent door opening)
- Stationary (separate) deep freezer with constant temperature -19 C (0 F) - 6 months or longer.
Currently, there is a wide choice of containers for storing milk. You can use both glass and plastic containers - this issue is not at all important, the main thing is that the container must be of high quality, sterile, close tightly and be convenient for you. These can be bottles, special plastic boxes, and even bags designed to store breast milk. Plastic bags are convenient because they are attached to breast pumps, and some are even included in the kit. They are convenient to use and do not take up much space when stored. You should not store milk in ordinary plastic bags; this material is not intended for such purposes and they may tear when heated.
Feed your baby breast milk, even if you can’t put him to your breast or be close to him all the time. In the modern world, the process of collecting and storing breast milk can be greatly simplified thanks to numerous devices.
Healthy newborns enter the world well hydrated and maintain this supply if they are exclusively breastfed - day and night - even in the hottest and driest climates. However, the practice of giving water to infants under 6 months of age (the recommended period for exclusive breastfeeding) persists in many countries and entails the most serious problems for their health and nutrition. This collection of frequently asked questions addresses these issues and the role of breastfeeding in meeting your baby's water needs.
How can infants get enough water?
Depending on the temperature and humidity of the environment, as well as on the child’s weight and activity, the average daily fluid requirement of a healthy child varies from 80-100 ml/kg in the first week of life to 140-160 ml/kg in the period from 3 to 6 months . The baby can easily obtain these amounts from breast milk if breastfeeding is exclusive and unlimited for two reasons:
Breast milk is low in salts. One of the main functions of water is to flush out excess salts from the body through urine. Salts mean dissolved substances (such as sodium, potassium, chlorine, nitrogen ions). The kidneys, although immature until about 3 months of age, are able to concentrate excess salts in the urine to keep the body functioning. Because breast milk contains few salts, a baby does not need as much water to excrete them as an older child or adult.
Can feeding a baby under 6 months old with water be harmful?
Supplementing with water increases the risk of malnutrition. Replacing breast milk with liquids that have little or no nutritional value may adversely affect the baby's well-being, survival, growth and development. Even small amounts of water drunk fill the baby's stomach and reduce his appetite and desire to eat nutrient-rich breast milk. Research shows that supplementing with water before 6 months can reduce milk consumption by even 11%. Supplementation with glucose solution in the first week of life is associated with greater weight loss and a longer stay in the hospital. Supplementing with water increases the risk of disease. Water and what it comes from can carry pathogenic microorganisms. Infants are at greater risk of exposure to microorganisms that cause diarrhea, especially in areas with poor sanitation and hygiene. In less developed countries, two out of five people do not have access to safe drinking water. Breast milk provides the baby with sufficient, always-available clean water. Studies from the Philippines confirmed the protective effect of exclusive breastfeeding and the harm of early supplementation with non-nutritive liquids on the risk of diarrhea. Depending on age, the risk of diarrhea for an infant given water, teas and herbal infusions was 2-3 times higher than for an exclusively breastfed infant.
What is the water requirement of children over 6 months?
Recommendations for water consumption in the second 6 months of a child’s life are not as clear as for the first half of infancy. At six months, you should start giving complementary foods - food that is given to the baby in addition to breast milk to meet the baby's increased nutritional needs. Your baby's water needs will be influenced by the type of complementary foods he receives. For the most part, a baby's water needs between 6 and 11 months are met by breast milk. Additional water can be offered in the form of fruit or fruit juices, vegetables, or small amounts of boiled water can be offered after the baby has eaten complementary foods.
Care must be taken to ensure that water and other liquids do not replace breast milk in the baby’s diet. Water can replace or dilute the nutritional value of energy-dense complementary foods. Liquid cereals, soups, broths and other liquid meals given to a baby are usually much less energy dense than the recommended 0.6 kcal/g for complementary foods. If less water is added to these complementary foods, the nutritional status of children in this age group may be improved.
Features of breast milk production
To answer the question of how breast milk is formed, you should know the structure of the mammary gland and the physiological processes of lactation.
The mammary gland consists of cavities between which there are narrow ducts. Near the nipple they expand and turn into milk sinuses. At the other base of the ducts there are cells that are responsible for milk production.
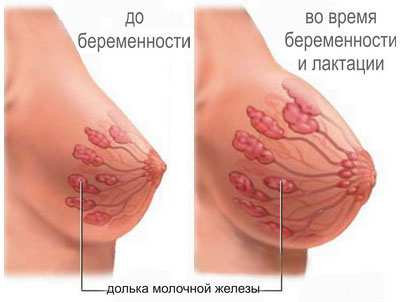
Several cells grouped together form an alveolus. There are several million similar alveoli in the mammary gland.
Prolactin is responsible for the production of milk in the alveoli. It enters a woman's blood after the birth of a child. If for some reason breastfeeding is postponed, there is no need to worry. Prolactin remains in large quantities even after a month. During sucking, the muscles contract and fluid is released from the cells.
The hormone oxytocin is responsible for the functioning of muscle fibers that carry milk through the ducts of the mammary glands.
It dilates the lacteal sinuses so that it can be freely released during sucking. The work of oxytocin can be felt due to the appearance of a feeling of fullness in the chest.
- Colostrum is produced in the first 4 days. It is light yellow. It contains a large amount of nutrients and antibodies. Colostrum is necessary for the child to adapt to a new way of receiving food.
- After a few days and up to about a month, transitional milk is produced. There is more nutrients needed for the growth of the body.

- Mature milk begins to appear after 3-4 weeks. It is rich in fat and water. There are fewer proteins.
It is important to know how much mature milk should be produced per day. Its quantity should reach 1.5 liters. Mature milk is divided into fore and hind milk. Each of them has characteristic properties.
Foremilk is bluish in color and is liquid. Appears at the beginning of breastfeeding. It is rich in carbohydrates, salts and water. The anterior contents help replenish fluid loss and quench thirst.
Hindmilk is yellow and thick. This is a complete food for babies. The formation of posterior contents improves due to frequent latching of the baby to the breast, during night feeding and with prolonged and frequent latching on the same breast. Hindmilk improves intestinal microflora.
In order for the baby to receive fore and hind milk evenly, you can give a different breast at each feeding. It happens that the baby refuses to suck out hind milk, as it requires energy. The woman hastily offers the other breast. As a result, the baby receives only foremilk. But foremilk cannot satisfy hunger.

As the baby ages, the composition of breast milk also changes. It adapts to the needs of a growing organism, which needs some vitamins in larger quantities, others in smaller quantities.
When the baby reaches 6 months, the need for fats and proteins decreases. A large amount of lipids and carbohydrates is produced. During tooth growth, the amount of calcium increases. It is useful to continue feeding after a year.
It is a great source of vitamins and antibodies that protect against infections. At this stage the milk is very thick and yellow.
Colostrum
This is the earliest milk that the mother feeds the baby immediately after birth and during the first 3-5 days of life. Colostrum is released in a volume of 30 ml per day. Such a small amount is due to the fact that in the first days of life the baby is not functionally ready to process a large volume of liquid.
In terms of its composition, colostrum is the richest type of human milk. It contains more protein, vitamins and microelements. Its calorie content is 2 times higher compared to mature ones. But it contains much less lactose and fat, so a baby with insufficient enzymes can easily digest this food.
It is surprising that in the process of natural completion of lactation, mature breast milk again approaches colostrum. This is inherent in nature itself, so the mother gives the maximum amount of nutrients before completely switching to regular food.
Characteristics of milk
Many factors affect what breast milk looks like. The main characteristics that determine its appearance are:
- color (yellow, white);
- taste (salty, sweet);
- consistency (thick, liquid).
The color of the milk is influenced by its consistency and the time of day at which feeding occurs. Liquid milk has a bluish color. Thick – yellow or white.

The color of the liquid depends on the food. For example, the orange color of milk may come from carrots or pumpkin. Greenish milk may indicate the presence of spinach and broccoli in the diet. Sometimes a pink color may be observed. This indicates blood penetration (cracks in the nipples, rupture of blood vessels). You can drink it in any case.
The taste of milk depends on the products that the woman consumed. It can be salty or sweet. Sometimes children may refuse to drink such milk. The emotional state of the mother also determines the taste and color of breast milk.
Salty milk becomes so due to the large amount of mineral salts. This phenomenon is related to the needs of the baby. As soon as his body gets enough of them, salted milk will lose this property.
Breast milk is constantly renewed. For example, from four months the amount of calcium increases. This is due to the fact that the baby begins to learn to sit down and stand up. During this period, the first teeth appear. If a child is in pain, a painkiller component appears in the milk. In the case when the mother has a viral infection, the antibodies in the milk increase and it can be drunk. The amount of lysozyme increases when the child himself gets sick.

The milk is renewed almost every minute. This is very convenient, since the baby’s condition can also change very often.
Beneficial characteristics of breast milk
The beneficial properties contained in woman's milk are necessary for the full growth and development of the baby.
- It is a source of nutrition and thirst quenching.
- Breast milk contains enzymes that help the baby's body adapt to other foods.
- The feeding process is associated with the production of the hormone oxytocin (the hormone of joy and tenderness). The child and mother become calm and stress is relieved.
- Milk can fight cancer cells.
- Immunity is strengthened. The child’s body’s resistance to various pathogenic bacteria increases. Stem cells, which are contained in milk (2%), help fight various diseases. Through the intestinal mucosa, these substances penetrate into the baby’s blood, activating the body’s defenses.

- Breast milk has antibacterial properties. They can treat diseases of the nose and eyes in young children. You can also treat cracks and wounds on the nipples of the woman herself.
- Milk is an excellent remedy against allergies. Milk contains antigens that, when combined with antibodies, form a protective barrier against food allergies.
Breast milk is a source of all the essential nutrients necessary for brain development and for the normal functioning of the digestive system. It strengthens the child’s immunity and can protect him from infectious diseases.
This is an excellent preventative against diseases such as allergies, pneumonia, diarrhea, and atherosclerosis.
The question often arises whether a woman can drink her own milk. It won't do any harm, but you still shouldn't drink it. Some women do not produce enzymes that can break down the complex composition of breast milk. If you drink your own milk, you may experience signs of indigestion (nausea, heartburn, abdominal pain, bowel movements).

The dairy products that we are used to buying in stores undergo complex fermentation processing. As a result, complex proteins break down and are easily digested.
It is very important to establish lactation from the first days. Mother's milk cannot replace any other product. It improves the functioning of all organs and has a beneficial effect on the emotional sphere of not only the baby, but also the mother.











