Young children are often considered capricious: they constantly demand something, cry for no reason. However, if you carefully observe the baby, you will notice that “bad” periods, when the baby often cries, sleeps poorly and eats restlessly, are replaced by weeks of relatively good “behavior.” What is the reason for this and how can such information help a young mother?
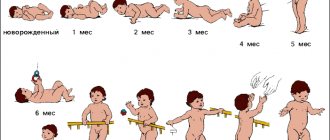
Every month the baby grows, develops and acquires new skills, both motor and emotional. Such changes do not pass without leaving a trace. Each new leap in development, physical and psychological, can be accompanied by a crisis: the baby seems to be cramped within the framework of the previous, established behavior, and he tries his hand at a new one.
Growth spurts help a child make a physical and psycho-emotional leap forward. Children begin to roll over from their back to their stomach and back, stand on all fours, sit down, learn to crawl, stand on a support and begin to walk, understand speech and try to reproduce it. And all this is accompanied by crises. Based on the baby’s behavior, it immediately becomes clear when the crisis began and at what point it began to decline. Let's look at each of them separately.
First month crisis (usually begins between the 4th and 5th weeks).
After several weeks of “hibernation,” which is often observed by parents after childbirth, when the baby only eats and sleeps, the child takes a serious step in physical development and improvement of the senses. Here are the signs of this age leap:
- The baby begins to show interest in everything.
- The amount of daytime sleep becomes less.
- Frequent whims
- Requires mom to be nearby.
- The quality of sleep deteriorates.
Crisis of the third month (11-12th week)
At this age, the baby has more opportunities for exploration: he can not only study his own hands, but also try to grab toys with them, asks to be carried “in a column” and shown everything around. The baby begins to understand and realize a lot, but does not always cope with it. This may appear like this:
- The child worries with or without reason.
- He’s crying and trying to say that he’s scared and doesn’t always understand what’s happening to him.
- Stops eating well.
- Sleep gets worse.
Child development 8 months
Physically, the baby’s activity in the eighth month increases day by day. He can already do quite easily without outside help when he crawls, sits, or takes out a toy he likes. With the help of crawling, the child actively explores all the space available to him, and some babies, holding on and standing up for support, are already trying to take their first steps. Since the child’s legs are quite strong by this time, many children love to jump, and often do this in the crib, holding on to its sides. If you begin to notice that the child spends quite a long time crawling in the crib and tries to stand up, holding on to the sides, do not keep him there for long. The child should have room to explore the world around him. Also, you should not allow your baby to crawl in the crib for a long time for another reason - there may be difficulties with sleep, because. A child’s bed should be associated with falling asleep and restful sleep, and not with active games. For this purpose, for active pastime, it is recommended to place the baby on the floor, thereby increasing the opportunity for a wider study of the world around him. But it is definitely very important to provide the child with a safe living space, removing in advance all dangerous objects, household chemicals, sharp objects, as well as small things that a curious baby can reach and swallow or get hurt.
But it happens that an 8-month-old baby experiences difficulty when trying to sit or stand on his own. This is due to the fact that the back muscles or leg bones are not yet strong enough and cannot bear increased loads. This usually occurs in overweight babies. Such children, as a rule, begin to sit down or stand up a little later than their peers. In this case, you shouldn’t worry too much and force things, because the time will come and your baby will make up for everything lost. In the meantime, you can try to help your baby by doing various exercises to strengthen his back or leg muscles. To stimulate the spinal muscles, the following exercise is very useful: the baby is seated on a flat surface, one leg is straightened forward, slightly moved to the side, the second, bent at the knee, is moved in the other direction. The baby is supported on his arms in front of him, which are placed between his legs at some distance from each other. You can put a toy nearby, and the child, forgetting himself and picking it up, ends up in a sitting position. You can find many such exercises, the main thing is to perform them correctly. Also very useful in this case are massage and gymnastics performed by qualified specialists.
By the eighth month, the baby usually has two, or even four, incisors. But it also happens that there are no teeth yet. Before you worry about this, you need to examine the child's mouth - run a clean finger over his gums. Perhaps in this way you will just come across a swollen area of the mucous membrane, or even a barely noticeable corner of the tooth. If nothing of the kind was found, then you can contact a specialist. It is likely that such a delay occurred due to errors in nutrition or a lack of vitamin D, so it would be better if the baby is examined by a doctor and prescribes a correction in the child’s diet.
Well, if your baby is the happy owner of the first two or more teeth, then you can slowly accustom your child to solid food and chewing small lumps. Experts come to a consensus, believing that the sooner a child begins to learn to chew, the better. Chewing massages the gums and improves their blood circulation, promoting tooth growth. If you cook the porridge yourself, you can make it thicker. At this time, the baby does not need to grind vegetables in a blender, but simply mash them well with a fork. At first, you can grind the meat twice through a meat grinder (or grind it using a blender). You can also introduce baby cookies into your baby’s diet, simply offering them to chew on and then drinking them down. A light salad of grated cucumber, tomato pulp and a couple of drops of oil can be given to your child for lunch in addition to the main course. Finely chopped vegetables and fruits, freed from skins and seeds, pieces of cheese can be offered to the baby in between main meals. And many other recipes for an 8-month-old baby can be found in our article “Recipes for babies from 6 to 9 months.”
But the child’s development continues at a rapid pace not only physically, but also psychologically. In the emotional development of the baby in the eighth month, already acquired skills are also improved and new ones are acquired. At this time, the period of babbling continues; the child often and with different modulations likes to pronounce individual syllables, and then falls silent and listens to the spoken “speeches”. Such a conversation does not yet carry any semantic load, the baby is simply practicing pronunciation. But he, in turn, loves to watch you, your lips, how you speak, and what you do. Therefore, if your baby is in the mood to “talk”, then it will be very useful to communicate with him slowly and so that he sees your lips.
Also at this time, there comes a period in emotional development when the child feels anxiety due to the absence of his mother. The baby is excellent at dividing people into “friends” and “strangers” and easily panics at the sight of a stranger, especially if he tries to touch him. This behavior of the baby is absolutely normal and should not worry you, this is how the child’s social instincts are formed.
At this age, babies are able to understand many phrases and fulfill simple requests. For example, he already understands that he can wave his hand to the person leaving, give his hand to an adult’s request, etc. In addition, the baby began to understand that he himself could demand or ask for something. Usually in such cases, the child begins to point with his pen to what is interesting to him, or to where he wants to go. It happens that when a child doesn’t get what he wants, he can throw a tantrum, demanding the item he loves. In this case, you can advise distracting the baby with something else. And here we can say a few words about the stubbornness and beginning whims of the child.
Your baby is growing little by little and understands more and more every day. There comes a time when the child suddenly realizes that with his cry of protest he can achieve a lot from mom or dad. Sometimes parents make the mistake of giving up and allowing the child to take possession of an object that was previously prohibited. Under no circumstances should you do this. If you give in to your child once, this will only mark the beginning of his whims, and the next time he will try to achieve anything by shouting. It is a mistake to believe that the situation can be corrected later when the child gets older. Then it will be much more difficult to do this, so you need to raise your child right away, because a child is a subtle psychologist. The baby must understand that the parents’ word is adamant, and his whims will not go away. But he also needs help on your part: if possible, you should try to remove from the baby’s field of vision those things that you do not want to fall into his hands, thereby reducing the possibility of hysterics to a minimum.
If you feel that the baby is starting to be capricious and does not want to calm down, then you can advise distracting him with something interesting, for example, a favorite toy or a new colorful book. At the age of 8 months, babies are very fond of active games, for example, “hide and seek”, i.e. you hide behind a handkerchief, and then look out and say “peek-a-boo!” “Okay” is also a favorite children’s game. You can cover a toy with a handkerchief, and then invite the baby to find it. When he guesses to pull the edge of the scarf and sees the hidden toy, there will be no limit to his delight! Also at this age, kids love to engage in research activities - sorting out various boxes, drawers, and sometimes they can get into their mother’s bag. Now is the time to buy your baby his first pyramid; stringing rings is a great workout! You can play with cubes with your child, showing how to place them one on top of the other, making pyramids. Excellent for games, as well as for development, including on the water, are special waterproof books with large, bright illustrations, sometimes even equipped with teethers on the edges. But at the same time, make sure that more active and noisy games do not occur before bedtime, since it will be more difficult for an excited baby to go to bed. Before bedtime, calmer and quieter games are recommended.
Coup crisis
It is associated with the first major motor skill - the child learns to roll over from his back to his tummy and a little later - back. This occurs in different babies between 3 and 6 months (approximately 14 to 25 weeks). Such a serious breakthrough in physical development also affects emotional development: the baby already understands that there are objects in the world that exist on their own, and not just when they are taken or touched.
The main features of this crisis period:
- Loses interest in everything.
- Appetite worsens.
- Sudden change of mood.
- Requires constant presence of mother.
Baby's physical skills at 6 months
At six months, many children actively begin to change the position of their body in space. They roll over, sit down, and try to crawl. This manifestation of activity is facilitated by a strengthened muscle corset and a desire for new achievements, such as:
- The baby gets on all fours and rocks in this position.
- By 6 months, the baby can already turn not only from his back to his tummy, but also back. Lying on his stomach, the little one tries to stand up, lifting his tummy from the surface. If there is something to grab onto, the baby will be able to pull up his body and sit down. Now he does it very well.

Lying on his stomach, the baby can support his body, leaning on only one hand; the other is needed to pick up toys. Now the child understands that he has two hands and can pick up two toys at once. Soon he will begin to realize that he needs to let go of something in order to take on another thing.
- At 6 months the child is already making attempts to move around. But everyone does it differently. Some spin around on their tummy, moving their arms and legs, or move backwards, others push themselves forward, moving like a frog, or crawl, moving their arms and legs alternately.
- The little one has learned to sit, but he still can’t sit for long and falls over on his side. The back muscles have not yet become stronger, and the child does not hold well in an upright position. The time will come and he will sit down himself.
- Some babies rise up and try to stand on their feet, holding onto a support. Other babies actively prepare for their first steps by squatting and dancing when they are upright. The baby is not yet ready to walk at this time; the muscles of his legs are too weak.
- The baby's fine motor skills are now quite well developed and he can pick up small objects. And if before he did this clumsily with his whole palm, now he understands that it is more convenient to take these small objects with two fingers. The baby's fingers become more mobile, he confidently takes and holds toys in his hands. The baby coordinates movements better when trying to reach or lift small toys.
- The baby's neck muscles are completely strengthened and he can control his head well.
- He can hold tightly to an adult's fingers and lift himself up.
- The baby learned to express his desires using gestures. He persistently stretches out his hands when he wants to be taken out of the crib, points to objects that he certainly wants to get. Now he tries to copy the actions of adults, carefully observing them. For example, if you clap your hands, the baby will also start playing clap.
Thus, at six months, many children actively begin to change the position of their body in space. They roll over, sit down, and try to crawl. This manifestation of activity is facilitated by a strengthened muscle corset and a desire for new achievements. Now you need to prepare your home for the safe exploration and movement of the child. We talked in more detail in the article: “How to secure a home for a child.”
Six-month crisis (weeks 23-28)
Every day the baby controls his movements better and better. Depending on the pace of physical development, he can either train turning over from back to stomach and back, or get up on all fours from a position lying on his stomach, or try to sit down from a position lying on his back, or even learn to crawl. Psycho-emotionally, at this time he discovers a world of relationships. The baby realizes that the mother may be busy not only with him, but also with other things, and this seriously worries him.
Signs of a crisis:
- Appetite gets worse.
- Restless behavior when strangers are around.
- Begins to react sharply to diaper changes or attempts to change clothes.
- The chest becomes a way to calm down.
- Anxious crying for no reason.
- Deterioration of sleep.

Crisis surges in children under one year of age by week
If we take the age of babies up to 12 months week by week, then difficult crises in development are observed at certain times. Let's find out when parents should approximately expect a growth spurt in their child.
5 weeks
Pediatricians believe that the first crisis period in newborns occurs around the fifth week. Right now it seems to the mother that she and the baby are already accustomed to each other and suddenly everything goes wrong. The toddler begins to cry, refuses to eat, and constantly demands to be held. It is quite simple to explain this behavior of a child, because now he is going through his first difficult stage. Now his nervous system and sensory organs are actively developing.

How does the baby feel? Doctors suggest that around the fifth week of life, the baby begins to understand that his world will no longer be the same and he has a strong desire to return to his mother’s womb. That is why the baby every now and then tries to be as close as possible to his loved one, to be in his mother’s arms. To calm him down, take the baby in your arms more often, talk to him, and put him to your breast as required. This will make him feel protected and calm down.
8 weeks
Closer to two months of development, another growth spurt is observed in children under one year old. Now the baby is exploring the world and learning a lot of new information. The toddler begins to absorb information like a sponge and often his psyche cannot cope with it. This leads to emotional overload and discomfort. The only ones who can help the little man are his mom and dad. Parents must clearly understand this and under no circumstances lose self-control, even if it is very difficult for them.
As during the first crisis stage, the mother should now try to support her son or daughter as much as possible. Give your baby as much attention as possible, pick him up, stroke him, sing songs, tell him stories. It often seems to parents that their child’s crying is completely unreasonable, but this is not the case. If a baby calms down in his arms, he is simply looking for protection in his mother's arms. This should not be assessed as whims. Growth spurt symptoms at 8 weeks:
- A sharp increase in head circumference.
- The toddler begins to examine with interest his body parts, arms, legs.
- Moodiness appears.
- Sleep is often disturbed, which is associated with psycho-emotional stress.
- Appetite increases or, conversely, decreases.
Having discovered such signs, mommy should not sound the alarm and get upset. Just try to pay more attention to the baby.
Read more about what a toddler should be able to do at 8 months in this article.
12 weeks
At the twelfth week, parents should prepare for another difficult period. Signs of a growth spurt may include:
- The toddler begins to demand much more attention from his mother than usual.
- Your son or daughter begins to feel embarrassed when meeting strangers.
- The child constantly asks to be held. If he doesn't get what he wants, he cries and throws hysterics.
- Sleep is restless, and difficulty falling asleep often occurs.
At 12 weeks, the baby realizes that he can make smooth transitions in movements and voice. He is learning to change the position of his body; his movements are no longer so sharp. The same applies to speech.

The baby makes lingering sounds. In addition, another skill appears. A toddler at this age can swallow solid food. This is precisely why complementary foods begin to be introduced from the age of 4 months.
19 weeks
At 5 months, children experience a developmental spurt. At this age, a boy or girl acquires the following skills:
- The fidget holds her head confidently and knows how to turn it.
- Now children are making their first attempts to crawl.
- The baby pulls himself up, holding his mother’s hands.
- The child rolls over from back to stomach and back.
- The baby smiles when he sees his family and frowns when he hears a stern tone.
- At this age, he already has toys that the baby prefers.
- Movements become more confident.
- The toddler holds the toys tightly and takes them on his own.
- It stands on its legs if you support its armpits.
You might be interested in: Shoe sizes for children by age: table
At five months, the baby listens attentively to the conversation of his family, he frowns at loud sounds, and smiles if you speak to him kindly. Despite the fact that each baby develops individually, he experiences a growth spurt at this age.
26 weeks
Like previous crisis stages, the growth spurt in children under one year old at 26 weeks has its own signs and characteristics. More often, parents encounter the following symptoms:
- Sleep is disturbed. Moreover, difficulties are observed when falling asleep. Some children refuse to sleep during the day.
- When in contact with strangers, the baby shows embarrassment, turns away, looks for his mother, and cries.
- The baby strives to spend all his time with his mother. If she leaves the room even for a short time, he cries and looks for her with his eyes.
- Appetite increases. This is explained by intensive growth and high energy costs.
- Some children, on the contrary, lose their appetite and even refuse their usual foods.
- The toddler leans against warm and soft objects (soft toy, blanket, blanket). This gives him a feeling of security.
Try to give your child maximum attention. Support him physically and mentally.

Very soon the difficult stage will end and everything will fall into place again. Be patient. Parents can sit with the baby alternately, giving each other a rest.
36 weeks
At this age, the baby begins to gradually realize that the world around him is actually not as simple as it seemed. Now the baby can already pick up small objects with two fingers and look at them for a long time. While eating, your son or daughter takes food with his hands, squeezes it, and watches this process for a long time. The baby already clearly separates living people from inanimate objects and looks for similarities between them.
As during previous growth spurts, symptoms such as increased moodiness, loss of appetite, or, conversely, an increase in it, are now observed. The little man constantly strives to be with his mother, literally does not get away with it, throws tantrums at the slightest reason.
46 weeks
The following symptoms may indicate that your child will soon move to a new level of development:
- Constant desire to be in mother's arms or next to her. As soon as you try to leave the room, the little fidget will try in every possible way to hold you back, grab your clothes, cry, throw tantrums.
- A boy or girl becomes shy. This is especially true if a stranger tries to talk to him or touch him. The little one immediately looks for his mother with his eyes, tries to hide behind her, and presses himself to his chest.
- At 46 weeks of development, children experience a symptom such as jealousy. As soon as mommy starts talking to someone or starts communicating on the phone, the baby immediately tries to attract her attention, clings to her, and carries toys.
- The child experiences frequent mood swings. This is one of the common signs of a growth spurt. Loud laughter can be replaced by bitter crying and vice versa.
- The baby begins to protest when trying to change his clothes or change his diaper.
- Some children have the so-called “ideal command”. This helps them get what they want from their mother.
At 46 weeks, parents already fully understand what is happening to their child, because this is not the first crisis stage.

As before, it is now recommended to remain calm and not give in to children's tantrums. Remember, your son or daughter needs you now more than ever.
Crisis of the eighth month (from the 32nd to the 38th week)
The baby begins to understand speech, becomes more emotional, hears and sees objects better, observes more what is happening around him, and wants to try new foods. What can you notice in his behavior?
- Cry.
- Apathy.
- Some children want to be more affectionate: they hug and ask to be kissed more often, they want to be closer to their mother.
- They start to feel shy.
- The child seems to go back in his behavior and become “like a little one.”
- Protest while changing clothes.
- Taste preferences change.
Crisis “Mom, don’t go!” (from 9 months, approximately 40 to 47 weeks)
A new physical skill - crawling - changes the baby's ideas about the world around him, now he sees it differently, from a more elevated position. The overabundance of information received in this way changes the child’s way of thinking. All this provokes another growth spurt, which can manifest itself as follows:
- The baby may cry a lot as soon as the mother leaves the room.
- Shyness, especially in front of others.
- Begins to find fault with complementary foods.
- Jealousy appears.
- Needs a lot of attention from mom.
Crisis of the first year (usually begins from the 49th to 56th week)
The baby is getting better at moving around - he has learned to crawl, and maybe even walk, and is becoming more independent. At the same time, the baby’s nervous system does not have time to process a large flow of new information.
Signs of this age leap:
- The baby practically hangs on his mother, clinging to clothes. Requires more physical contact.
- Jealousy when mom pays attention to someone else besides him.
- Disobedience.
- The mood changes sharply.
What is sleep regression?
When sleep regression occurs, it can be easily identified by a sharp deterioration in the quality of night and daytime sleep. Physically, nothing bothers the baby, all external factors are adjusted, the daily routine is set up perfectly. In other words, sleep deteriorates for no apparent reason.
How to understand that sleep regression has occurred:
- It’s as if the child has been replaced; he doesn’t want to live under the old regime.
- Refuses to lay down in the usual way.
- Ignores the established daytime sleep pattern.
- The quality of night sleep deteriorates, the baby begins to wake up frequently, and needs his mother’s help to prolong his sleep.
Sleep regression can last from 2 to 6 weeks. To help the baby overcome this stage, support and assistance from parents is needed. Give your baby more attention and affection than usual, and then the regression will be much calmer.
Sleep regression in a child: characteristics of the phenomenon
From the day of birth until the age of three, there may be several stages of sleep regression in a child. The first appears at approximately 6 weeks. For parents, it goes almost unnoticed due to the fact that there are many other reasons for concern.
It is important to know! Subsequently, a child’s sleep regression occurs at 3-4, 5-6, 6-7, 8-9 months, at one year, one and a half and two years. Most parents sigh with relief when their baby turns three years old. His sleep returns to normal, the baby himself becomes less restless.
To this day, there is debate between pediatricians and child psychologists about what actually serves as a provoking factor for the appearance of such a phenomenon.

Manifestations of the disorder
Despite the fact that children have their own individual characteristics, their sleep disorders manifest themselves in almost the same way.
Each period has its own specific recurring features:
- Great difficulties arise when putting the baby to bed in the evening. This is accompanied by his whims and prolonged falling asleep.
- The child's daytime rest time is significantly reduced. His sleep becomes sensitive. The baby wakes up from the slightest rustle or noise.
- At night, there are frequent awakenings for no apparent reason. They are often accompanied by crying.
- A baby or an already grown-up baby becomes restless, nervous, and excited. They are constantly capricious.
- The baby's appetite noticeably worsens, which sometimes affects weight. There are times when he, on the contrary, begins to eat more.
It is important to know! In such a situation, the child shows an increasing desire to always be in contact with his mother, he constantly asks to be held and wants to be close to her. In this case, possible colds or infectious diseases are excluded due to the absence of symptoms.
This behavior does not leave caring parents indifferent, who by the age of three months the child began to get used to a more stable pattern of his sleep and wakefulness.
Main reasons
If you look at this issue in more detail and approach sleep regression from a philosophical perspective, then parents will understand that, in principle, nothing terrible is happening.
This behavior and condition of children is associated with the stage of their active development. Each regressive episode is another step towards the baby’s maturation, growth and personality formation, and not damage to the nervous system.
Undoubtedly, over the course of a child’s development, changes occur in his psyche; this is felt every month and manifests itself in the form of regressive sleep. But this state of affairs should not frighten parents if everything is within normal limits.
Dangerous periods by month: distinctive features
The main reasons for the appearance of age-related regressions in children are the following:
- At 4 months of age, the child is already well oriented in space with his eyes and easily understands in which direction his mother is moving. Her departure to another room can turn into a real tragedy, foreshadowing separation. This becomes the first reason, the beginning of sleep problems in a child.
- At 6 months, the baby experiences two important changes in his life - teething and an increase in wakefulness. Daytime sleep becomes two times a day. It follows that at night the baby is unable to get a full night's sleep due to toothache, and during the day new impressions interfere with this. Only after 2-3 weeks does everything return to normal.
- At the age of 9 months, the child actively explores the world and acquires communication skills. During this period, his first intelligible words are spoken, communication with peers occurs, and attempts are made to walk. Every day the baby has new impressions, which are not easy for the child’s psyche to follow. In the evening, this makes it difficult for the child to plunge into dreams. And during the day he does not want to sleep because of new and interesting activities.
- At the age of one, children's first fears are formed. Their memories are filled with frightening moments that happened in their short lives. The child does not quite understand what is happening. He is frightened by the darkness and sharp sounds. He becomes afraid when he is left alone in a room. From this age, babies can have scary dreams that are difficult for them to distinguish from reality, which greatly interferes with falling asleep.
- At one and a half years old, a child develops self-awareness, the little person begins to realize how important he is. In some cases, he is stubborn and stands his ground. The psyche is involved in the formation of one’s own “I”. This takes a lot of energy. During the daytime, the “self” is expressed in contact with surrounding people. In the evening, the baby tries to persist when he is put to bed.
- At two years old, most children join society. At this age, many go to preschool for the first time. If we look at this situation from one side, there is an obvious benefit. Parents have the opportunity to go to work while their child is under the supervision of qualified specialists. The other side of this situation is not as bright as it seems at first glance. Many children find it difficult to cope with parting with their mother, leaving their comfort zone and finding themselves in an unusual environment. Some people can easily cope with a change in environment, while others experience real psychological stress, which affects the quality of their sleep.