03/07/2018 Category: Nutrition for a nursing mother Author: Olga Petrova
Breastfeeding involves certain restrictions in the mother's diet. The diet becomes especially strict if the child has digestive problems or allergic reactions. Then the woman should adhere to a hypoallergenic diet.
- The effect of hypoallergenic nutrition on the body of mother and baby
- Principles of nutrition
List of permitted and prohibited products
What is a hypoallergenic diet for nursing mothers and its importance?
"Hypo" translated from Latin means "lack, lack." From this it becomes clear that the word “hypoallergenic” implies a low content of allergens. The purpose of such a diet is to prohibit the consumption of foods that often cause allergic reactions. The principles of such nutrition include completeness (the body of a nursing mother must have enough proteins, fats, carbohydrates and nutrients), as well as ease for the gastrointestinal tract.
The rationality of nutrition in the hypoallergenic menu is the most important difference from the diet of many other diets, which cannot be followed during breastfeeding. Protein, low-carbohydrate, and even more so monocomponent diets can greatly undermine a woman’s health during breastfeeding and cause a deficiency of essential nutrients in the child’s body. If a mother wants to lose a couple of extra pounds, she is allowed to use only the principles of rational nutrition.
Moreover, under no circumstances should you go hungry. Fasting can lead to fainting, dizziness, and deterioration of lactation, which is not at all necessary for a young mother with a small child in her arms.
Adhering to a hypoallergenic diet is recommended not only for those women whose children suffer from allergies or digestive problems, but also in the first month after childbirth. This is due to the fragile system of the baby’s gastrointestinal tract, which is just beginning to work in new conditions. During this period, she does not need any additional burden at all.
A hypoallergenic diet involves eliminating highly allergenic foods from the diet.
Indications for diet

First of all, it is important to determine whether the cause of negative reactions in the toddler’s body is actually a food allergy.
The fact is that in children of the first year of life, undesirable reactions can occur due to another allergen:
- powder for washing things for toddlers, rinse aid;
- strong odors from perfumes;
- care product;
- animal fur, if they live in the apartment;
- plant pollen.
In this case, following a diet will not help solve the problem or relieve the little one from allergies. That is why it would not be superfluous to contact a specialist to accurately determine the condition.
A diet for allergies in a child is needed in the following cases:
- in the first four weeks from the start of breastfeeding;
- if there is a pathology of the digestive system in the toddler, for example problems with absorption, hereditary diseases that affect the digestion process;
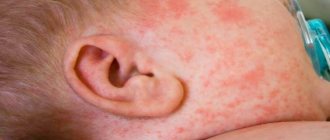
- manifestation of allergic reactions in the toddler, in particular pimples, rashes, diathesis, atopic dermatitis;
- if there is a family history of allergies.
The effect of hypoallergenic nutrition on the body of mother and baby
An allergy is the body’s reaction to substances that the immune system perceives as “foreign” and begins to fight them. Often the cause of allergies is a lack of enzymes capable of digesting a particular product. With age, the baby’s digestive system adapts and there is a high probability that as an adult, the child will no longer be allergic to the food that previously caused him a reaction. That is why it is recommended to follow a hypoallergenic diet in the first month of a baby’s life.
By eliminating all potential allergens from the diet, the load on the child’s body is reduced, allergic reactions do not appear, he is not bothered by digestive problems, and the immunity of both mother and baby is strengthened. The effectiveness and safety of hypoallergenic nutrition has been proven. Only with its help is it possible to continue breastfeeding a child whose body reacts with an allergic reaction to the mother’s food or has digestive problems. The effect of the diet comes quite quickly: from several days to 3 weeks.
The big advantage of this type of nutrition is the absence of contraindications.
Giving up on even the slightest signs of food allergies (for example, slight peeling on the cheeks) can create serious health problems for the child in the future: severe manifestations of allergic reactions, asthma, and others.
Principles of nutrition
Eating food on a hypoallergenic diet comes down to the following rules:
- exclusion from the diet of all potentially “dangerous” products from the point of view of allergies;
- cooking should be done by steaming, food should be boiled or baked in the oven;
- frequent meals (5–6 times a day) in small portions (250 g each);
- It is recommended to soak fruits and vegetables for 1 hour before eating;
- cook the soup in the “second” broth (that is, after boiling, drain the water, fill the pan with fresh water and cook the first courses only in this broth);
- It is recommended to keep a food diary, which records everything that the mother ate during the day and the child’s reaction to the food;
- eating the same product once every 2-3 days.
List of permitted and prohibited products
Success in eliminating allergic reactions primarily depends on correctly selected products in the mother’s diet.
All food products can be divided into groups: highly allergenic, with an average allergic index and low allergenic. Foods from the first group must be completely excluded from the diet of a nursing mother who adheres to a hypoallergenic diet. These products include:
- fatty or salted fish;
- seafood (shrimp, squid, etc.) and crayfish;
- caviar;
- cow's milk;
- hard cheese such as Gouda, Cheddar, etc.;
- eggs;
- fatty meats, lard, smoked meat products;
- sausages, frankfurters and other industrially produced meat products;
- red and orange vegetables (tomatoes, carrots, beets, pumpkin, sweet peppers);
- pickled white cabbage;
- eggplant, sorrel and celery;
- root vegetables radish, radish and horseradish;
- orange and red fruits and berries (strawberries, red apples, pomegranates, etc.), as well as grapes, blueberries, blueberries, blackberries, melon and pineapple;
- citrus;
- dried fruits (dried apricots, raisins, dates, figs) and nuts;
- mushrooms;
- honey;
- sweets and baked goods.
This list also includes foods that should never be eaten by any nursing mother, even if she does not adhere to a hypoallergenic diet:
- alcohol;
- any food with dyes, preservatives and other chemical additives;
- coffee and cocoa;
- hot, spicy and overly salty dishes;
- sauces, mayonnaise, marinades;
- smoked and canned foods;
- soda (even sparkling mineral water).
The second group consists of products that can cause severe allergies in one person, but not in another. Such food should be consumed with extreme caution, carefully observing the baby’s reaction to the new product. Also, food with an average allergy index can be eaten once every three days, since allergens tend to accumulate in the body and lead to a negative reaction.
The second group includes:
- potato;
- some types of meat (pork, lamb, horse meat, rabbit, turkey);
- buckwheat, corn, semolina;
- beans;
- green bell pepper;
- berries such as lingonberries, cranberries, currants (red, black), watermelon;
- bananas, apricots, peaches.
Mom should introduce any new product into her diet extremely carefully: starting with a very small piece and not consuming more than one new product once every 2-3 days.
The hypoallergenic diet of a nursing woman should consist of products from the third group, which include:
- low-fat fermented milk products: fermented baked milk, yogurt, kefir, cottage cheese, natural yoghurts without fillers;
- pickled cheeses such as feta cheese, feta, Adyghe;
- beef and chicken;
- some types of fish (sea bass, hake, cod, etc.);
- oat and rice cereals;
- offal (tongue, kidneys and liver);
- green and white vegetables and herbs (spinach, lettuce, parsley, dill, cauliflower, white cabbage, Chinese and Brussels sprouts, broccoli, cucumbers, zucchini, squash, zucchini, potatoes, turnips, rutabaga);
- cereals (barley, oatmeal, rice);
- olive oil, sunflower oil and butter;
- green and white berries and fruits (pears, apples, gooseberries, cherries, white currants);
- prunes, dried pears and apples;
- still mineral water;
- weak and herbal tea.
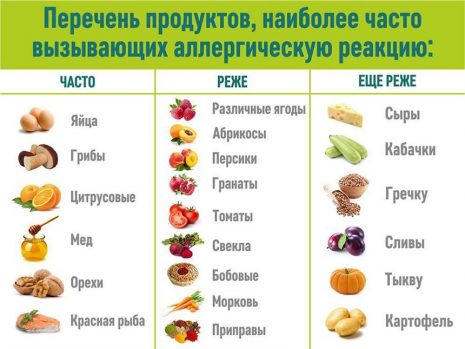
All food products are divided into high-, medium- and low-allergenic
Nutritional considerations for allergy to cow's milk protein
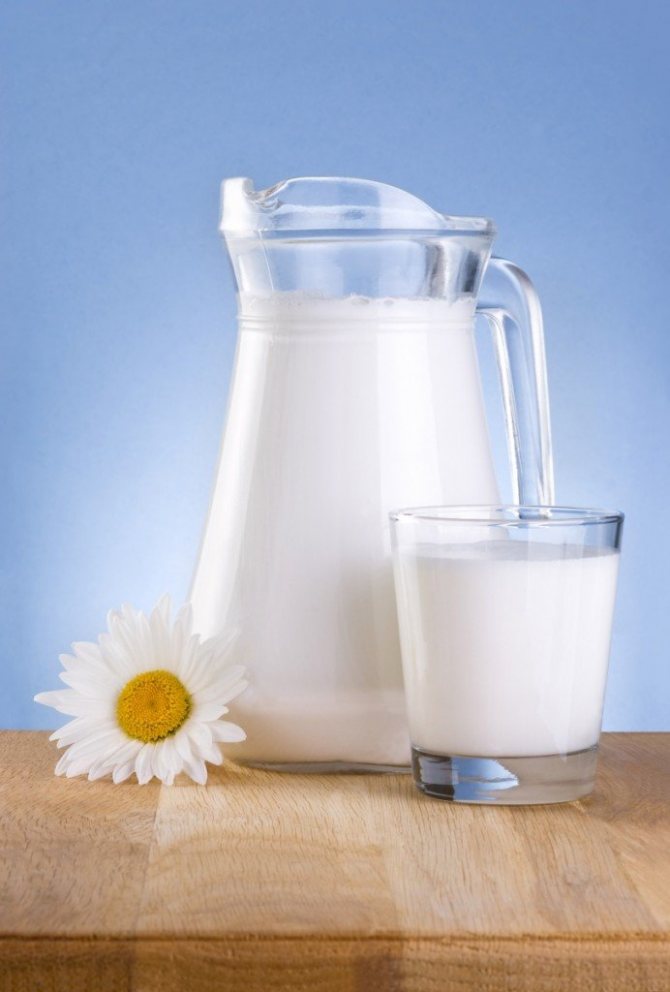

A baby's allergy to cow's milk protein can lead to calcium deficiency in the body of a nursing mother.
An allergy to cow protein is a challenge for nursing mothers accustomed to dairy products. After all, this type of nutrition is a significant source of essential vitamins and micro- and macroelements. Including calcium, which is so necessary for the baby during the period of skeletal growth.
At the same time, there are children who react differently to different dairy products. My daughter categorically cannot tolerate any “sour milk”, whole milk and cheese. But it reacts quite adequately to processed cottage cheese - in various casseroles. Of course, in limited quantities: no more than 200 g per day. Thus, you can try different types of dairy products little by little - no more than 1 teaspoon. If the allergy intensifies, it is necessary to stop the experiments.
If the baby is allergic to cow protein, the nursing mother needs to exclude not only dairy products, but also fish, eggs and nuts. This will significantly improve his condition.
Allergies are often confused with a lack of enzymes to digest cow's milk. Lack of enzymes is a temporary condition and goes away on its own by 6 months, when the baby’s digestive tract is formed.
However, for the first six months of a child’s life, a diet for a nursing mother is mandatory. It includes the following prohibited foods in addition to the hypoallergenic diet:
- any dairy products;
- beef;
- chicken and chicken eggs;
- cookies with both butter and margarine (including “Maria” and “Leningradskoe”).
Once your baby is 6 months old and his digestive tract has become more mature to digest complex substances, you can begin to carefully introduce dairy products in the following sequence:
- A very thin layer of butter with bread at breakfast.
- A teaspoon of low-fat cottage cheese.
- Hard cheese - 20 g;
- 0.5 teaspoon of pasteurized milk per plate of porridge cooked in water.
Ghee occupies a special place among dairy products. Being a storehouse of vitamins, this product very rarely causes allergies even in children with intolerance to cow's milk.
I have seen from my own experience the benefits of clarified butter. Being a “dairy” person, before giving birth I drank fermented baked milk every day, periodically consumed milk and could not imagine my day without a snack with a sandwich with a thick layer of butter and a large piece of cheese. Therefore, a dairy-free diet was (and still is) a big challenge for me. Therefore, when my mother handed over this product from the village, I decided to try it. Yes, if you eat this oil in large quantities, allergies appear. But it turned out to be quite possible to afford 3-4 sandwiches with butter a day and a bowl of porridge seasoned with this product. The main thing to remember is that any dairy product is introduced starting with very small quantities - no more than 10-20 g per day. And the increase in portions also occurs more slowly than when introducing other products. So, the recommended increase in portion is 10 g once every 2 days.
Sample menu for the week
At first glance, it seems that a large number of prohibitions in the diet of a hypoallergenic diet lead to poor nutrition. But that's not true. Even from such a not very large list of products, you can diversify your meals quite well.
| 1 day | ||
| Breakfast | Dinner | Dinner |
| Cottage cheese casserole without eggs | Vegetable soup and boiled chicken breast | Vegetable stew and steamed beef cutlet |
| Day 2 | ||
| Breakfast | Dinner | Dinner |
| Oatmeal on water | Chicken noodles with chicken breast broth | Meat goulash and buckwheat porridge |
| Day 3 | ||
| Breakfast | Dinner | Dinner |
| Baked apple, natural yogurt | Meatball soup | Meat casserole with vegetables |
| 4 day | ||
| Breakfast | Dinner | Dinner |
| Sandwiches with cheese and butter | Vegetable soup with a piece of boiled meat | Boiled potatoes with a piece of baked fish |
| 5 day | ||
| Breakfast | Dinner | Dinner |
| Cottage cheese with sour cream and baked fruit | Soup with second meat broth | Boiled rice and steam cutlet |
| Day 6 | ||
| Breakfast | Dinner | Dinner |
| Rice porridge with goat milk | Chicken broth soup with dumplings | Vegetable stew and a piece of boiled meat |
| Day 7 | ||
| Breakfast | Dinner | Dinner |
| Baked fruit, natural yogurt, toasted piece of bread | "White" cabbage soup | Vegetable salad with a piece of meat |
In the intervals between main meals, you are allowed to eat some fruit, toast with butter or cheese, or a fermented milk product.
Basic principles
This diet has the following principles:
- You should not eat fried, smoked, fatty or spicy foods. Products are prepared during the cooking process. baking or steaming.
- Seasonings are prohibited.
- Alcoholic and sweet carbonated drinks are prohibited.
- It is not recommended to pass, portions should be small.
- Products must contain vitamins and nutrients. It is recommended to eat vegetables and fruits.
- You need to drink at least 1.5 liters of water per day.
- It is necessary to arrange snacks that include fruits, vegetables, or compotes.
Is it possible to do fasting days during pregnancy? Isn't this dangerous for the mother and unborn child?
Find out from this article how to eat properly if you have increased gas. Permitted and prohibited products.
Duration of diet and its tolerance
The duration of compliance with a hypoallergenic diet during breastfeeding depends on the individual characteristics of the baby, his state of health and the severity of the allergic reaction. For the first month, a young mother's diet should consist only of low-allergenic foods . Until three months, the diet should also not be expanded with highly allergenic foods. You can add food from the moderate allergenicity group to it. And only after 3 months is it allowed to gradually add those foods that quite often cause allergic reactions and eating disorders. It is important to monitor the child’s condition.
In cases where the baby suffers from skin rashes, peeling skin, dermatitis and other manifestations of food allergies, the need to adhere to a hypoallergenic diet may last until the end of breastfeeding. But, in most cases, after the symptoms of allergy disappear, it is allowed to gradually introduce foods with a high allergic index, while monitoring the child’s condition. If a reaction to a particular product is detected, it is enough to simply exclude it from the diet.
Since the hypoallergenic diet is a balanced diet, it is easily tolerated. An additional pleasant bonus to maintaining your baby’s health is a smooth weight loss. No side effects were found from using this diet.
Approximate three-day menu

- First day:
- boiled rice);
- boiled pork (lean);
- kefir;
- corn or buckwheat bread;
- apple compote;
- steamed cauliflower.
- Second:
- kefir;
- oatmeal;
- chicken fillet (boiled);
- fruit compote;
- boiled potatoes.
- The third day:
- kefir;
- buckwheat;
- boiled pork (lean areas);
- dried fruits compote;
- mashed potatoes;
- breads.
The menu will expand over time: in small quantities, one product at a time, carefully monitoring the reaction of the baby’s body. If there are no negative manifestations, then the portion is gradually increased.
Now you know what a mother’s diet is like for her child’s allergies. You must understand that during the period of breastfeeding, the health of the little one directly depends on your nutrition and state of mind. Make sure that your diet does not contain allergenic foods; over time, gradually introduce them into your menu, but in small portions.
Feedback from nursing mothers
I followed a strict 4-month period (just out of curiosity to see if I can do it) - the child does not and has not had any problems. As a result, minus 20 kg I gained without effort. My hair is growing faster than before, everything else is fine.
Natalia
https://deti.mail.ru/forum/nashi_deti/kormim_grudju/kto_sobljudaet_dietu_pri_gv/?page=2
My hypoallergenic diet with rotation helped us a lot (each product is not repeated for the next two to three days). For a couple of weeks I sat only on hypoallergenic foods (buckwheat, rice, corn, rabbit, turkey, lean pork, zucchini, all types of cabbage, green apples and pears, gooseberries, vegetable oil) rotating them. I soaked the meat and grains before cooking, the rashes went away within these two weeks. Then I added other products one by one and watched the reaction. A food diary helps a lot to avoid getting confused. The last, after 6 months, gradually introduced highly allergenic foods - eggs, dairy products, wheat, beef, chicken, nuts, fish. After 8 months, the child stopped responding to my food. Now I eat everything, but I still rotate foods, and complementary foods are also rotated. He responded to complementary feeding with the beginning of the introduction, and returned to full breastfeeding. From 8 months there is practically no reaction to complementary feeding, but I will introduce milk only after a year.
Low absinthe
https://www.babyblog.ru/user/id2128805/100695